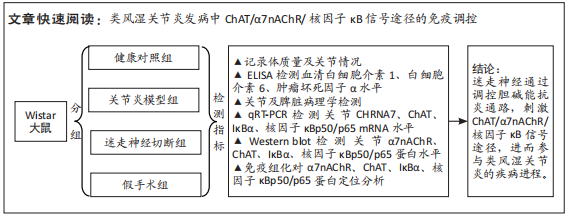
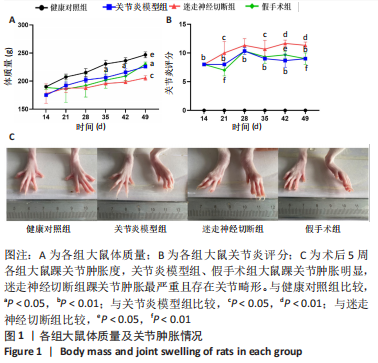
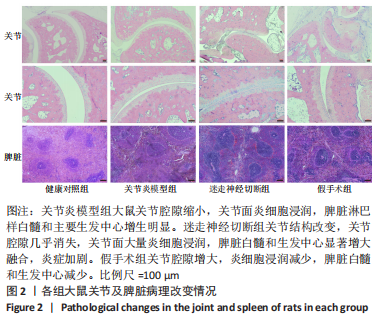
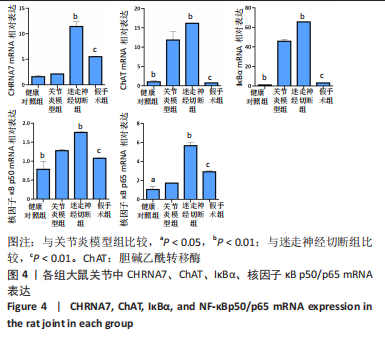
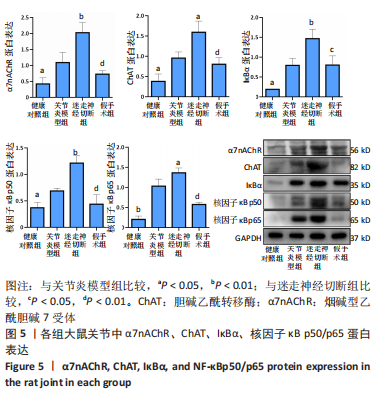
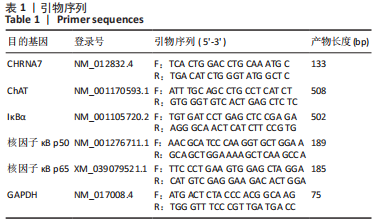
[1] FIRESTEIN GS, BUDD RC, GABRIEL SE. 凯利风湿病学[M].10版.栗占国等,译.北京:北京大学医学出版社,2020:1.
[2] SPARKS JA. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 2019;170(1):ITC1-ITC16.
[3] LV J, JI X, LI Z, et al. The role of the cholinergic anti‐inflammatory pathway in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Scand J Immunol. 2021; 94(4):e13092.
[4] YUAN H, SILBERSTEIN SD. Vagus nerve and vagus nerve stimulation, a comprehensive review: part I. Headache. 2016;56(1):71-78.
[5] BUTT MF, ALBUSODA A, FARMER AD, et al. The anatomical basis for transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation. J Anat. 2020;236(4): 588-611.
[6] VAN MAANEN MA, VERVOORDELDONK MJ, TAK PP. The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: towards innovative treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009;5(4):229-232.
[7] DI LASCIO S, FORNASARI D, BENFANTE R. The Human-Restricted Isoform of the α7nAChR, CHRFAM7A: A Double-Edged Sword in Neurological and Inflammatory Disorders . Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(7): 3463.
[8] Winick-Ng W, Caetano FA, Winick-Ng J, et al. 82-kDa choline acetyltransferase and SATB1 localize to β-amyloid induced matrix attachment regions. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):1-17.
[9] 王东岩,杨海永,董旭,等.针刺调控 α7nAchR 激活胆碱能抗炎通路的研究现状[J].上海针灸杂志,2020,39(1):116-122.
[10] 殷勤,吴义金.基于胆碱能抗炎通路对炎症治疗及其相关信号机制研究[J].中国药物经济学,2020,15(7):119-123.
[11] 樊文香,张锦璐,徐驰.α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体在中枢神经系统性疾病中作用的研究进展[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2021,26(9): 1065-1072.
[12] 秦雨涵,侯宏卫,胡清源.α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体在胆碱能抗炎通路中的作用机制及应用现状[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2022,38(10):1304-1310.
[13] EBERHARDSON M, TARNAWSKI L, CENTA M, et al. Neural control of inflammation: bioelectronic medicine in treatment of chronic inflammatory disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2020;10(3): a034181.
[14] LI T, ZUO X, ZHOU Y, et al. The vagus nerve and nicotinic receptors involve inhibition of HMGB1 release and early pro-inflammatory cytokines function in collagen-induced arthritis. J Clin Immunol. 2010; 30(2):213-220.
[15] RASMUSSEN SE, PFEIFFER-JENSEN M, DREWES AM, et al. Vagal influences in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 2018;47(1):1-11.
[16] LI Z, HAO H, GAO Y, et al. Expression and localization analyses of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway and α7nAchR in different tissues of rats with rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Histochem. 2019;121(6):742-749.
[17] SEYEDABADI M, RAHIMIAN R, GHIA JE. The role of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in inflammatory bowel disease: involvement of different cellular pathways. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018;22(2):161-176.
[18] 张艳艳,刘伟,张超,等.基于胆碱能抗炎通路的类风湿关节炎治疗机制与中医药作用机制研究进展 [J].山东中医杂志,2018,37(12): 1038-1040.
[19] IMAMURA M, MUKAINO A, TAKAMATSU K, et al. Ganglionic acetylcholine receptor antibodies and autonomic dysfunction in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(4):1332.
[20] MURRAY K, REARDON C. The cholinergic anti‐inflammatory pathway revisited. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2018;30(3):10.1111/nmo.13288.
[21] FERREIRA-VIEIRA TH, GUIMARAES IM, SILVA FR, et al. Alzheimer’s disease: targeting the cholinergic system. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2016; 14(1):101-115.
[22] HAJIASGHARZADEH K, KHABBAZI A, MOKHTARZADEH A, et al. Cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway and connective tissue diseases. Inflammopharmacology. 2021;29(4):975-986.
[23] 项水英,丛文娟,刘自兵.胆碱能抗炎通路及其在中医药抗炎效应中的研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2018,20(2):140-143.
[24] PRESCOTT SL, LIBERLES SD. Internal senses of the vagus nerve Neuron. 2022;110(4):579-599.
[25] BUTT MF, ALBUSODA A, FARMER AD, et al. The anatomical basis for transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation. J Anat. 2020;236(4): 588-611.
[26] YUAN H, SILBERSTEIN SD. Vagus nerve and vagus nerve stimulation, a comprehensive review: part I. Headache. 2016;56(1):71-78.
[27] YUAN H, SILBERSTEIN SD. Vagus nerve and vagus nerve stimulation, a comprehensive review: part II. Headache. 2016;56(2):259-266.
[28] CHAVAN SS, TRACEY KJ. Essential neuroscience in immunology. J Immunol. 2017;198(9):3389-3397.
[29] COURTIES A, BERENBAUM F, SELLAM J. Vagus nerve stimulation in musculoskeletal diseases. Joint Bone Spine. 2021;88(3):105149.
[30] LEVINE YA, FALTYS M, CHERNOFF D. Harnessing the inflammatory reflex for the treatment of inflammation-mediated diseases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2020;10(1):a034330.
[31] HOOVER DB. Cholinergic modulation of the immune system presents new approaches for treating inflammation. Pharmacol Ther. 2017; 179:1-16.
[32] VALENTINE G, SOFUOGLU M. Cognitive effects of nicotine: recent progress. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018;16(4):403-414.
[33] CHEUNG TT, MCINNES IB. Future therapeutic targets in rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Immunopathol. 2017;39(4):487-500.
[34] KOOPMAN FA, STOOF SP, STRAUB RH, et al. Restoring the balance of the autonomic nervous system as an innovative approach to the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Mol med. 2011;17(9):937-948.
[35] 张胜凯,李红兵,张程,等.胆碱能系统对脓毒症炎症与免疫调控机制的研究进展[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2021,29(10):132-140.
[36] WU Y, WANG L, JI C, et al. The role of α7nAChR-mediated cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in immune cells. Inflammation. 2021;44(3): 821-834. |