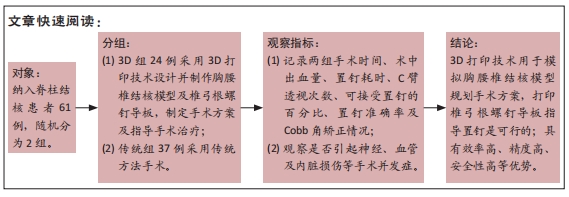
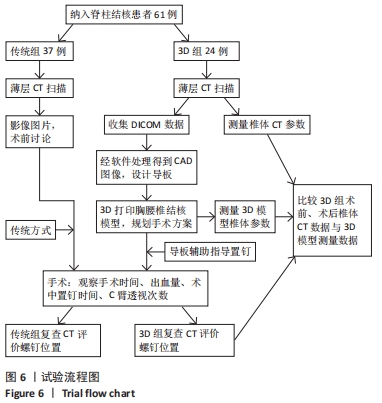
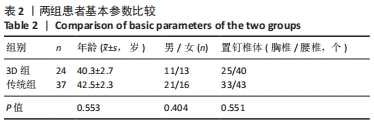
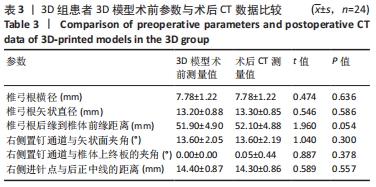
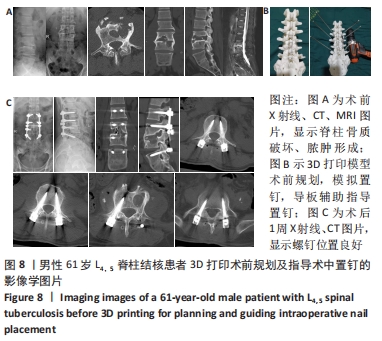
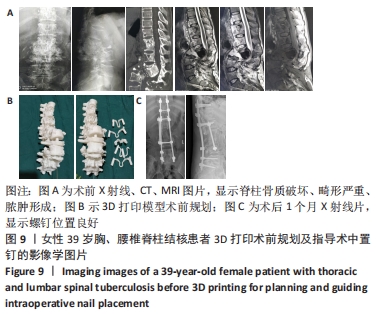
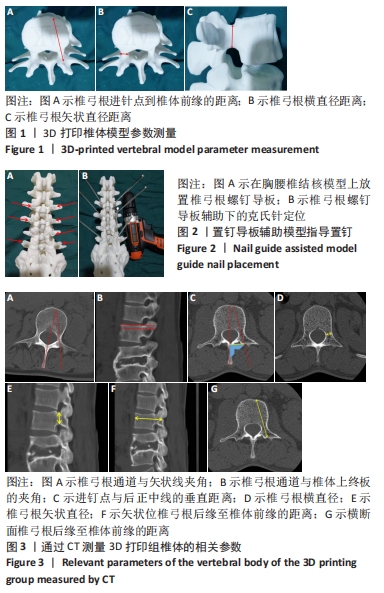
[1] 高静韬,刘宇红.2018年世界卫生组织全球结核病报告要点解读[J].国际呼吸杂志,2019,39(19):1441-1446.
[2] DUNN RN,BEN HUSIEN M. Spinal tuberculosis: review of current management. Bone Joint. 2018;100-B(4):425-431.
[3] ELLIS H. Percival Pott; Pott’s fracture, Pott’s disease of the spine, Pott’s paraplegia. J Perioper Pract. 2012;22(11):366-367.
[4] 杨学军,霍洪军,肖宇龙,等.胸腰椎结核一期病灶清除重建脊柱前中柱功能[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2010,24(1):37-40.
[5] JAIN AK. Tuberculosis of the spine: a fresh look at an old disease. Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(7):905-913.
[6] MOON MS. Tuberculosis of spine: current views in diagnosis and management. Asian Spine. 2014;8(1):97-111.
[7] SOARES DO BRITO J, BATISTA N, TIRADO A, et al. Surgical Treatment of Spinal Tuberculosis: An Orthopedic Service Experience. Acta Med Port. 2013;26(4):349-356.
[8] JUTTE PC, VAN LOENHOUT-ROOYACKERS JH. Routine surgery in addition to chemotherapy for treating spinal tuberculosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006;(5):CD004532.
[9] KHANNA K, SABHARWAL S. Spinal tuberculosis: a comprehensive review for the modern spine surgeon. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2019; 19(11):1858-1870.
[10] BERGESON RK, SCHWEND RM, DELUCIA T, et al. How accurately do novice surgeons place thoracic pedicle screws with the free hand technique. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(15):501-507.
[11] UPENDRA BN, MEENA D, CHOWDHURY B, et al. Outcome-based classification for assessment of thoracic pedicular screw placement. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(4):384-390.
[12] SMORGICK Y, MILLGRAM MA, ANEKSTEIN Y,et al. Accuracy and safety of thoracic pedicle screw placement in spinal deformities. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18(6):522-526.
[13] DI SILVESTRE M, PARISINI P, LOLLI F, et al. Complications of thoracic pedicle screws in scoliosis treatment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32(15):1655-1661.
[14] CARBONE JJ, TORTOLANI PJ, QUARTARARO LG. Fluoroscopically assisted pedicle screw fixation for thoracic and thoracolumbar injuries: technique and short-term complications. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28(1):91-97.
[15] MOHANTY SP, BHAT SN, PAI KANHANGAD M, et al. Pedicle screw fixation in thoracolumbar and lumbar spine assisted by lateral fluoroscopic imaging: a study to evaluate the accuracy of screw placement. Musculoskelet Surg. 2018;102(1):47-55.
[16] YINGSAKMONGKOL W, HANGSAPHUK N, LERDLAM S. The accuracy of pedicle screw placement in thoracic spine using the Funnel technique in idiopathic scoliosis. Med Assoc Thailand. 2007;90(1): 96-105.
[17] LIAO Y, YE R, TANG Q, et al. Is it necessary to perform the second surgery stage of anterior debridement in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis. World Neurosurg. 2019;3(19):1878-1883.
[18] MUHEREMU A, NIU X, WU Z, et al. Study on anterior and posterior approaches for spinal tuberculosis: a meta-analysis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25(1):69-76.
[19] SIVERSSON C, AKHONDI-ASL A, BIXBY S, et al. Three-dimensional hip cartilage quality assessment of morphology and dGEMRIC by planar maps and automated segmentation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(10):1511-1515.
[20] BASTAWROUS S, WAKE N, LEVIN D, et al. Principles of three-dimensional printing and clinical applications within the abdomen and pelvis. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2018;43(10):2809-2822.
[21] GALVEZ M, MONTOYA CE, FUENTES J, et al. Error Measurement Between Anatomical Porcine Spine, CT Images, and 3D Printing. Acad Radiol. 2020;27(5):651-660.
[22] VENTOLA CL. Medical Applications for 3D Printing: Current and Projected Uses. Pharm Ther. 2014;39(10):704.
[23] GALVEZ M, ASAHI T, BAAR A, et al. Use of Three-dimensional Printing in Orthopaedic Surgical Planning. Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2018;2(5):71.
[24] CHAE MP, LIN F, SPYCHAL RT, et al. 3D-Printed haptic “Reverse”models for preoperative planning in soft tissue reconstruction: A case report. Microsurgery. 2015;35(2):148-153.
[25] LI XS, WU ZH, XIA H, et al. The development and evaluation of individualized templates to assist transoral C2 articular mass or transpedicular screw placement in TARP-IV procedures: adult cadaver specimen study. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2014;69(11):750-757.
[26] LEE GY, MASSICOTTE EM, RAMPERSAUD YR. Clinical accuracy of cervicothoracic pedicle screw placement: a comparison of the “open” lamino-foraminotomy and computer-assisted techniques. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2007;20(1):25-32.
[27] KOLLER H, HITZL W, ACOSTA F, et al. In vitro study of accuracy of cervical pedicle screw insertion using an electronic conductivity device (ATPS part III). Eur Spine J. 2009;18(9):1300-1313.
[28] FU M, LIN L, KONG X, et al. Construction and accuracy assessment of patient-specific biocompatible drill template for cervical anterior transpedicular screw (ATPS) insertion: an in vitro study. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):3580.
[29] REICHLE E, MORLOCK M, SELLENSCHLOH K, et al.Definition of pedicle malposition. Primary stability and loosening characteristics of pedicle screws in relation to position: spongious anchoring, cortical anchoring, perforation and malposition. Orthopade. 2002;31(4):402-405.
[30] WU AM, LIN JL, KWAN K, et al. 3D-printing techniques in spine surgery: the future prospects and current challenges. Exp Rev Med Dev. 2018; 15(6):399-401.
[31] IZATT MT, THORPE PL, THOMPSON RG, et al. The use of physical biomodelling in complex spinal surgery. Eur Spine. 2007;16(9):1507-1518.
[32] D’URSO PS, WILLIAMSON OD, THOMPSON RG. Biomodeling as an aid to spinal instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(24):2841-2845.
[33] WU AM, SHAO ZX, WANG JS, et al. The accuracy of a method for printing three-dimensional spinal models. PLoS One. 2015;10(4):4291.
[34] WILCOX B, MOBBS RJ, WU AM, et al.Systematic review of 3D printing in spinal surgery: the current state of play. Spine Surg. 2017;3(3):433-443.
[35] WU AM, WANG S, WENG WQ, et al. The radiological feature of anterior occiput-to-axis screw fixation as it guides the screw trajectory on 3D printed models: a feasibility study on 3D images and 3D printed models. Medicine (Baltimore). 2014;93(28):242.
[36] WU ZX, HUANG LY, SANG HX, et al. Accuracy and safety assessment of pedicle screw placement using the rapid prototyping technique in severe congenital scoliosis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2011;24(7):444-450.
[37] GUARINO J, TENNYSON S, MCCAIN G, et al. Rapid prototyping technology for surgeries of the pediatric spine and pelvis: benefits analysis. Pediatric Orthop. 2007;27(8):955-960.
[38] GRANT CA, IZATT MT, LABROM RD, et al. Use of 3D Printing in Complex Spinal Surgery. Techniq Orthop. 2016;31(3):172-180.
[39] LU S, XU YQ, CHEN GP, et al. Efficacy and accuracy of a novel rapid prototyping drill template for cervical pedicle screw placement. Comput Aided Surg. 2011;16(5):240-248.
[40] SHAO ZX, WANG JS, LIN ZK, et al. Improving the trajectory of transpedicular transdiscal lumbar screw fixation with a computer-assisted 3D-printed custom drill guide. Peer. 2017;5(3):3564.
[41] SUGAWARA T, HIGASHIYAMA N, KANEYAMA S, et al. Multistep pedicle screw insertion procedure with patient-specific lamina fit-and-lock templates for the thoracic spine: clinical article. Neurosurg Spine. 2013; 19(2):185-190.
[42] SHETTY A, KANNA RM, RAJASEKARAN S. TB Spine – Current Aspects on Clinical Presentation, Diagnosis And Management Options. Semin Spine Surg. 2015;28(3):85-90.
[43] SAE-JUNG S, WONGBA N, LEURMPRASERT K. Predictive factors for neurological deficit in patients with spinal tuberculosis. Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2019;27(3):8813.
[44] ZENG Y, CHENG P, TAN J, et al. Comparison of three surgical approaches for thoracolumbar junction (T12-L1) tuberculosis: a multicentre, retrospective study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):524.
[45] PARK DW, SOHN JW, KIM EH, et al. Outcome and Management of Spinal Tuberculosis According to the Severity of Disease. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(4):130-135.
[46] COQUEUGNIOT H, DUTAILLY B, DESBARATS P, et al. Three-dimensional imaging of past skeletal TB: From lesion to process. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2015;95(1):73-79.
[47] MOBBS RJ, COUGHLAN M, THOMPSON R, et al. The utility of 3D printing for surgical planning and patient-specific implant design for complex spinal pathologies: case report. J Neurosurg Spine. 2017; 26(4):513-518.
[48] TAN LA, YERNENI K, TUCHMAN A, et al. Utilization of the 3D-printed spine model for freehand pedicle screw placement in complex spinal deformity correction. Spine Surg. 2018;4(2):319-327.
[49] SUGAWARA T, HIGASHIYAMA N, KANEYAMA S, et al. Accurate and Simple Screw Insertion Procedure With Patient-Specific Screw Guide Templates for Posterior C1-C2 Fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42(6):340-346.
[50] PROVAGGI E, LEONG J, KALASKAR DM. Applications of 3D printing in the management of severe spinal conditions. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2017;231(6):471-486.
[51] DENG T, JIANG M, LEI Q, et al. The accuracy and the safety of individualized 3D printing screws insertion templates for cervical screw insertion. Comput Assist Surg (Abingdon). 2016;21(1):143-149.
[52] LIU K, ZHANG Q, LI X, et al. Preliminary application of a multi-level 3D printing drill guide template for pedicle screw placement in severe and rigid scoliosis. Eur Spine. 2017;26(6):1684-1689.
[53] PLOS ONE EDITORS. Correction: Individualized 3D printing navigation template for pedicle screw fixation in upper cervical spine. PLoS One. 2019;14(2):2213.
[54] GUO F, DAI J, ZHANG J, et al. Individualized 3D printing navigation template for pedicle screw fixation in upper cervical spine. PLoS One. 2017;12(2):1509.
[55] TIAN NF, XU HZ. Image-guided pedicle screw insertion accuracy: a meta-analysis. Int Orthop. 2009;33(4):895-903.
[56] MENDELSOHN D, STRELZOW J, DEA N, et al. Patient and surgeon radiation exposure during spinal instrumentation using intraoperative computed tomography-based navigation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016; 16(3):343-354.
[57] OTSUKI B, TAKEMOTO M, FUJIBAYASHI S, et al. Utility of a custom screw insertion guide and a full-scale, color-coded 3D plaster model for guiding safe surgical exposure and screw insertion during spine revision surgery. Neurosurg Spine. 2016;25(1):94-102.
[58] CHEN H, WU D, YANG H, et al. Clinical Use of 3D Printing Guide Plate in Posterior Lumbar Pedicle Screw Fixation. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21(2): 3948-3954.
[59] LIN CL, FANG JJ, LIN RM. Resection of giant invasive sacral schwannoma using image-based customized osteotomy tools. Eur Spine. 2016; 25(12):4103-4107.
[60] TU Q, DING HW, CHEN H, et al. Three-Dimensional-Printed Individualized Guiding Templates for Surgical Correction of Severe Kyphoscoliosis Secondary to Ankylosing Spondylitis: Outcomes of 9 Cases. World Neurosurg. 2019;130(3):961-970.
[61] KANEYAMA S, SUGAWARA T, SUMI M, et al. A novel screw guiding method with a screw guide template system for posterior C-2 fixation: clinical article. Neurosurg Spine. 2014;21(2):231-238.
|