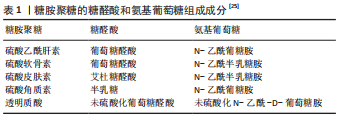
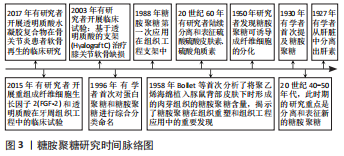
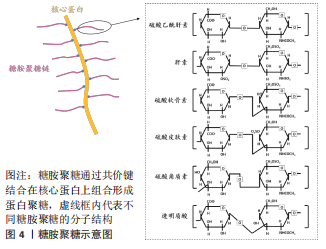
[1] YAZDANPANAH Z, JOHNSTON JD, COOPER D, et al. 3D bioprinted scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: state-of-the-art and emerging technologies. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:824156.
[2] HAO Z, LI H, WANG Y, et al. Supramolecular peptide nanofiber hydrogels for bone tissue engineering: from multihierarchical fabrications to comprehensive applications. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(11):e2103820.
[3] WU H, SHANG Y, SUN W, et al. Seamless and early gap healing of osteochondral defects by autologous mosaicplasty combined with bioactive supramolecular nanofiber-enabled gelatin methacryloyl (BSN-GelMA) hydrogel. Bioact Mater. 2023;19:88-102.
[4] ALAMAN-DIEZ P, GARCIA-GARETA E, ARRUEBO M, et al. A bone-on-a-chip collagen hydrogel-based model using pre-differentiated adipose-derived stem cells for personalized bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2023;111(1):88-105.
[5] GUAN Y, YANG B, XU W, et al. Cell-derived extracellular matrix materials for tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2022;28(5):1007-1021.
[6] WICKRAMASINGHE ML, DIAS GJ, PREMADASA K. A novel classification of bone graft materials. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2022; 110(7):1724-1749.
[7] SUBBIAH R, RUEHLE MA, KLOSTERHOFF BS, et al. Triple growth factor delivery promotes functional bone regeneration following composite musculoskeletal trauma. Acta Biomater. 2021;127:180-192.
[8] FANG H, ZHU D, YANG Q, et al. Emerging zero-dimensional to four-dimensional biomaterials for bone regeneration. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):26.
[9] CHEN X, CHEN D, BAN E, et al. Glycosaminoglycans modulate long-range mechanical communication between cells in collagen networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022;119(15):e2116718119.
[10] WU J, TIAN Y, HAN L, et al. FAM20B-catalyzed glycosaminoglycans control murine tooth number by restricting FGFR2b signaling. BMC Biol. 2020;18(1):87.
[11] YU C, PEALL IW, PHAM SH, et al. Syndecan-1 facilitates the human mesenchymal stem cell osteo-adipogenic balance. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(11):3884.
[12] ARTIACH G, CARRACEDO M, SEIME T, et al. Proteoglycan 4 is increased in human calcified aortic valves and enhances valvular interstitial cell calcification. Cells. 2020;9(3):684.
[13] HAO JX, SHEN MJ, WANG CY, et al. Regulation of biomineralization by proteoglycans: from mechanisms to application. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;294:119773.
[14] GAVVA C, PATEL K, KUDRE T, et al. Glycosaminoglycans from fresh water fish processing discard -Isolation, structural characterization, and osteogenic activity. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;145:558-567.
[15] ZHENG Z, HU L, GE Y, et al. Surface modification of poly (ether ether ketone) by simple chemical grafting of strontium chondroitin sulfate to improve its anti-inflammation, angiogenesis, osteogenic properties. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(13):e2200398.
[16] HAYES AJ, MELROSE J. Aggrecan, the primary weight-bearing cartilage proteoglycan, has context-dependent, cell-directive properties in embryonic development and neurogenesis: aggrecan glycan side chain modifications convey interactive biodiversity. Biomolecules. 2020;10(9):1244.
[17] LIMA L G, HAM S, SHIN H, et al. Tumor microenvironmental cytokines bound to cancer exosomes determine uptake by cytokine receptor-expressing cells and biodistribution. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):3543.
[18] TANG X, CHEN R, MESIAS V, et al. A SURF4-to-proteoglycan relay mechanism that mediates the sorting and secretion of a tagged variant of sonic hedgehog. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022;119(11): e2113991119.
[19] SEPURU KM, RAJARATHNAM K. Structural basis of a chemokine heterodimer binding to glycosaminoglycans. Biochem J. 2021;478(5): 1009-1021.
[20] BOJARSKI KK, SAMSONOV SA. Role of oligosaccharide chain polarity in protein-glycosaminoglycan interactions. J Chem Inf Model. 2021; 61(1):455-466.
[21] FU L, SUFLITA M, LINHARDT RJ. Bioengineered heparins and heparan sulfates. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;97:237-249.
[22] VARKI A, CUMMINGS RD, AEBI M, et al. Symbol nomenclature for graphical representations of glycans. Glycobiology. 2015;25(12):1323-1324.
[23] MIGLIORINI E, GUEVARA-GARCIA A, ALBIGES-RIZO C, et al. Learning from BMPs and their biophysical extracellular matrix microenvironment for biomaterial design. Bone. 2020;141:115540.
[24] SOARES DCD, REIS RL, PASHKULEVA I. Sulfation of glycosaminoglycans and its implications in human health and disorders. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2017;19:1-26.
[25] IOZZO RV, SCHAEFER L. Proteoglycan form and function: a comprehensive nomenclature of proteoglycans. Matrix Biol. 2015;42: 11-55.
[26] VLODAVSKY I, BARASH U, NGUYEN HM, et al. Biology of the heparanase-heparan sulfate axis and its role in disease pathogenesis. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2021;47(3):240-253.
[27] FUNDERBURGH JL. Keratan sulfate: structure, biosynthesis, and function. Glycobiology. 2000;10(10):951-958.
[28] IDA-YONEMOCHI H, MORITA W, SUGIURA N, et al. Craniofacial abnormality with skeletal dysplasia in mice lacking chondroitin sulfate N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase-1. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):17134.
[29] SHABBIR R, NALBANT G, AHMAD N, et al. Homozygous CHST11 mutation in chondrodysplasia, brachydactyly, overriding digits, clino-symphalangism and synpolydactyly. J Med Genet. 2018;55(7):489-496.
[30] SCHNEEBERGER PE, VON ELSNER L, BARKER EL, et al. Bi-allelic pathogenic variants in hs2st1 cause a syndrome characterized by developmental delay and corpus callosum, skeletal, and renal abnormalities. Am J Hum Genet. 2020;107(6):1044-1061.
[31] NURCOMBE V, GOH FJ, HAUPT LM, et al. Temporal and functional changes in glycosaminoglycan expression during osteogenesis. J Mol Histol. 2007; 38(5):469-481.
[32] GRIFFIN ME, SORUM AW, MILLER GM, et al. Sulfated glycans engage the Ang-Tie pathway to regulate vascular development. Nat Chem Biol. 2021;17(2):178-186.
[33] MURALI S, RAI B, DOMBROWSKI C, et al. Affinity-selected heparan sulfate for bone repair. Biomaterials. 2013;34(22):5594-5605.
[34] SMITH R, MURALI S, RAI B, et al. Minimum structural requirements for BMP-2-binding of heparin oligosaccharides. Biomaterials. 2018;184: 41-55.
[35] HUA R, NI Q, ELIASON T D, et al. Biglycan and chondroitin sulfate play pivotal roles in bone toughness via retaining bound water in bone mineral matrix. Matrix Biol. 2020;94:95-109.
[36] MIYAZAKI T, MIYAUCHI S, TAWADA A, et al. Oversulfated chondroitin sulfate-E binds to BMP-4 and enhances osteoblast differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 2008;217(3):769-777.
[37] KOIKE T, IZUMIKAWA T, TAMURA J, et al. Chondroitin sulfate-E fine-tunes osteoblast differentiation via ERK1/2, Smad3 and Smad1/5/8 signaling by binding to N-cadherin and cadherin-11. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;420(3):523-529.
[38] SHANG L, MA B, WANG F, et al. Nanotextured silk fibroin/hydroxyapatite biomimetic bilayer tough structure regulated osteogenic/chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells for osteochondral repair. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(11):e12917.
[39] LI X, TENG Y, LIU J, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation of BMSCs encapsulated in chondroinductive polysaccharide/collagen hybrid hydrogels. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5(26):5109-5119.
[40] KANEKO K, HIGUCHI C, KUNUGIZA Y, et al. Hyaluronan inhibits BMP-induced osteoblast differentiation. FEBS Lett. 2015;589(4):447-454.
[41] KAWANO M, ARIYOSHI W, IWANAGA K, et al. Mechanism involved in enhancement of osteoblast differentiation by hyaluronic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;405(4):575-580.
[42] ZHANG LT, LIU RM, LUO Y, et al. Hyaluronic acid promotes osteogenic differentiation of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells via the TGF-beta/Smad signalling pathway. Life Sci. 2019;232:116669.
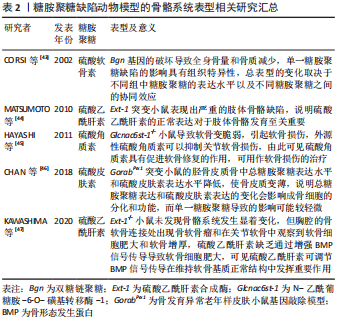
[43] CORSI A, XU T, CHEN XD, et al. Phenotypic effects of biglycan deficiency are linked to collagen fibril abnormalities, are synergized by decorin deficiency, and mimic Ehlers-Danlos-like changes in bone and other connective tissues. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17(7):1180-1189.
[44] MATSUMOTO Y, MATSUMOTO K, IRIE F, et al. Conditional ablation of the heparan sulfate-synthesizing enzyme Ext1 leads to dysregulation of bone morphogenic protein signaling and severe skeletal defects. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(25):19227-19234.
[45] HAYASHI M, KADOMATSU K, KOJIMA T, et al. Keratan sulfate and related murine glycosylation can suppress murine cartilage damage in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;409(4):732-737.
[46] CHAN WL, STEINER M, WITKOS T, et al. Impaired proteoglycan glycosylation, elevated TGF-beta signaling, and abnormal osteoblast differentiation as the basis for bone fragility in a mouse model for gerodermia osteodysplastica. PLoS Genet. 2018;14(3):e1007242.
[47] KAWASHIMA K, OGAWA H, KOMURA S, et al. Heparan sulfate deficiency leads to hypertrophic chondrocytes by increasing bone morphogenetic protein signaling. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(11):1459-1470.
[48] HAUPT LM, MURALI S, MUN FK, et al. The heparan sulfate proteoglycan (HSPG) glypican-3 mediates commitment of MC3T3-E1 cells toward osteogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2009;220(3):780-791.
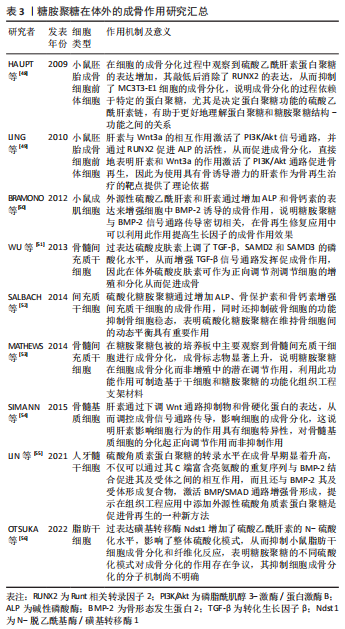
[49] LING L, DOMBROWSKI C, FOONG KM, et al. Synergism between Wnt3a and heparin enhances osteogenesis via a phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt/RUNX2 pathway. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(34):26233-26244.
[50] BRAMONO DS, MURALI S, RAI B, et al. Bone marrow-derived heparan sulfate potentiates the osteogenic activity of bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2). Bone. 2012;50(4):954-964.
[51] WU B, MA X, ZHU D, et al. Lentiviral delivery of biglycan promotes proliferation and increases osteogenic potential of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. J Mol Histol. 2013;44(4):423-431.
[52] SALBACH-HIRSCH J, ZIEGLER N, THIELE S, et al. Sulfated glycosaminoglycans support osteoblast functions and concurrently suppress osteoclasts. J Cell Biochem. 2014;115(6):1101-1111.
[53] MATHEWS S, MATHEW SA, GUPTA PK, et al. Glycosaminoglycans enhance osteoblast differentiation of bone marrow derived human mesenchymal stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2014;8(2):143-152.
[54] SIMANN M, SCHNEIDER V, LE BLANC S, et al. Heparin affects human bone marrow stromal cell fate: promoting osteogenic and reducing adipogenic differentiation and conversion. Bone. 2015;78:102-113.
[55] LIN W, ZHU X, GAO L, et al. Osteomodulin positively regulates osteogenesis through interaction with BMP2. Cell Death Dis. 2021; 12(2):147.
[56] OTSUKA T, KAN HM, MASON TD, et al. Overexpression of NDST1 attenuates fibrotic response in murine adipose-derived stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2022. doi: 10.1089/scd.2022.0053.
[57] PARK SS, PARK M, LEE BT. Autologous stromal vascular fraction-loaded hyaluronic acid/gelatin-biphasic calcium phosphate scaffold for bone tissue regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2022;132:112533.
[58] KLARA J, MARCZAK A, LATKIEWICZ A, et al. Lysine-functionalized chondroitin sulfate improves the biological properties of collagen/chitosan-based injectable hydrogels. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;202: 318-331.
[59] D’ALBIS G, D’ALBIS V, PALMA M, et al. Use of hyaluronic acid for regeneration of maxillofacial bones. Genesis. 2022;60(8-9):e23497.
[60] KIM HD, LEE EA, AN YH, et al. Chondroitin sulfate-based biomineralizing surface hydrogels for bone tissue engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(26):21639-21650.
[61] POLDERVAART MT, GOVERSEN B, DE RUIJTER M, et al. 3D bioprinting of methacrylated hyaluronic acid (MeHA) hydrogel with intrinsic osteogenicity. PLoS One. 2017;12(6):e177628.
[62] ABBADESSA A, BLOKZIJL MM, MOUSER VH, et al. A thermo-responsive and photo-polymerizable chondroitin sulfate-based hydrogel for 3D printing applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;149:163-174.
[63] KRIEGHOFF J, PICKE AK, SALBACH-HIRSCH J, et al. Increased pore size of scaffolds improves coating efficiency with sulfated hyaluronan and mineralization capacity of osteoblasts. Biomater Res. 2019;23:26.
[64] HAUCK S, ZAGER P, HALFTER N, et al. Collagen/hyaluronan based hydrogels releasing sulfated hyaluronan improve dermal wound healing in diabetic mice via reducing inflammatory macrophage activity. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(12):4342-4359.
[65] HEMPEL U, MATTHAUS C, PREISSLER C, et al. Artificial matrices with high-sulfated glycosaminoglycans and collagen are anti-inflammatory and pro-osteogenic for human mesenchymal stromal cells. J Cell Biochem. 2014;115(9):1561-1571.
[66] LI X, XU Q, JOHNSON M, et al. A chondroitin sulfate based injectable hydrogel for delivery of stem cells in cartilage regeneration. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(11):4139-4148.
[67] CORRADETTI B, TARABALLI F, MINARDI S, et al. Chondroitin sulfate immobilized on a biomimetic scaffold modulates inflammation while driving chondrogenesis. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(5):670-682.
[68] ZHOU Q, LYU S, BERTRAND AA, et al. Stiffness of nanoparticulate mineralized collagen scaffolds triggers osteogenesis via mechanotransduction and canonical wnt signaling. Macromol Biosci. 2021;21(3):e2000370.
[69] LIU L, JIA W, ZHOU Y, et al. Hyaluronic acid oligosaccharide-collagen mineralized product and aligned nanofibers with enhanced vascularization properties in bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;206:277-287.
[70] FENBO M, SIJING L, RUIZ-ORTEGA LI, et al. Effects of alginate/chondroitin sulfate-based hydrogels on bone defects healing. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;116:111217.
[71] KIM YS, GUO JL, LAM J, et al. Synthesis of injectable, thermally responsive, chondroitin sulfate-cross-linked Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019;5(12):6405-6413.
[72] LIU Y, WANG R, CHEN S, et al. Heparan sulfate loaded polycaprolactone-hydroxyapatite scaffolds with 3D printing for bone defect repair. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;148:153-162.
[73] SHI H, YE X, ZHANG J, et al. Enhanced osteogenesis of injectable calcium phosphate bone cement mediated by loading chondroitin sulfate. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019;5(1):262-271.
[74] RACHMIEL D, ANCONINA I, RUDNICK-GLICK S, et al. Hyaluronic acid and a short peptide improve the performance of a pcl electrospun fibrous scaffold designed for bone tissue engineering applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2425.
[75] REBAUDI A, SILVESTRINI P, TRISI P. Use of a resorbable hydroxyapatite-collagen chondroitin sulfate material on immediate postextraction sites: a clinical and histologic study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2003;23(4):371-379.
[76] LORENZ J, BARBECK M, KIRKPATRICK CJ, et al. Injectable bone substitute material on the basis of beta-tcp and hyaluronan achieves complete bone regeneration while undergoing nearly complete degradation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;33(3):636-644.
[77] GAO X, HWANG M P, WRIGHT N, et al. The use of heparin/polycation coacervate sustain release system to compare the bone regenerative potentials of 5 BMPs using a critical sized calvarial bone defect model. Biomaterials. 2022;288:121708.
[78] QUANG LB, CHUN TT, LEE SB, et al. A biomimetic collagen-bone granule-heparan sulfate combination scaffold for BMP2 delivery. Gene. 2021;769:145217.
[79] ANDREWS S, CHENG A, STEVENS H, et al. Chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycan scaffolds for cell and recombinant protein-based bone regeneration. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(6):575-585.
[80] LIM JJ, TEMENOFF JS. The effect of desulfation of chondroitin sulfate on interactions with positively charged growth factors and upregulation of cartilaginous markers in encapsulated MSCs. Biomaterials. 2013; 34(21):5007-5018.
[81] KARUMBAIAH L, ENAM SF, BROWN AC, et al. Chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycan hydrogels create endogenous niches for neural stem cells. Bioconjug Chem. 2015;26(12):2336-2349.
[82] HUANG B, WU Z, DING S, et al. Localization and promotion of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 bioactivity on extracellular matrix mimetic chondroitin sulfate-functionalized calcium phosphate cement scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2018;71:184-199.
[83] LI Y, LIU L, LI S, et al. Impaired bone healing by enoxaparin via inhibiting the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells towards osteoblasts. J Bone Miner Metab. 2022;40(1):9-19.
[84] CHEN YH, NARIMATSU Y, CLAUSEN TM, et al. The GAGOme: a cell-based library of displayed glycosaminoglycans. Nat Methods. 2018; 15(11):881-888.
[85] POMIN VH, WANG X. Synthetic oligosaccharide libraries and microarray technology: a powerful combination for the success of current glycosaminoglycan interactomics. Chem Med Chem. 2018;13(7):648-661. |