中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (12): 2185-2190.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.12.014
• 药物控释材料 drug delivery materials • 上一篇 下一篇
水溶性脂质体运载基因药物复合物治疗大鼠神经病理性痛
胡春奎1,陆建华1,陈 昊1,熊家祥2
- 1解放军广州军区广州总医院麻醉科,广东省广州市 510010
2解放军第三军医大学生理教研室,重庆市 400038
Water-soluble lipopolymer carrying gene drugs for treatment of neuropathic pain in rats
Hu Chun-kui1, Lu Jian-hua1, Chen Hao1, Xiong Jia-xiang2
- 1 Department of Anesthesiology, Guangzhou General Hospital of Guangzhou Military Command of Chinese PLA, Guangzhou 510010, Guangdong Province, China
2 Department of Physiology, Third Military Medical University, Chongqing 400038, China
摘要:
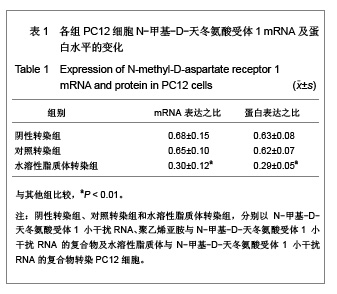
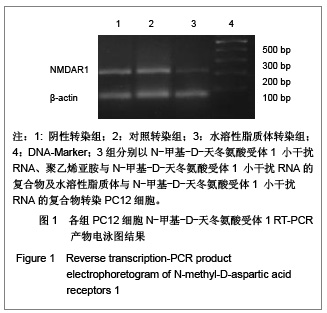
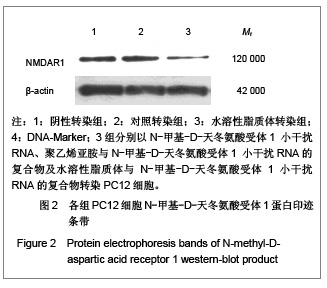
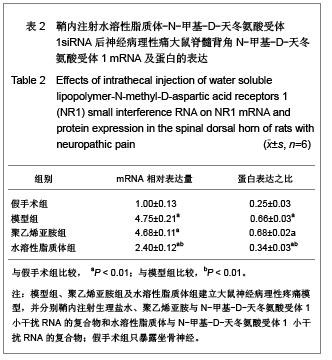
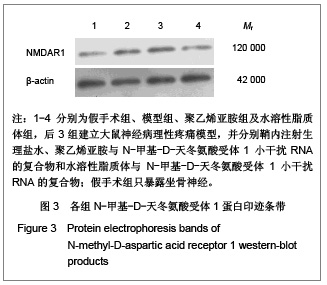
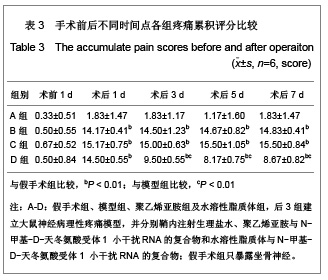
背景:有研究报道病毒载体运载N-甲基-D天冬氨酸受体1小干扰RNA可有效缓解大鼠炎性疼痛,但病毒载体存在安全隐患。 目的:探讨水溶性脂质体运载N-甲基-D天冬氨酸受体1小干扰RNA在体内外沉默N-甲基-D天冬氨酸受体1的效应和治疗神经病理性痛的可行性。 方法:将PC12随机分为阴性转染组、对照转染组和水溶性脂质体转染组,分别以N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体1 小干扰RNA、聚乙烯亚胺与N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体1 小干扰RNA的复合物及水溶性脂质体与N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体1 小干扰RNA的复合物转染PC12细胞,检测各组N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体1 基因mRNA及蛋白水平表达的变化。将48只SD大鼠随机分为假手术组、模型组、聚乙烯亚胺组及水溶性脂质体组,后3组建立大鼠神经病理性疼痛模型,并分别鞘内注射生理盐水、聚乙烯亚胺与N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体1 小干扰RNA的复合物和水溶性脂质体与N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体1 小干扰RNA的复合物;假手术组只暴露坐骨神经。 结果与结论:水溶性脂质体转染组N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体1的 mRNA与蛋白表达水平明显低于其他两组(P < 0.01)。与假手术组比较,模型组、聚乙烯亚胺组及水溶性脂质体组N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体1 的mRNA和蛋白表达上调,累积疼痛评分升高(P < 0.01);与模型组比较,水溶性脂质体转染组脊髓背角N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体1 mRNA与蛋白表达及累积疼痛评分下降(P < 0.01),聚乙烯亚胺组上述指标无明显变化(P > 0.05)。表明在体内条件下水溶性脂质体可有效运载N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体1 小干扰RNA,抑制N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体1 的过度表达,还可减轻大鼠神经病理性痛。
中图分类号: