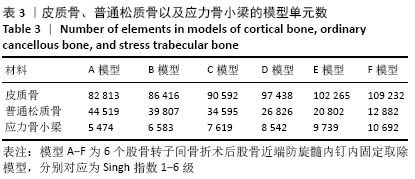
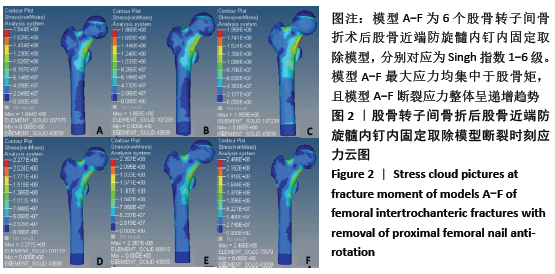
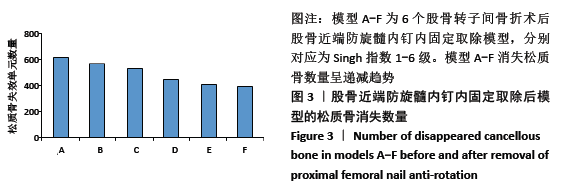
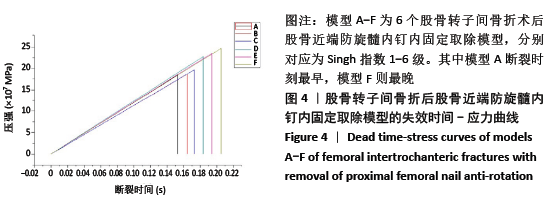
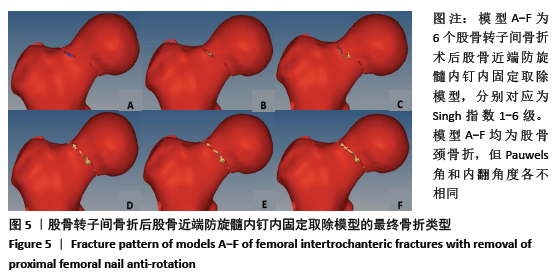
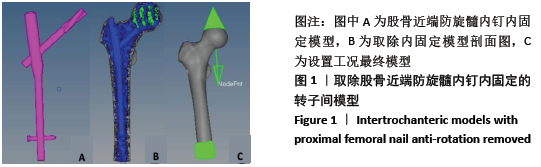
[1] XIA WB, HE SL, XU L, et al. Rapidly increasing rates of hip fracture in Beijing, China. J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27(1):125-129.
[2] WANG J, WANG Y, LIU WD, et al. Hip fractures in Hefei, China: the Hefei osteoporosis project. J Bone Miner Metab. 2014;32(2):206-214.
[3] ADIB HAJBAGHERY M, ABBASINIA M. Quality of life of the elderly after hip fracture surgery: a case-control study. J Caring Sci. 2013;2(1):53-59.
[4] CLOSE JD, SWARTZ K, DEU R. Hip fracture in older patients: tips and tools to speed recovery. J Fam Pract. 2013;62(9):484-492.
[5] GUO Y, YANG HP, DOU QJ, et al. Efficacy of femoral nail anti-rotation of helical blade in unstable intertrochanteric fracture. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(3 Suppl):6-11.
[6] XU R, RU J, JI F, et al. Comparison of efficacy, complications and TGF-β2 expression between DHS and PFNA in elderly patients with osteoporotic femoral intertrochanteric fracture. Exp Ther Med. 2018; 16(1):394-399.
[7] 卞敏凯.股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗股骨转子间骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2020,23(3):402-405.
[8] 华长城,丁超,王小合,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年股骨转子间骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2020,23(3):412-414.
[9] 黄培镇,陈心敏,郑利钦,等.骨水泥增强股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗高龄不稳定型股骨转子间骨折的有限元分析[J].天津医药, 2020,48(5):385-390,466.
[10] 乔梁,曹贞国,李华,等.局麻下股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗高危患者股骨转子间骨折[J].中国骨伤,2020,33(4):317-321.
[11] 褚楷,张兴琳,鲁兴,等.股骨颈骨折内固定物取出后股骨头内部微骨折发生风险的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(9): 1091-1095.
[12] 刘泽民,吕欣,刘晋元,等.髋部骨折2342例流行病学分布特点的单中心分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(32):5085-5091.
[13] MATTISSON L, BOJAN A, ENOCSON A. Epidemiology, treatment and mortality of trochanteric and subtrochanteric hip fractures: data from the Swedish fracture register. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018; 19(1):369.
[14] 李木生,林梓凌,郑永泽,等.股骨皮质厚度参数及骨小梁密度在老年髋部骨折治疗中的临床意义[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2019, 27(4):11-14.
[15] SKULADOTTIR SS, GUDMUNDSDOTTIR E, MOGENSEN B, et al. Hip fractures among older people in Iceland between 2008 and 2012. Int J Orthop Trauma Nurs. 2019;32:27-31.
[16] 金成春,王德平,马辉.基于断裂力学的应力性骨折研究现状[J].同济大学学报(医学版),2019,40(4):523-528.
[17] 李木生,林梓凌,郑利钦,等.基于断裂力学的骨质疏松性大鼠股骨颈骨折有限元仿真[J].医学研究生学报,2019,32(9):915-919.
[18] 黄培镇,陈心敏,郑利钦,等.骨质疏松影响股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗股骨转子间骨折的有限元仿真[J].中国组织工程研究,2020, 24(24):3808-3814.
[19] KAWABATA Y, MATSUO K, NEZU Y, et al. The risk assessment of pathological fracture in the proximal femur using a CT-based finite element method. J Orthop Sci. 2017;22(5):931-937.
[20] WANG J, MA JX, LU B, et al. Comparative finite element analysis of three implants fixing stable and unstable subtrochanteric femoral fractures: Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA), Proximal Femoral Locking Plate (PFLP), and Reverse Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS). Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020;106(1):95-101.
[21] VAN HOUCKE J, SCHOUTEN A, STEENACKERS G, et al. Computer-based estimation of the hip joint reaction force and hip flexion angle in three different sitting configurations. Appl Ergon. 2017;63:99-105.
[22] 王亦璁,刘沂,姜保国.骨与关节损伤[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2007:1155-1156.
[23] 冯森,林志,范国宇.基于断裂力学理论的结构裂纹扩展机理分析[J].工程建设,2020,52(1):6-11.
[24] 金成春,王德平,马辉.基于断裂力学的应力性骨折研究现状[J].同济大学学报(医学版),2019,40(4):523-528.
[25] 李长洲,庞炎旭,于利,等.骨密度在髋部骨质疏松性骨折风险评估中的价值[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(7):1023-1027.
[26] 崔洋洋,宫赫,关夏莉,等.基于髋部骨骼属性预测骨折风险研究进展[J].医用生物力学,2019,34(5):555-559.
[27] 石淇允,李无阴,张颖,等.老年髋部骨折危险因素的研究进展[J].中医正骨,2019,31(8):45-47.
[28] YU Z, WANG G, TANG T, et al. Long-term effects of ovariectomy on the properties of bone in goats. Exp Ther Med. 2015;9(5):1967-1973.
[29] 吴子祥,雷伟,胡蕴玉,等.骨质疏松绵羊模型松质骨及皮质骨的微观结构及力学性能变化的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2007,13 (8):537-541,546.
[30] 徐丛,徐飞,杜元良,等.绝经后女性不同Singh指数骨扫描电镜特点[J].中国老年学杂志,2016,36(4):936-938.
[31] 张翘,武云涛,于涛,等.股骨颈松质骨的应力松弛方程[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(2):272-275.
[32] THOMAS CD, MAYHEW PM, POWER J, et al. Femoral neck trabecular bone: loss with aging and role in preventing fracture. J Bone Miner Res. 2009;24(11):1808-1818.
[33] KOIVUMÄKI JE, THEVENOT J, PULKKINEN P, et al. Cortical bone finite element models in the estimation of experimentally measured failure loads in the proximal femur. Bone. 2012;51(4):737-740.
[34] NAWATHE S, NGUYEN BP, BARZANIAN N, et al. Cortical and trabecular load sharing in the human femoral neck. J Biomech. 2015;48(5): 816-822.
[35] 梅炯.“股骨距”还是“股骨矩”?[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2016,5(7): 557-559.
[36] ZANI L, ERANI P, GRASSI L, et al. Strain distribution in the proximal Human femur during in vitro simulated sideways fall. J Biomech. 2015; 48(10):2130-2143.
[37] 刘庆宇.髓芯减压打压植骨腓骨支撑术对改善早中期股骨头坏死患者髋关节功能的效果[J].河南外科学杂志, 2019,25(4):69-70.
[38] 黄柏鑫,蒙德,黄俊潮,等.髓芯减压打压植骨腓骨支撑术治疗股骨头缺血性坏死的疗效分析[J].中国处方药, 2019,17(5):140-141.
[39] 刘晨阳.关节镜监视下打压植骨腓骨支撑术对围塌陷期非创伤性股骨头坏死患者术后Harris评分的影响[J].首都食品与医药,2020, 27(13):58.
[40] 徐景利,陈达,林天烨,等.腓骨柱联合空心螺钉与3枚空心螺钉比较治疗股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[J].新疆医科大学学报,2019, 42(3):301-308,313.
[41] 凌观汉,李永斌,潘学文,等.中日友好医院分型股骨头坏死腓骨植入治疗的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(18): 2817-2822.
[42] 武少坤,邬耀军,顾志谦,等.股骨成形术对于预防骨质疏松性髋部骨折的生物力学研究[J].中国骨伤,2020,33(6):572-575.
[43] 吴琼.辛伐他汀联合阿仑膦酸钠对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠骨代谢的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(7):1049-1053.
[44] 楼家晖,杨鸫祥,郑明轩,等.强筋健骨方对PMOP大鼠骨密度及生物力学影响的实验研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(7):978-982. |