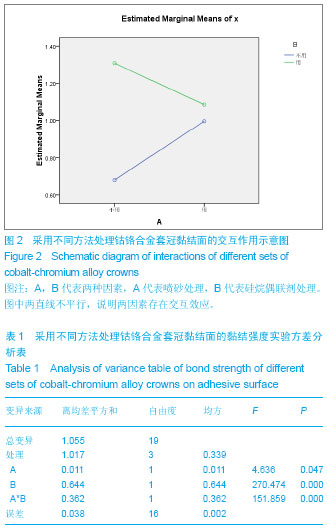
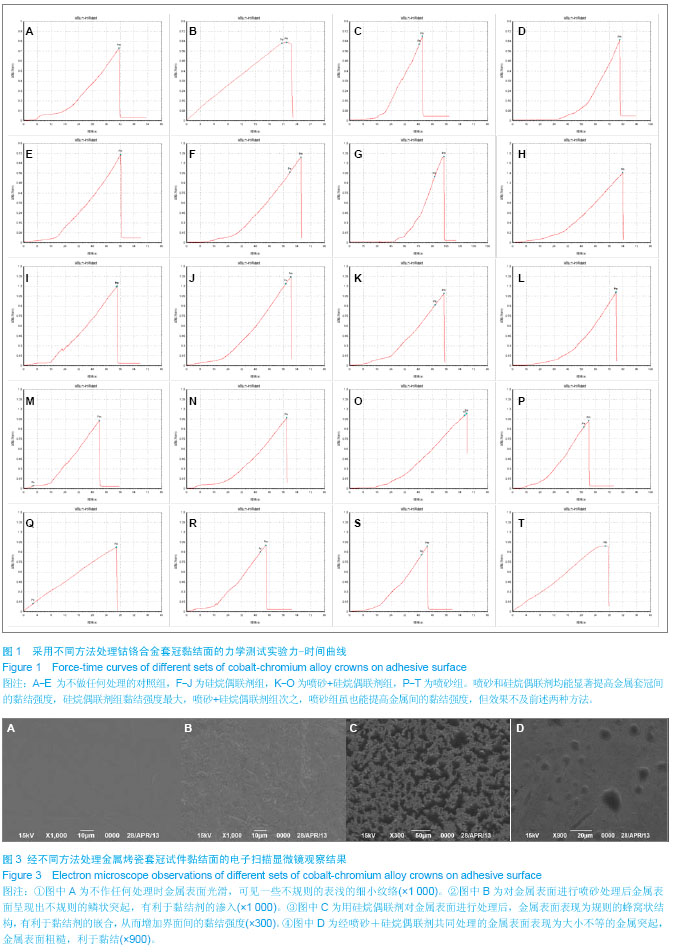
| [1] 岳进,常缨,陆逊.23例金属烤瓷冠修复失败的原因分析[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2009,31(1):92-93.[2] 陈新,王月娥.金属烤瓷冠桥修复失败的原因及处理[J].当代医学,2011,17(20):81.[3] 张静. 34例金属烤瓷冠修复失败的原因分析[J].中国实用医药, 2011,6(34):90-91.[4] 黄海蓉. 金瓷修复体崩瓷修补技术的临床应用[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2007,34(1):65-67.[5] 耿宏杰.金属烤瓷冠桥修复后并发症的原因及处理[J].临床实用医学,2010,15(43):145-146.[6] 赵煜,巢永烈.金属烤瓷冠崩瓷的临床修补[J].北京口腔医学, 2005, 13(4):262-265.[7] 刘洋,英晓霞.邻面开口式部分冠修复金-瓷固定桥崩瓷[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(3)496-499.[8] 马轩祥.′98全国口腔烤瓷修复问题与对策专题研讨会纪要[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2009,34(5):311.[9] 樊中全,任煜光.介绍一种烤瓷桥体崩瓷修复方法[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2002,3(4):246.[10] ]秦雍,刘剑锋,张静.前牙 PFM 颈缘三维有限元受力分析[J].中国医药指南,3009,7(2):17-18.[11] Van NR,Howard IC.Leached components from dental composites in oral simulatingfluids and the resultant composite strengths.Dent Res.1991;70(5):889.[12] 陈治清,管利民.口腔粘接学[M].北京:北京医科大学中国协和医科大学联合出版社,1992.[13] Bona AD,Van NR. Effects of curing time and filler concentration on curing and post curing of urethane dimethacrylate composites:a microcalorimetric study.Dent Res.1995;74(9):1591.[14] 吴峻岭,巢永烈,王少安.金属一复合树脂粘接修复中金属粘接面的处理[J].国外医学:口腔医学分册,2003,30(6):461-463.[15] Sarac YS,Elekdag-Turk S,Sarac D,et al.Surface conditioning methods and polishing techniques effect on surface roughness of a feldspar ceramic.Angle Orthod.2009;77(4): 723-728.[16] 马岭,傅进友,王林.烤瓷表面金属托槽剪切强度的体外研究[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2006,7(3):166-168.[17] Ibrahim FT.Resin shear bond strength to porcelain and a base metal alloy using two polymerisation schemes.J Prosthet Dent. 2000;83:181-186.[18] 张汉平,卫彦,郑刚,等.口内喷砂增强Ni-Cr合金与复合树脂间粘接强度的研究[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2005,19(2):2-3.[19] 邱憬,陈亚明,冯丽君.非贵金属烤瓷基底口内喷砂对瓷修补树脂黏结强度的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(29): 5383-5386.[20] 王尊一,卫彦,胡晓阳,等.不同合金烤瓷基底冠与树脂修复材料粘接强度的对比实验[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2005,19(3):312-313.[21] Frankenberger R,Krämer N,Sindel J.Repair strength of etched vs silica-coated metal-ceramic and all-ceramic restorations.Oper Dent.2010;25(3):209-215.[22] 殷榕灿,张文保.硅烷偶联剂的研究进展[J].中国科技信息杂志, 2010,5(10):44-46.[23] 沈玺,高雅男,徐政.硅烷偶联剂的研究与应用[J].上海生物医学工程,2006,26(1):14-17.[24] 伊元夫.偶联剂在金属-树脂粘接中的应用[J].国外医学:口腔医学分册,2000,27(6):364-367.[25] 林艺翚,史建陆,张端强.不同处理方法的陶瓷托槽再黏结抗剪切强度比较[J].中国实用口腔医学杂志,2010,3(1):24-26.[26] 白鸣霞,李长福,徐连来.偶联剂在口腔材料中的应用及研究现状[J].天津医科大学学报,2004,10(4):598-600.[27] Petrie CS,Eick JD,Williams K,et al.A comparison of 3 alloy surface treatments for resin-bonded prostheses.J Prosthodont. 2001;10(4):217-223.[28] Vallittu PK, Ekstrand K.In vitro cytotoxicity of fibre-polymethyl methacrylate composite used in dentures.J Oral Rehabil. 1999; 26(8):666.[29] Matsumura H,Taira Y,Yoshida K,et al.Bond strength of a metal adhesive system joined to noble alloys.J Dent Res.1997; 76(1):380.[30] 余涛,曹军,张兆德,等.不同表面处理方法对金属托槽与不同瓷修复体黏结强度影响的研究[J].中国美容医学,2009,18(11): 1660-1663. |