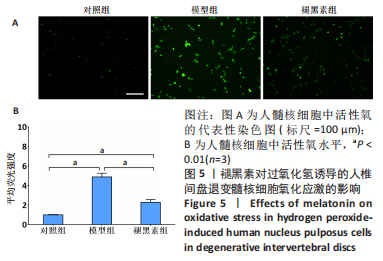
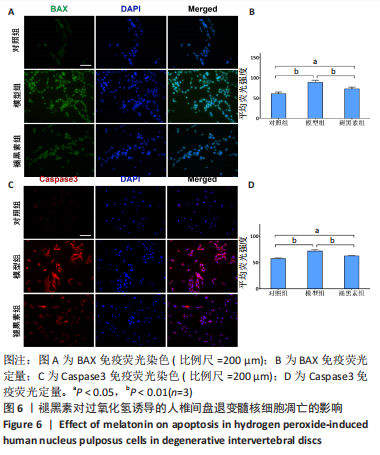
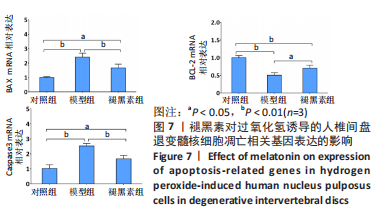
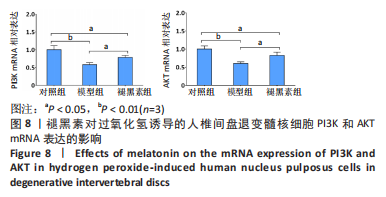
[1] MADIGAN L, VACCARO AR, SPECTOR LR, et al. Management of symptomatic lumbar degenerative disk disease. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2009;17(2):102-111.
[2] SUN K, JIANG J, WANG Y, et al. The role of nerve fibers and their neurotransmitters in regulating intervertebral disc degeneration. Ageing Res Rev. 2022;81:101733.
[3] ZEHRA U, TRYFONIDOU M, IATRIDIS JC, et al. Mechanisms and clinical implications of intervertebral disc calcification. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022; 18(6):352-362.
[4] LYU FJ, CUI H, PAN H, et al. Painful intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation: from laboratory evidence to clinical interventions. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):7.
[5] LI Z, LI X, CHEN C, et al. Melatonin inhibits nucleus pulposus (NP) cell proliferation and extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling via the melatonin membrane receptors mediated PI3K-Akt pathway. J Pineal Res. 2017;63(3). doi: 10.1111/jpi.12435.
[6] CHENG Z, XIANG Q, WANG J, et al. The potential role of melatonin in retarding intervertebral disc ageing and degeneration: A systematic review. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;70:101394.
[7] BUONFIGLIO D, HUMMER DL, ARMSTRONG A, et al. Angelman syndrome and melatonin: What can they teach us about sleep regulation. J Pineal Res. 2020;69(4):e12697.
[8] CIPOLLA-NETO J, AMARAL FGD. Melatonin as a Hormone: New Physiological and Clinical Insights. Endocr Rev. 2018;39(6):990-1028.
[9] CHRUSTEK A, OLSZEWSKA-SŁONINA D. Melatonin as a powerful antioxidant. Acta Pharm. 2020;71(3):335-354.
[10] GE J, ZHOU Q, NIU J, et al. Melatonin Protects Intervertebral Disc from Degeneration by Improving Cell Survival and Function via Activation of the ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:5120275.
[11] BOGA JA, CABALLERO B, POTES Y, et al. Therapeutic potential of melatonin related to its role as an autophagy regulator: A review. J Pineal Res. 2019; 66(1):e12534.
[12] MAJIDINIA M, REITER RJ, SHAKOURI SK, et al. The role of melatonin, a multitasking molecule, in retarding the processes of ageing. Ageing Res Rev. 2018;47:198-213.
[13] ZHAO L, HU C, ZHANG P, et al. Melatonin preconditioning is an effective strategy for mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for kidney disease. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(1):25-33.
[14] YAN R, DING J, WEI Y, et al. Melatonin Prevents NaAsO2-Induced Developmental Cardiotoxicity in Zebrafish through Regulating Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(7):1301.
[15] HWANG SJ, JUNG Y, SONG YS, et al. Enhanced anti-angiogenic activity of novel melatonin-like agents. J Pineal Res. 2021;71(1):e12739.
[16] TURGUT M, BAŞALOĞLU HK, YENISEY C, et al. Surgical pinealectomy accelerates intervertebral disc degeneration process in chicken. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(5):605-612.
[17] HE R, CUI M, LIN H, et al. Melatonin resists oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells. Life Sci. 2018;199:122-130.
[18] XIE L, ZHAO Z, CHEN Z, et al. Melatonin Alleviates Radiculopathy Against Apoptosis and NLRP3 Inflammasomes Via the Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy Pathway. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2021;46(16):E859-E868.
[19] GAO Z, LIN Y, ZHANG P, et al. Sinomenine ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration via inhibition of apoptosis and autophagy in vitro and in vivo. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(9):5956-5966.
[20] LIU L, CAO JX, SUN B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibition of chronic ethanol-induced oxidative damage via upregulation of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt and modulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 activation in PC12 cells and neurons. Neuroscience. 2010;167(4): 1115-1124.
[21] LUO C, YANG Q, LIU Y, et al. The multiple protective roles and molecular mechanisms of melatonin and its precursor N-acetylserotonin in targeting brain injury and liver damage and in maintaining bone health. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;130:215-233.
[22] HARTVIGSEN J, HANCOCK MJ, KONGSTED A, et al. What low back pain is and why we need to pay attention. Lancet. 2018;391(10137):2356-2367.
[23] XIN J, WANG Y, ZHENG Z, et al. Treatment of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(7):1271-1280.
[24] WANG Y, CHE M, XIN J, et al. The role of IL-1β and TNF-α in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110660.
[25] YANG RZ, XU WN, ZHENG HL, et al. Involvement of oxidative stress-induced annulus fibrosus cell and nucleus pulposus cell ferroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration pathogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(4):2725-2739.
[26] YANG S, ZHANG F, MA J, et al. Intervertebral disc ageing and degeneration: The antiapoptotic effect of oestrogen. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;57:100978.
[27] CHEUNG KM, KARPPINEN J, CHAN D, et al. Prevalence and pattern of lumbar magnetic resonance imaging changes in a population study of one thousand forty-three individuals. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(9):934-940.
[28] TORDJMAN S, CHOKRON S, DELORME R, et al. Melatonin: Pharmacology, Functions and Therapeutic Benefits. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017;15(3): 434-443.
[29] LOW TL, CHOO FN, TAN SM. The efficacy of melatonin and melatonin agonists in insomnia - An umbrella review. J Psychiatr Res. 2020;121:10-23.
[30] MARKOWSKA M, NIEMCZYK S, ROMEJKO K. Melatonin Treatment in Kidney Diseases. Cells. 2023;12(6):838.
[31] SAMANTA S. Physiological and pharmacological perspectives of melatonin. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2022;128(5):1346-1367.
[32] LI J, WANG C, XUE L, et al. Melatonin Suppresses Apoptosis of Nucleus Pulposus Cells through Inhibiting Autophagy via the PI3K/Akt Pathway in a High-Glucose Culture. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:4604258.
[33] CHEN Y, WU Y, SHI H, et al. Melatonin ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration via the potential mechanisms of mitophagy induction and apoptosis inhibition. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(3):2136-2148.
[34] ZHANG Z, LIN J, TIAN N, et al. Melatonin protects vertebral endplate chondrocytes against apoptosis and calcification via the Sirt1-autophagy pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(1):177-193.
[35] TAN DX, MANCHESTER LC, ESTEBAN-ZUBERO E, et al. Melatonin as a Potent and Inducible Endogenous Antioxidant: Synthesis and Metabolism. Molecules. 2015;20(10):18886-18906.
[36] COYOY-SALGADO A, SEGURA-URIBE JJ, GUERRA-ARAIZA C, et al. The Importance of Natural Antioxidants in the Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury in Animal Models: An Overview. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:3642491.
[37] DADSENA S, KING LE, GARCÍA-SÁEZ AJ. Apoptosis regulation at the mitochondria membrane level. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2021; 1863(12):183716.
[38] ROBERTS JZ, CRAWFORD N, LONGLEY DB. The role of Ubiquitination in Apoptosis and Necroptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29(2):272-284.
[39] OUYANG ZH, WANG WJ, YAN YG, et al. The PI3K/Akt pathway: a critical player in intervertebral disc degeneration. Oncotarget. 2017;8(34):57870-57881.
[40] WANG W, LI P, XU J, et al. Resveratrol attenuates high glucose-induced nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and senescence through activating the ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(2):BSR20171454.
[41] SUN K, WANG X, ZHANG X, et al. The antagonistic effect of melatonin on TBBPA-induced apoptosis and necroptosis via PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in swine testis cells. Environ Toxicol. 2022;37(9):2281-2290.
[42] GU H, LI J, ZHANG R. Melatonin upregulates DNA-PKcs to suppress apoptosis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells via inhibiting miR-101 under H2O2-induced oxidative stress. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(2):1283-1292.
|