| [1] Voigt C,Schönaich M,Lill H.Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: state of the art.Eur J Trauma.2006;32(4): 332-339.
[2] 敖英芳,田得祥,崔国庆,等.运动员前交叉韧带损伤的流行病学研究[J].体育科学,2000,20(4):47-49.
[3] Barenius B,Nordlander M,Ponzer S,et al. Quality of life and clinical outcome after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using patellar tendon graft or quadrupled semitendinosus graft: an 8-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial.Am J Sports Med.2010;38(8):1533-1541.
[4] Longo UG,Buchmann S,Franceschetti E,et al.A systematic review of single-bundle versus double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.Br Med Bull. 2012;103(1): 147-168.
[5] Maffulli N,Spiezia F,King JB,et al. Figure-of-four pivot shift test: a technical note. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis.2011;69(2):173-176.
[6] Ge Z,Goh JCH,Lee EH.Selection of cell source for ligament tissue engineering.Cell Transplant.2005;14(8):573-583.
[7] Hoffmann A,Gross G.Tendon and ligament engineering in the adult organism: mesenchymal stem cells and gene-therapeutic approaches.Int Orthop. 2007;31(6): 791-797.
[8] Broese M,Toma I,Haasper C,et al.Seeding a human tendon matrix with bone marrow aspirates compared to previously isolated hBMSCs–An in vitro study.Technol Health Care.2011; 19(6):469-479.
[9] Abraham GA,Murray J,Billiar K,et al.Evaluation of the porcine intestinal collagen layer as a biomaterial.J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;51(3):442-452.
[10] 王成学,谷贵山,胡春明,等.老年骨质疏松动物模型韧带胶原蛋白含量测定[J].中国老年学杂志,2009,29(11):38-39.
[11] Grant RA.Estimation of hydroxyproline by the AutoAnalyser.J Clin Pathol.1964;17(6):685.
[12] Hankemeier S,Keus M,Zeichen J,et al.Modulation of proliferation and differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells by fibroblast growth factor 2: potential implications for tissue engineering of tendons and ligaments. Tissue Eng.2005;11(1-2):41-49.
[13] Haasper C,Zeichen J,Meister R,et al.Tissue engineering of osteochondral constructs in vitro using bioreactors.Injury. 2008;39(1):66-76.
[14] Hernigou P,Daltro G,Filippini P,et al.Percutaneous implantation of autologous bone marrow osteoprogenitor cells as treatment of bone avascular necrosis related to sickle cell disease.Open Orthop J.2008;2:62.
[15] Asahara T,Masuda H,Takahashi T,et al.Bone marrow origin of endothelial progenitor cells responsible for postnatal vasculogenesis in physiological and pathological neovascularization.Circ Res.1999;85(3):221-228.
[16] Cristino S,Grassi F,Toneguzzi S,et al.Analysis of mesenchymal stem cells grown on a three‐dimensional HYAFF 11®‐based prototype ligament scaffold. J Biomed Mater Res A.2005;73(3):275-283.
[17] Garlet TP,Coelho U,Silva JS,et al.Cytokine expression pattern in compression and tension sides of the periodontal ligament during orthodontic tooth movement in humans.Eur J Oral Sci. 2007;115(5):355-362.
[18] 王洪,赵玉鑫,杨述华,等.半月板纤维软骨细胞与小肠粘膜下层相容性的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2007,24(9):1149-1149.
[19] 王茂源,赵建宁.小肠粘膜下层在骨科组织工程学中的进展[J].中国骨伤,2006,19(1):61-63.
[20] Liang R,Woo SLY,Takakura Y,et al.Long-term effects of porcine small intestine submucosa on the healing of medial collateral ligament: a functional tissue engineering study.J Orthop Res.2006;24(4):811-819.
[21] 王洪,李艳军,杨述华,等.单螺旋和3股螺旋蚕丝纤维支架的力学性能及其细胞黏附性能比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007,11(18):3523-3526.
[22] 崔树北,王洪,杨述华,等.小肠黏膜下层包绕丝素纤维复合韧带的生物力学测定[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(3): 517-520.
[23] Bertone AL,Goin S,Kamei SJ,et al.Metacarpophalangeal collateral ligament reconstruction using small intestinal submucosa in an equine model.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008;84(1):219-229. |
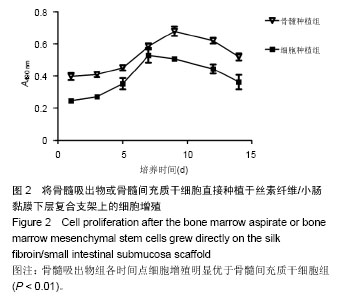
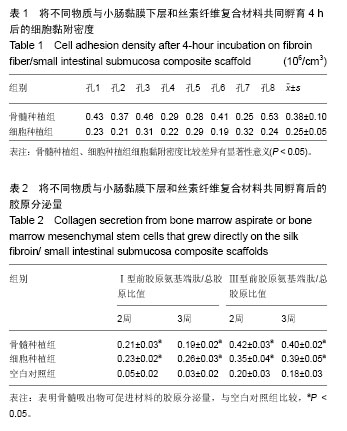
.jpg)
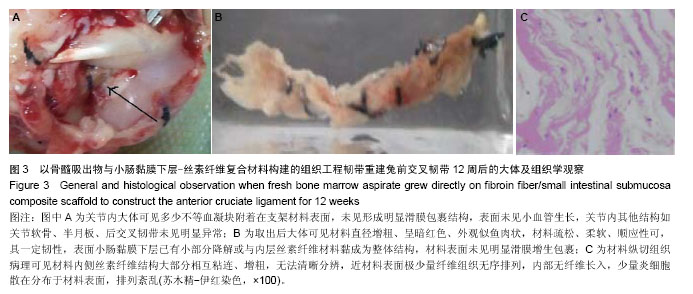
.jpg)