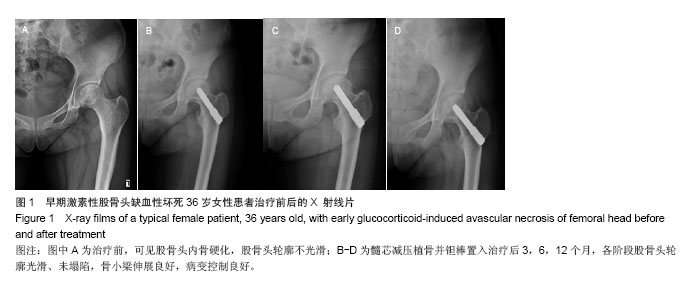
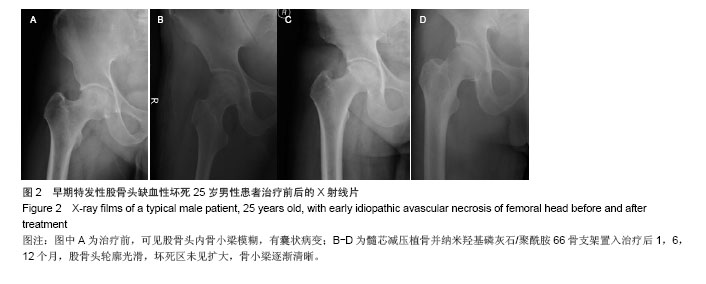
| [1]孙伟.股骨头坏死的病因、病理和发病机制[J].中华全科杂志, 2006,5(2):75-77.
[2]Song HJ,Lan BS,Cheng B,et al.Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for ischemic femoral head necrosis.Transplant Proc.2010;42(5):1862-1864.
[3]Hamilton TW,Goodman SM,Figgie M.SAS weekly rounds:avascular necrosis.HSS J.2009;5(2):99-113.
[4]Lieberman JR,Berry DJ,Mont MA,et al.Osteonecrosis of the hip: Management in the 21st Century.Instr Course Lect. 2003; 52:337-355.
[5]FicatRP.Idiopathic bone necrosis of the femoral head. Early diagnosis and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg.1985;67(1):43-49.
[6]Collaborative Osteonecrosis Group. Symptomatic multifocal osteonecrosis. A multicenter study.Clin Orthop. 1999;369: 312-326.
[7]康鹏德,裴福兴,沈彬,等.钻孔减压自体松质骨打压植骨结合同种异体腓骨棒植入治疗早期股骨头坏死的近期疗效观察[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2012,6(2):17-21.
[8]Ohzono K,Saito M,Takaoka K,et al.Natural history of nontraumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head.J Bone Joint Stag Br.1991;73(1):68-72.
[9]Yang P,Bian C,Huang X,et al.Core decompression in combination with nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 66 rod for the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2014;134(1):103-112.
[10]Gupta AK,Frank RM,Harris JD,et al.Arthroscopic-assisted core decompression for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Arthrosc Tech.2013;3(1):e7-e11.
[11]张鹤山,李子荣.股骨头坏死诊断与治疗的专家建议[J].中华骨科杂志.2007,27(2):146-148.
[12]Zheng W,Li J,Zhao J,et al.Development of a Valid Simpli?ed Chinese Version of the Oxford Hip Score in Patients With Hip Osteoarthritis.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2014;472(5):1545-1551.
[13]时冠军,刘世敬,张景僚,等.钻孔减压术加服中药治疗早期股骨头坏死30例[J].云南中医学院学报,2010,33(4):42-45.
[14]Marker DR,Seyler TM,McGrath MS,et al.Treatment of earlystage osteoneerosis of the femoral head.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2008;90:175-187.
[15]Marker DR,Seyler TM,Ulrich SD,et al.Do modem techniquesimprove core decompression outcomes for hip osteonecrosis.ClinOrthop Relat Res.2008;466:1093-1103.
[16]李国东,康一凡,蔡郑东,等.多孔钽棒植入治疗早期股骨头骨坏死(附二例报告) [J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008,23(12): 1032- 1033.
[17]尚咏,虞攀峰,赵旭红,等.髓芯减压钽棒+自体骨植入治疗成人早期股骨头缺血性坏死的短期疗效观察[J].山西医科大学学报, 2013, 44(3):240-244.
[18]康鹏德,裴福兴,沈彬,等.钻孔减压自体松质骨打压植骨结合同种异体腓骨棒植入治疗早期股骨头坏死的近期疗效观察[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2012,6(2):17-21.
[19]VaritimidisSE,DimitrouliasAP,KarachaliosTS,et al.Outcome after tantalum rod implantation for treatment of femoral head osteonecrosis: 26 hips followed for an average of 3 years. Acta Orthop.2009;1:20-25.
[20]Tsao AK,Roberson JR,Christie MJ,et al.Biomechanical and clinical evaluations of a porous tantalum implant for the treatment of early-stage osteonecrosis.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(2):22-27.
[21]Zhu J,Wang Y,Deng J,et al.Treatment of avascular necrosis of the femoral head by lesions clearance, compact bone grafting, and porous tantalumrodimplantation.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2011;25(11):1335-1338.
[22]Tanzer M,Bobyn JD,Krygier JJ,et al.Histopathologic retrieval analysis of clinically failed porous tantalum osteonecrosis implants.J Bone Joint surg(Am).2008;90(6):1282-1289.
[23]Nadeau M,Séguin C,Theodoropoulos JS,et al.Short term clinical outcome of a porous tantalum implant for the treatment of advanced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Mcgill J Med.2007;10(1):4-10.
[24]房明亮,王建强,朱自强,等.减压植骨加钽棒植入治疗早期股骨头坏死的临床疗效[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2011,32(21): 3476- 3477.
[25]Shuler MS,Rooks MD,Roberson JR.Porous tantalum implant in early osteonecrosis of the hip: preliminary report on operative, survival, and outcomes results. J Arthroplasty. 2007; 22: 26-31.
[26]Li J,Zuo Y,Cheng X,et al.Preparation and characterization ofnano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 66 composite GBR membrane withasymmetric porous structure. J Mater Sci Mater Med.2009;20(5):1031-1038.
[27]Zhang J,Huang C,Xu Q,et al.Biological properties of a biomimetic membrane for guided tissue regeneration: a study in rat calvarial defects. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010;21(4): 392-397.
[28]Yamaski N.Porous HAP Ceramica Prepared by Hydrothermal Hot- pressing. J Mater Sci L ett.1990;9(10):1150-1151.
[29]Shuai C,Gao C,Feng P,et al.Grain growth associates mechanical properties in nano-hydroxyapatite bone scaffolds.J Nanosci Nanotechnol.2013;13(8):5340-5345.
[30]Dorner-Reisel A,Klemm V,Irmer G,et al.Nano- and microstructure of short fibre reinforced and unreinforced hydroxyaptite.Biomed Tech (Berl).2002;47 Suppl Suppl Pt 1: 397-400.
[31]Ma Z,Gao C,Gong Y,et al.Cartilage tissue engineering PLLA scaffold with surface immobilized collagen and basic fibroblast growth factor.Biomaterials.2005;26(11):1253-1259.
[32]Yang P,Bian C,Huang X,et al.Core decompression in combination with nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 66 rod for the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2014;134(1):103-112. |