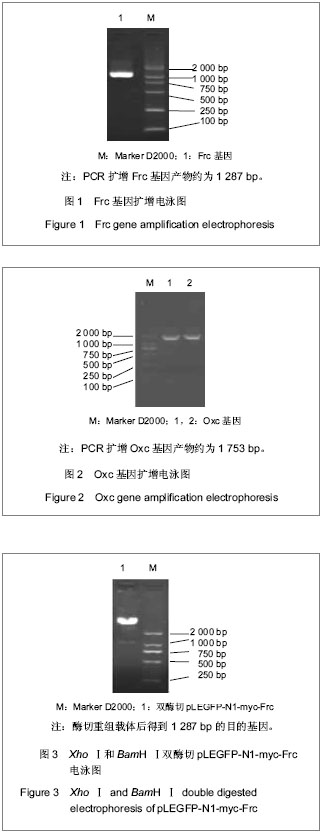
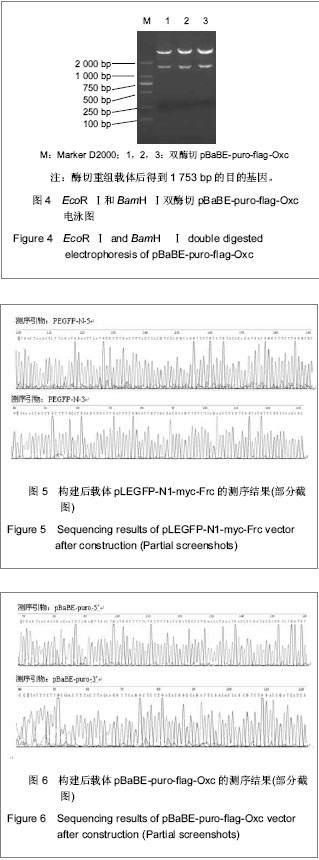
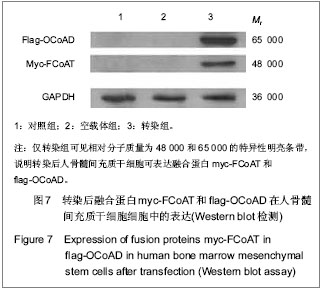
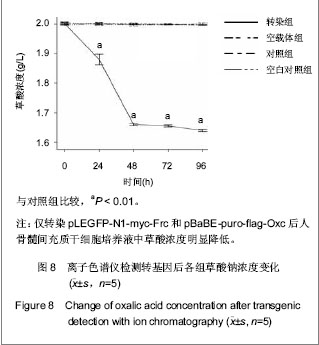
| [1] Mittal RD, Kumar R. Gut-inhabiting bacterium Oxalobacter formigenes: role in calcium oxalate urolithiasis. J Endourol. 2004;18(5):418-424.[2] Ogawa Y, Miyazato T, Hatano T. Oxalate and urinary stones. World J Surg. 2000;24(10):1154-1159. [3] Anantharam V, Allison MJ, Maloney PC. Oxalate: formate exchange. The basis for energy coupling in Oxalobacter. J Biol Chem. 1989;264(13):7244-7250.[4] Baetz AL, Allison MJ. Purification and characterization of oxalyl-coenzyme A decarboxylase from Oxalobacter formigenes. J Bacteriol. 1989;171(5):2605-2608.[5] Baetz AL, Allison MJ. Purification and characterization of formyl-coenzyme A transferase from Oxalobacter formigenes. J Bacteriol.1990;172(7):3537-3540.[6] Ye ZQ, Kong DB, Chen ZQ, et al. Stable expression of the oxc and frc genes from Oxalobacter formigenes in human embryo kidney 293 cells: implications for gene therapy of hyperoxaluria. Int J Mol Med. 2007;20(4):521-526.[7] 叶章群.泌尿系结石研究现况与展望[J].中华实验外科杂志,2005, 22(3):261-262.[8] Stamatelou KK, Francis ME, Jones CA, et al. Time trends in reported prevalence of kidney stones in the United States:1976-1994. Kidney Int. 2003;63(5):1817-1823.[9] Koul H, Kennington L, Honeyman T, et al. Activation of c-myc gene mediates the mitogenic effects of oxalate in LLC-PK1 cells, a line of renal epithelial cells. Kidney Int. 1996;50(5): 1525-1530.[10] Khan SR, Shevock PN, Hackett RL. Acute hyperoxaluria, renal injury and calcium oxalate urolithiasis. J Urol. 1992; 147(1):226-230.[11] Huang MY, Chaturvedi LS, Koul S, et al. Oxalate stimulates IL-6 production in HK-2 cells, a line of human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. Kidney Int. 2005;68(2):497-503.[12] Koul S, Chaturvedi LS, Sekhon A, et al. Effects of oxalate on the re-initiation of DNA synthesis in LLC-PK1 cells do not involve p42/44 MAP kinase activation. Kidney Int. 2002;61(2): 525-533.[13] Chaturvedi LS, Koul S, Sekhon A, et al. Oxalate selectively activates p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase signal transduction pathways in renal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(15):13321-13330. [14] Bhandari A, Koul S, Sekhon A, et al. Effects of oxalate on HK-2 cells, a line of proximal tubular epithelial cells from normal human kidney. J Urol. 2002;168(1):253-259.[15] Sidhu H, Schmidt ME, Cornelius JG, et al. Direct correlation between hyperoxaluria/oxalate stone disease and the absence of the gastrointestinal tract-dwelling bacterium Oxalobacter formigenes: possible prevention by gut recolonization or enzyme replacement therapy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10 Suppl 14:S334-340.[16] Sidhu H, Allison MJ, Chow JM, et al. Rapid reversal of hyperoxaluria in a rat model after probiotic administration of Oxalobacter formigenes. J Urol. 2001;166(4):1487-1491.[17] Hoppe B, Beck B, Gatter N, et al. Oxalobacter formigenes: a potential tool for the treatment of primary hyperoxaluria type 1. Kidney Int. 2006;70(7):1305-1311.[18] Duncan SH, Richardson AJ, Kaul P, et al. Oxalobacter formigenes and its potential role in human health. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2002;68(8):3841-3847.[19] Koul S, Johnson T, Pramanik S, et al. Cellular transfection to deliver alanine-glyoxylate aminotransferase to hepatocytes: a rational gene therapy for primary hyperoxaluria-1 (PH-1). Am J Nephrol. 2005;25(2):176-182. [20] Azcarate-Peril MA, Bruno-Bárcena JM, Hassan HM, et al. Transcriptional and functional analysis of oxalyl-coenzyme A (CoA) decarboxylase and formyl-CoA transferase genes from Lactobacillus acidophilus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006;72(3): 1891-1899.[21] 陈志强,刘冠琳,叶章群,等.表达产甲酸草酸杆菌草酸分解基因的人肝细胞系的构建[J].临床泌尿外科杂志,2007,22(2):143-145.[22] 叶章群,刘冠琳,陈志强,等.可分解草酸小鼠肠干细胞群的构建[J].中华医学杂志,2009,89(16):1130-1134.[23] 赖德辉,雷鸣,李逊,等.基因工程构建表达融合蛋白GST-FCoAT的益生大肠杆菌EcN-Frc[J].实用医学杂志,2010,26(24):4480- 4482.[24] Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL, et al. Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow. Nature. 2002;418(6893):41-49. [25] 张泽,欧莉莉,曾国华,等.离子色谱法同时测定24小时尿草酸和枸橼酸的应用价值[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2010,28(z1):75-77. |
.jpg)