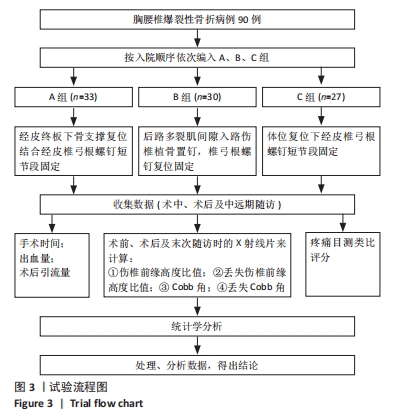
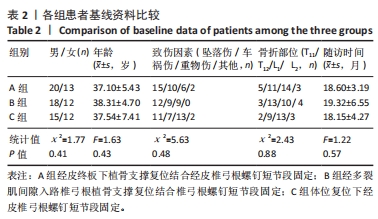
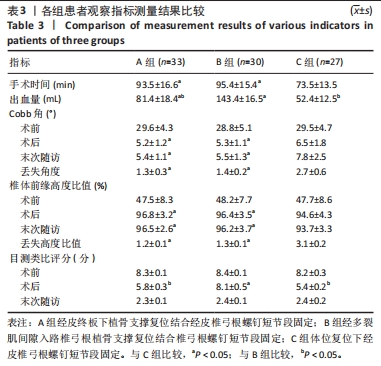
[1] TRUNGU S, RICCIARDI L, FORCATO S. Percutaneous pedicle screw fixation without arthrodesis of 368 thoracolumbar fractures: long-term clinical and radiological outcomes in a single institution. Eur Spine J. 2023;32(1):75-83.
[2] BUTLER AJ, COLMAN MW, LYNCH J, et al. Augmented reality in minimally invasive spine surgery: early efficiency and complications of percutaneous pedicle screw instrumentation. Spine J. 2023;23(1):27-33.
[3] NORIEGA DC, CRESPO-SANJUAN J, OLAN WJ, et al. Treatment of Thoracolumbar Type A3 Fractures Using a Percutaneous Intravertebral Expandable Titanium Implant: Long-term Follow-up Results of a Pilot Single Center Study. Pain Physician. 2021;24(5):E631-E638.
[4] TRUNGU S, RICCIARDI L, FORCATO S, et al. Percutaneous pedicle screw fixation without arthrodesis of 368 thoracolumbar fractures: long-term clinical and radiological outcomes in a single institution. Eur Spine J. 2023;32(1):75-83.
[5] XU J,LIU C,LIN Y, et al. Microscopic minimally invasive keyhole technique for surgical resection of spinal dumbbell tumors. World Neurosurg. 2018;109:e110-e117.
[6] MOON MS, YU CG, JEON JM, et al. Usefulness of Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation for Treatment of Lower Lumbar Burst (A3-A4) Fractures: Comparative Study with Thoracolumbar Junction Fractures. Indian J Orthop. 2023;57(9):1415-1422.
[7] KUMAR N, CHIN BZ, CHUA CXK, et al. Unipedicular-Screw Index Vertebra Manipulation Technique for Minimally Invasive Short-Segment Thoracolumbar Fracture Fixation. Int J Spine Surg. 2023:8524.
[8] MARTIN-SOMOZA FJ, CANTERO ESCRIBANO JM, RAMIREZ-VILLAESCUSA JV. Long-Term Reliability of the Two-Segment Fusion Technique in the Treatment of Thoracolumbar Fractures Using Screws in the Fractured Vertebra. Int J Spine Surg. 2021;15(1):169-178.
[9] 付建仲,冯慧峰.后路椎弓根内固定术联合椎体成形术治疗老年胸腰段脊柱骨折疗效分析[J].中国烧伤创疡杂志,2022,34(6):418-421.
[10] WANG H, ZHANG L, DU H, et al. Efficacy and Safety Evaluation of Bilateral Pedicle Approach Combined with Positional Reduction for the Treatment of Osteoporotic Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures. Altern Ther Health Med. 2023;29(6):176-181.
[11] KOCIS J, KELBL M, KOCIS T, et al. Percutaneous versus open pedicle screw fixation for treatment of type A thoracolumbar fractures. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2020;46(1):147-152.
[12] 尹稳,焦伟,于海洋.经皮椎弓根螺钉置钉辅助技术及应用进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2022,32(8):743-747.
[13] KANNO H, AIZAWA T, HASHIMOTO K, et al. Enhancing percutaneous pedicle screw fixation with hydroxyapatite granules: A biomechanical study using an osteoporotic bone model. PLoS One. 2019;14(9):e0223106.
[14] ANANIA CD, BONO BC, TROPEANO M, et al. Single-Stage Posterior Transpedicular Corpectomy and 360-Degree Reconstruction for Thoracic and Lumbar Burst Fractures: Technical Nuances and Outcomes. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2023;84(5):489-497.
[15] SUBRAMANIAN P, RAMACHANDRAN K, ARUMUGAM T, et al. Evaluation of Disc and Endplate Degeneration in AO Type A Fractures Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2023:S1878-8750(23)01107-5.
[16] XU C, BAI X, RUAN D, et al. Comparative finite element analysis of posterior short segment fixation constructs with or without intermediate screws in the fractured vertebrae for the treatment of type a thoracolumbar fracture. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2023:1-12.
[17] WANG P, HU X. Biomechanical finite element analysis of superior endplate collapse after thoracolumbar fracture surgery. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(12):753.
[18] 孙家安,李亚男,王肖虎,等.经皮椎体成形术治疗老年胸腰椎骨折对患者手术创伤程度及脊柱功能的影响[J].中国老年学杂志, 2023,43(2):318-321.
[19] 高志祥,肖聪,杨红涛,等.胸腰椎爆裂骨折伴神经损伤围术期隐性失血的统计学决策树模型分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(15):2364-2369.
[20] 刘凌,孙佳佳,季一鸣,等.伤椎置钉短节段固定韧带复合体损伤胸腰椎骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(22):2060-2064.
[21] 王子奡,宋文慧,刘昌文.胸腰椎爆裂骨折短节段固定:方法改良及减少失败的策略[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(24):3902-3907.
[22] 韩雪昆,任永信,张慰.经皮伤椎置钉植骨治疗胸腰椎骨折疗效观察[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2020,40(1):115-118.
[23] 赵继荣,王兴盛,邓强,等.微创经皮椎弓根螺钉联合经伤椎植骨固定治疗胸腰椎骨折42例[J].中国微创外科杂志,2017,17(12): 1112-1116.
[24] CHEN L, LIU H, HONG Y, et al. Minimally Invasive Decompression and Intracorporeal Bone Grafting Combined with Temporary Percutaneous Short-Segment Pedicle Screw Fixation for Treatment of Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture with Neurological Deficits. World Neurosurg. 2020;135: e209-e220.
[25] TOYONE T, TANAKA T, KATO D, et al. The treatment of acute thoracolumbar burst fractures with transpedicular intracorporeal hydroxyapatite grafting following indirect reduction and pedicle screw fixation: a prospective study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(7): E208-E214.
[26] 邵建树,刘伟峰,叶维,等.经椎弓根椎体内植骨联合短节段固定治疗老年脊柱骨折临床效果及对预后的影响[J].中国老年学杂志, 2022,42(20):5001-5004.
[27] CIRILLO JI, FARIAS I, DEL PINO C, et al. Surgical timing prevails as the main factor over morphologic characteristics in the reduction by ligamentotaxis of thoracolumbar burst fractures. BMC Surg. 2023; 23(1):166.
[28] LIMTHONGKUL W, WANNARATSIRI N, SUKJAMSRI C, et al. Biomechanical Comparison Between Posterior Long-Segment Fixation, Short-Segment Fixation, and Short-Segment Fixation With Intermediate Screws for the Treatment of Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture: A Finite Element Analysis. Int J Spine Surg. 2023;17(3):442-448.
[29] ALANDER DH, CUI S. Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Stabilization: Surgical Technique, Fracture Reduction, and Review of Current Spine Trauma Applications. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2018;26(7):231-240.
[30] ZOU P, YANG J, WANG X, et al. Comparison of Clinical and Radiologic Outcome Between Mini-Open Wiltse Approach and Fluoroscopic-Guided Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Placement: A Randomized Controlled Trial. World Neurosurg . 2020:144:e368-e375.
[31] CHEN ZD, WU J, YAO XT, et al. Comparison of Wiltse’s paraspinal approach and open book laminectomy for thoracolumbar burst fractures with greenstick lamina fractures: a randomized controlled trial. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):43.
[32] WANG F, NAN L, FENG X, et al. The efficacy and safety of multiple-dose intravenous tranexamic acid in reducing perioperative blood loss in patients with thoracolumbar burst fracture. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020:193:105766.
[33] 丁其瑞,凡进,任永信,等.经皮椎弓根螺钉短节段固定结合不同经伤椎椎体内植骨方法治疗胸腰椎骨折的早期疗效比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(10):1311-1317.
[34] GONZALES-PORTILLO GS, MAMARIL-DAVIS JC, RIORDAN K, et al. Evaluation of the Thoracolumbar Injury Classification and Severity (TLICS) Score Over a Two-Year Period at a Level One Trauma Center. Cureus. 2023;15(8):e43762.
[35] NISHIDA N, SUZUKI H, JIANG F, et al. Posterior Fixation for Different Thoracic-Sacrum Alignments Containing a Thoracolumbar Vertebral Fracture: A Finite Element Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2023:S1878-8750(23)00922-1.
[36] SCHNAKE KJ, SCHROEDER GD, VACCARO AR. AO Spine Classification Systems (Subaxial, Thoracolumbar). J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31 Suppl 4:S14-S23.
[37] TIAN D, ZHONG H, ZHU B, et al. Unilateral biportal endoscopic technique combined with percutaneous transpedicular screw fixation for thoracolumbar burst fractures with neurological symptoms: technical note and preliminary report. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023; 18(1):584.
[38] WEI H, HSU D, KATTA H, et al. Safety and Effectiveness of Expandable Intravertebral Implant Use for Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2023;34(8):1409-1415.
[39] ZENG Z, ZHANG D, ZENG FL, et al. Posterior unilateral small fenestration of lamina combined with a custom-made Y-shaped fracture reduction device for the treatment of severe thoracolumbar burst fracture: a prospective comparative study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):529.
[40] KUMAR N, CHIN BZ, CHUA CXK, et al. Unipedicular-Screw Index Vertebra Manipulation Technique for Minimally Invasive Short-Segment Thoracolumbar Fracture Fixation. Int J Spine Surg. 2023: 17(5):652-660.
[41] 朱福良,郑道明,时宇博,等.后路钉棒反弓折顶技术结合椎弓根植骨治疗胸腰段椎体爆裂骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(12): 1817-1822.
[42] PARAJÓN A, ALIMI M, NAVARRO-RAMIREZ R, et al. Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Meta-analysis of the Fusion Rates. What is the Optimal Graft Material? Neurosurgery. 2017;81(6): 958-971.
[43] 徐世财,马飞,唐超,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66椎间融合器形状对颈椎前路融合效果的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2023, 27(30):4830-4835.
[44] ZHAO J, ZHAO X, YANG L, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty with granulated allogeneic bone grafting using screw-view model of navigation for thoracolumbar compressive fracture: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(20):e15715.
[45] KONG D, SHI Y, GAO Y, et al. Preparation of BMP-2 loaded MPEG-PCL microspheres and evaluation of their bone repair properties. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;130:110516.
[46] OUCHIDA J, KANEMURA T, SATAKE K, et al. True accuracy of percutaneous pedicle screw placement in thoracic and lumbar spinal fixation with a CT-based navigation system:Intraoperative and postoperative assessment of 763 percutaneous pedicle screws. J Clin Neurosci. 2020;79:1-6.
[47] HU B, WANG L, SONG Y, et al. Long-term outcomes of the nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide-66 cage versus the titanium mesh cage for anterior reconstruction of thoracic and lumbar corpectomy: a retrospective study with at least 7 years of follow-up. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):482. |