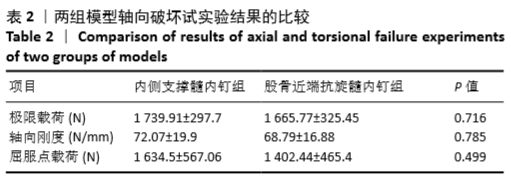
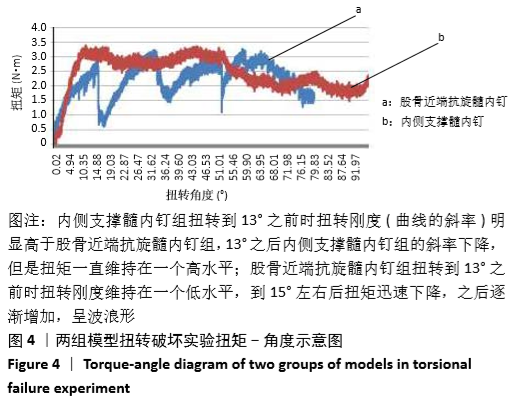
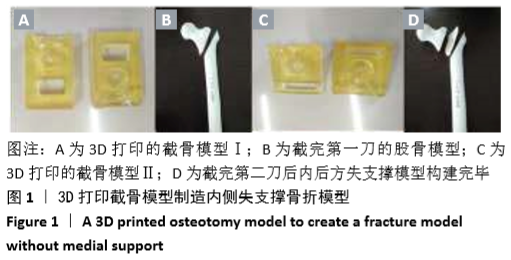
[1] KARAGIANNIS A, PAPAKITSOU E, DRETAKIS K, et al. Mortality rates of patients with a hip fracture in a southwestern district of Greece: ten-year follow-up with reference to the type of fracture. Calcif Tissue Int. 2006;78(2):72-77.
[2] BONNAIRE F, STRAßBERGER C, KIEB M, et al. Osteoporotic fractures of the proximal femur. What’s new? Chirurg.2012;83(10):882-891.
[3] WESTHOFF D, WITLOX J, KOENDERMAN L, et al. Preoperative cerebrospinal fluid cytokine levels and the risk of postoperative delirium in elderly hip fracture patients.J Neuroinflammation.2013; 10:122.
[4] ADEYEMI A, DELHOUGNE G. Incidence and Economic Burden of Intertrochanteric Fracture: A Medicare Claims Database Analysis.JB JS Open Access.2019;4(1):e0045.
[5] SOCCI AR, CASEMYR NE, LESLIE MP, et al. Implant options for the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures of the hip: rationale, evidence, and recommendations. Bone Joint J.2017;99-B(1):128-133.
[6] CUMMINGS SR, MELTON LJ. Epidemiology and outcomes of osteoporotic fractures.Lancet.2002; 359:1761-1767.
[7] KIM JW, KIM TY, HA YC, et al. Outcome of intertrochanteric fractures treated by intramedullary nail with two integrated lag screws:A study in Asian population.Indian J Orthop.2015;49(4):436-441.
[8] YU W, ZHANG X, ZHU X, et al. A retrospective analysis of the InterTan nail and proximal femoral nail anti-rotation-Asia in the treatment of unstable intertrochanteric femur fractures in the elderly.J Orthop Surg Res.2016;11:10.
[9] ZHANG H, ZHU X, PEI G, et al. A retrospective analysis of the InterTan nail and proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients with osteoporosis: a minimum follow-up of 3 years.J Orthop Surg Res.2017;12(1):147.
[10] WANG Q, YANG X, HE HZ, et al. Comparative study of InterTAN and Dynamic Hip Screw in treatment of femoral intertrochanteric injury and wound.Int J Clin Exp Med.2014;7(12):5578-5582.
[11] IMERCI A, AYDOGAN NH, TOSUN K. A comparison of the InterTan nail and proximal femoralfail antirotation in the treatment of reverse intertrochanteric femoral fractures. Acta Orthop Belg.2018;84(2):123-131.
[12] LI J, ZHANG L, ZHANG H, et al. Effect of reduction quality on post-operative outcomes in 31-A2 intertrochanteric fractures following intramedullary fixation: a retrospective study based on computerised tomography findings.Int Orthop.2019;43(8):1951-1959.
[13] CHANG SM, ZHANG YQ, MA Z, et al. Fracture reduction with positive medial cortical support: a key element in stability reconstruction for the unstable pertrochanteric hip fractures.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2015;135(6):811-818.
[14] KULKARNI SG, BABHULKAR SS, KULKARNI SM, et al. Augmentation of intramedullary nailing in unstable intertrochanteric fractures using cerclage wire and lag screws: a comparative study. Injury.2017;48 Suppl 2:S18-S22.
[15] LI J, HAN L, ZHANG H, et al. Medial sustainable nail versus proximal femoral nail antirotation in treating AO/OTA 31-A2.3 fractures: Finite element analysis and biomechanical evaluation. Injury.2019;50(3):648-656.
[16] FENSKY F, NÜCHTERN JV, KOLB JP, et al. Cement augmentation of the proximal femoral nail antirotation for the treatment of osteoporotic pertrochanteric fractures--a biomechanical cadaver study.Injury. 2013; 44(6):802-807.
[17] NÜCHTERN JV, RUECKER AH, SELLENSCHLOH K, et al. Malpositioning of the lag screws by 1- or 2-screw nailing systems for pertrochanteric femoral fractures: a biomechanical comparison of gamma 3 and intertan. J Orthop Trauma.2014;28(5):276-282.
[18] KNOBE M, GRADL G, MAIER KJ, et al. Rotationally stable screw-anchor versus sliding hip screw plate systems in stable trochanteric femur fractures: a biomechanical evaluation.J Orthop Trauma. 2013; 27(6):e127-e136.
[19] CHEN Y, LIU S, LIN P, et al. Comparative biomechanical study of reversed less invasive stabilization system and proximal femoral nail antirotation for unstable intertrochanteric fractures.Chin Med J(Engl). 2014;127(23):4124-4129.
[20] IMREN Y, GURKAN V, BILSEL K, et al. Biomechanical comparison of dynamic hip screw, proximal femoral nail, cannulated screw, and monoaxial external fixation in the treatment of basicervical femoral neck fractures.Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech.2015;82(2):140-144.
[21] SHIN WC, SEO JD, LEE SM, et al. Radiographic Outcomes of Osteosynthesis Using Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA) System in Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture: Has PFNA II Solved All the Problems? Hip Pelvis.2017;29(2):104-112.
[22] HUANG SG, CHEN B, ZHANG Y, et al. Comparison of the Clinical Effectiveness of PFNA, PFLCP, and DHS in Treatment of Unstable Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture.Am J Ther.2017;24(6):e659-e666.
[23] ARIRACHAKARAN A, AMPHANSAP T, THANINDRATARN P, et al. Comparative outcome of PFNA, Gamma nails, PCCP, Medoff plate, LISS and dynamic hip screws for fixation in elderly trochanteric fractures: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2017;27(7):937-952.
[24] NHERERA L, TRUEMAN P, HORNER A, et al. Comparison of a twin interlocking derotation and compression screw cephalomedullary nail (InterTAN) with a single screw derotation cephalomedullary nail (proximal femoral nail antirotation): a systematic review and meta-analysis for intertrochanteric fractures.J Orthop Surg Res.2018;13(1):46.
[25] MAKKI D, MATAR HE, JACOB N, et al. Comparison of the reconstruction trochanteric antigrade nail (TAN) with the proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) in the management of reverse oblique intertrochanteric hip fractures.Injury.2015;46(12):2389-2393.
[26] SHIN YS, CHAE JE, KANG TW, et al. Prospective randomized study comparing two cephalomedullary nails for elderly intertrochanteric fractures: Zimmer natural nail versus proximal femoral nail antirotation II.Injury.2017;48(7):1550-1557.
[27] LI J, CHENG L, JING J. The Asia proximal femoral nail antirotation versus the standard proximal femoral antirotation nail for unstable intertrochanteric fractures in elderly Chinese patients.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2015;101(2):143-146.
[28] SINGH NK, SHARMA V, TRIKHA V, et al. Is PFNA-II a better implant for stable intertrochanteric fractures in elderly population ? A prospective randomized study.J Clin Orthop Trauma.2019;10 (Suppl 1):S71-S76.
[29] ZOU J, XU Y, YANG H. A comparison of proximal femoral nail antirotation and dynamic hip screw devices in trochanteric fractures.J Int Med Res. 2009;37(4):1057-1064.
[30] WANG B, LIU Q, LIU Y, et al. Comparison of Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation and Dynamic Hip Screw Internal Fixation on Serum Markers in Elderly Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak.2019;29(7):644-648.
[31] MA KL, WANG X, LUAN FJ, et al. Proximal femoral nails antirotation, Gamma nails, and dynamic hip screws for fixation of intertrochanteric fractures of femur: A meta-analysis.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2014; 100(8):859-866.
[32] ZEHIR S, ZEHIR R, ZEHIR S, et al. Proximal femoral nail antirotation against dynamic hip screw for unstable trochanteric fractures; a prospective randomized comparison.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2015; 41(4): 393-400.
[33] MA JX, WANG J, XU WG, et al. Biomechanical outcome of proximal femoral nail antirotation is superior to proximal femoral locking compression plate for reverse oblique intertrochanteric fractures: a biomechanical study of intertrochanteric fractures.Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2015;49(4):426-432.
[34] HUANG Y, ZHANG C, LUO Y. A comparative biomechanical study of proximal femoral nail (InterTAN) and proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures.Int Orthop.2013; 37(12): 2465-2473.
[35] SINGH AK, NARSARIA N, GUPTA RK. A biomechanical study comparing proximal femur nail and proximal femur locking compression plate in fixation of reverse oblique proximal femur fractures. Injury.2017; 48(10):2050-2053.
[36] YE KF, XING Y, SUN C, et al. Loss of the posteromedial support: a risk factor for implant failure after fixation of AO 31-A2 intertrochanteric fractures.Chin Med J (Engl).2020;133(1):41-48.
[37] ZHANG S, ZHANG K, WANG Y, et al. Using three-dimensional computational modeling to compare the geometrical fitness of two kinds of proximal femoral intramedullary nail for Chinese femur.ScientificWorldJournal.2013;2013:978485.
[38] CHANG SM, SONG DL, MA Z, et al. Mismatch of the short straight cephalomedullary nail (PFNA-II) with the anterior bow of the Femur in an Asian population.J Orthop Trauma. 2014;28(1):17-22. |