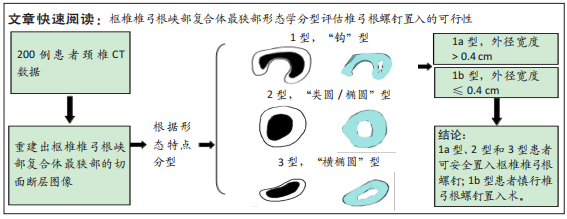
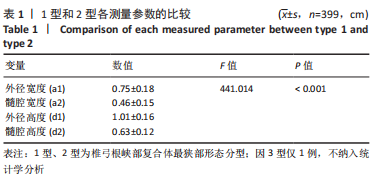
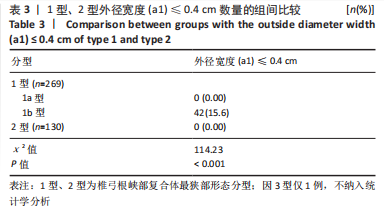
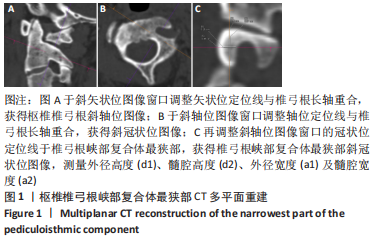
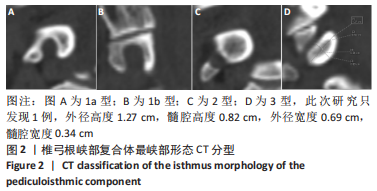
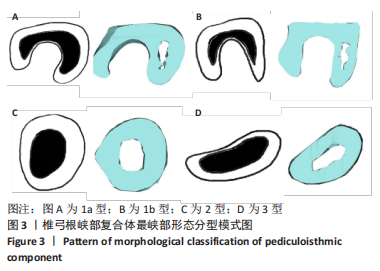
[1] GOEL A, LAHERI V. Plate and screw fixation for atlanto-axial subluxation. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1994;129(1-2):47-53.
[2] HARMS J, MELCHER RP. Posterior C1-C2 fusion with polyaxial screw and rod fixation.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(22):2467-2471.
[3] YOSHIDA M, NEO M, FUJIBAYASHI S, et al. Comparison of the anatomical risk for vertebral artery injury associated with the C2-pedicle screw and atlantoaxial transarticular screw. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(15):E513-517.
[4] SU BW,SHIMER AL, CHINTHAKUNTA S, et al. Comparison of fatigue strength of C2 pedicle screws, C2 pars screws,and a hybrid construct in C1-C2 fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(1):E12-19.
[5] VIZURRAGA DE, RHEE JM, BORDEN TC, et al. ”Inline” Axial Reconstructed CT Scans Provide a Significantly Larger Assessment of C2 Pedicle Diameter for Screw Placement Compared With “Standard” Axial Scans:Implications for Surgical Planning. Clin Spine Surg. 2017; 30(8):E1039-E1045.
[6] BLOCH O, HOLLY LT, PARK J, et al. Effect of frameless stereotaxy on the accuracy of C1-2 transarticular screw placement. J Neurosurg. 2001; 95(1 Suppl):74-79.
[7] DAVIDSON CT, BERGIN PF, VARNEY ET, et al. Planning C2 pedicle screw placement with multiplanar reformatted cervical spine computed tomography. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2019;10(1):46-50.
[8] 袁峰,李江山,徐凯,等.枢椎椎弓根最狭部形态学观察[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2009,27(2):170-173.
[9] MAKI S, KODA M, IIJIMA Y, et al. Medially-shifted rather than high-riding vertebral arteries preclude safe pedicle screw insertion. J Clin Neurosci. 2016;29:169-172.
[10] ABUMI K, TAKADA T, SHONO Y, et al. Posterior occipitocervical reconstruction using cervical pedicle screws and plate-rod systems.Spine. 1999;24(14):1425-34.
[11] BRANSFORD RJ, LEE MJ, REIS A. Posterior fixation of the upper cervical spine:contemporary techniques. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011;19(2):63-71.
[12] MADAWI AA, CASEY A, SOLANKI GA, et al. Radiological and anatomical evaluation of the atlantoaxial transarticular screw fixation technique.J Neurosurg. 1997;86(6):961-968.
[13] MANDEL IM, KAMBACH BJ, PETERSILGE CA, et al. Morphologic Considerations of C2 Isthmus Dimensions for the Placement of Transarticular Screws. Spine. 2000;25(12):1542-1547.
[14] XU HT, ZHENG S, DONG RP, et al. Combined 3-dimensional printing model and 3-dimensional fluoroscopic navigation to assist C2 pedicle screw insertion: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(43): e21838.
[15] GAO F, WANG Q, LIU C, et al. Individualized 3D printed model-assisted posterior screw fixation for the treatment of craniovertebral junction abnormality: a retrospective study. J Neurosurg Spine. 2017;27(1):29-34.
[16] LEE SH, PARK DH, KIM SD, et al. Analysis of 3-dimensional course of the intra-axial vertebral artery for C2 pedicle screw trajectory: a computed tomographic study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(17):E1010-E1014.
[17] 王建华,尹庆水,夏虹,等.枢椎椎动脉孔分型对枢椎椎弓根置钉的临床意义[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2007,17(8):593-595.
[18] 张力,吴月林,梁钊铨,等.CT重建技术评估枢椎椎弓根螺钉安全置钉可行性方法的对比研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2022,32(3): 200-206.
[19] 张艳,刘溢,王晓华.椎动脉CT血管造影多平面重组在枢椎椎弓根置钉中的价值[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014,24(3):217-221.
[20] YUAN F, YANG HL, GUO KJ, et al.A clinical morphologic study of the C2 pedicle and isthmus. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(1):39-45.
[21] ONO Y, MIYAKOSHI N, HONGO M, et al. Posterior spinal fusion using a unilateral C1 posterior arch screw and a C2 laminar screw for atlantoaxial fracture dislocation. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2019;7: 2050313X19849276.
[22] KOTHARI MK, DALVIE SS, GUPTA S, et al. The C2 pedicle width, pars length, and laminar thickness in concurrent ipsilateral ponticulus posticus and high-riding vertebral artery:A radiological computed tomography scan-based study. Asian Spine J. 2019;13(2):290-295.
[23] GOEL A, RANGNEKAR R, SHAH A, et al. Mobilization of the vertebral artery-surgical option for C2 screw fixation in cases with “high riding” vertebral artery. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown). 2020;18(6):648-651.
[24] DU YQ, YIN YH, QIAO GY, et al. C2 medial pedicle screw: a novel “in-out-in” technique as an alternative option for posterior C2 fixation in cases with a narrow C2 isthmus. J Neurosurg Spine. 2020;1:1-7.
[25] 高延征,高坤,余正红,等.“in-out-in”多皮质枢椎椎弓根螺钉在寰枢椎脱位或不稳后路手术中的应用[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2017, 27(1):55-60.
[26] WU F, LI H, WAN S, et al. The effect of axis pedicle and intra-axial vertebral artery on C2 pedicle screw placement. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022;36(7):866-872.
[27] 陈长青,冯万强,王成,等.后路内固定复位治疗上颈椎骨折脱位发生椎动脉损伤的临床分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2018,28(7): 607-612.
[28] SANELLI PC, TONG S, GONZALEZ RG, et al. Normal variation of vertebral artery on CT angiography and its implications for diagnosis of acquired pathology. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2002;26(3):462-470.
|