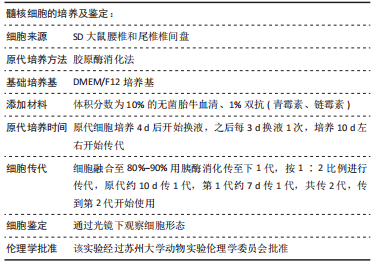
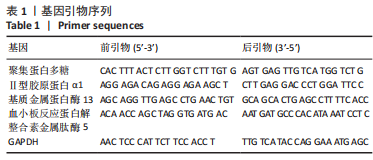
[1] BINCH ALA, FITZGERALD JC, GROWNEY EA, et al. Cell-based strategies for IVD repair: clinical progress and translational obstacles. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(3):158-175.
[2] LYU FJ, CUI H, PAN H, et al. Painful intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation: from laboratory evidence to clinical interventions. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):7.
[3] KAMALI A, ZIADLOU R, LANG G, et al. Small molecule-based treatment approaches for intervertebral disc degeneration: Current options and future directions. Theranostics. 2021;11(1):27-47.
[4] KERR GJ, VERAS MA, KIM MK, et al. Decoding the intervertebral disc: Unravelling the complexities of cell phenotypes and pathways associated with degeneration and mechanotransduction. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017;62:94-103.
[5] SILAGI ES, SHAPIRO IM, RISBUD MV. Glycosaminoglycan synthesis in the nucleus pulposus: Dysregulation and the pathogenesis of disc degeneration. Matrix Biol. 2018;71-72:368-379.
[6] WANG Y, CHE M, XIN J, et al. The role of IL-1beta and TNF-alpha in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131: 110660.
[7] RISBUD MV, SHAPIRO IM. Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: pain and disc content. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10(1): 44-56.
[8] VASEY C, MCBRIDE J, PENTA K. Circadian Rhythm Dysregulation and Restoration: The Role of Melatonin. Nutrients. 2021;13(10):3480.
[9] SATO K, MENG F, FRANCIS H, et al. Melatonin and circadian rhythms in liver diseases: Functional roles and potential therapies. J Pineal Res. 2020;68(3):e12639.
[10] CHENG Z, XIANG Q, WANG J, et al. The potential role of melatonin in retarding intervertebral disc ageing and degeneration: A systematic review. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;70:101394.
[11] NABAVI SM, NABAVI SF, SUREDA A, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of Melatonin: A mechanistic review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019; 59(sup1):S4-S16.
[12] LI Z, LI X, CHEN C, et al. Melatonin inhibits nucleus pulposus (NP) cell proliferation and extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling via the melatonin membrane receptors mediated PI3K-Akt pathway. J Pineal Res. 2017;63(3). doi: 10.1111/jpi.12435.
[13] CHEN F, JIANG G, LIU H, et al. Melatonin alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration by disrupting the IL-1beta/NF-kappaB-NLRP3 inflammasome positive feedback loop. Bone Res. 2020;8:10.
[14] HE Q, ZHANG J, LIAO Y, et al. Current advances in microsphere based cell culture and tissue engineering. Biotechnol Adv. 2020;39:107459.
[15] YUE K, TRUJILLO-DE SANTIAGO G, ALVAREZ MM, et al. Synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2015;73:254-271.
[16] XU P, JIANG F, ZHANG H, et al. Calcium Carbonate/Gelatin Methacrylate Microspheres for 3D Cell Culture in Bone Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2020;26(8):418-432.
[17] SHAO L, PAN B, HOU R, et al. User-friendly microfluidic manufacturing of hydrogel microspheres with sharp needle. Biofabrication. 2022; 14(2). doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/ac57a5.
[18] XU H, SUN M, WANG C, et al. Growth differentiation factor-5-gelatin methacryloyl injectable microspheres laden with adipose-derived stem cells for repair of disc degeneration. Biofabrication. 2020;13(1): 015010.
[19] CHEN P, XIA C, MEI S, et al. Intra-articular delivery of sinomenium encapsulated by chitosan microspheres and photo-crosslinked GelMA hydrogel ameliorates osteoarthritis by effectively regulating autophagy. Biomaterials. 2016;81:1-13.
[20] FONTANA G, SEE E, PANDIT A. Current trends in biologics delivery to restore intervertebral disc anabolism. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;84: 146-158.
[21] ZHAO X, MA H, HAN H, et al. Precision medicine strategies for spinal degenerative diseases: Injectable biomaterials with in situ repair and regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2022;16:100336.
[22] CLOUET J, FUSELLIER M, CAMUS A, et al. Intervertebral disc regeneration: From cell therapy to the development of novel bioinspired endogenous repair strategies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;146:306-324.
[23] ROH EJ, DARAI A, KYUNG JW, et al. Genetic Therapy for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1579.
[24] YANG W, YU XH, WANG C, et al. Interleukin-1beta in intervertebral disk degeneration. Clin Chim Acta. 2015;450:262-272.
[25] FENG C, YANG M, LAN M, et al. ROS: Crucial Intermediators in the Pathogenesis of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:5601593.
[26] HE R, CUI M, LIN H, et al. Melatonin resists oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells. Life Sci. 2018;199:122-130.
[27] LI B, LI H, YANG H, et al. Preparation and antibacterial properties of an AgBr@SiO(2)/GelMA composite hydrogel. Biomed Mater. 2022;17(2). doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/ac49f7.
[28] CHEN J, HUANG D, WANG L, et al. 3D bioprinted multiscale composite scaffolds based on gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA)/chitosan microspheres as a modular bioink for enhancing 3D neurite outgrowth and elongation. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2020;574:162-173.
[29] GUPTA V, KHAN Y, BERKLAND CJ, et al. Microsphere-Based Scaffolds in Regenerative Engineering. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2017;19:135-161.
[30] DONG Z, MENG X, YANG W, et al. Progress of gelatin-based microspheres (GMSs) as delivery vehicles of drug and cell. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;122:111949.
[31] JIANG G, LI S, YU K, et al. A 3D-printed PRP-GelMA hydrogel promotes osteochondral regeneration through M2 macrophage polarization in a rabbit model. Acta Biomater. 2021;128:150-162.
[32] XIAO L, LIN J, CHEN R, et al. Sustained Release of Melatonin from GelMA Liposomes Reduced Osteoblast Apoptosis and Improved Implant Osseointegration in Osteoporosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020; 2020:6797154.
|