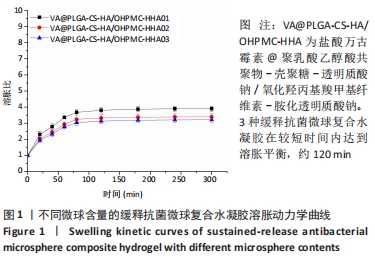
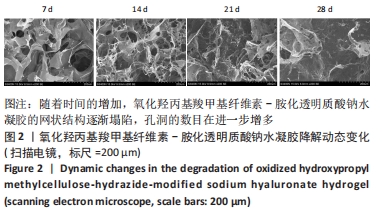
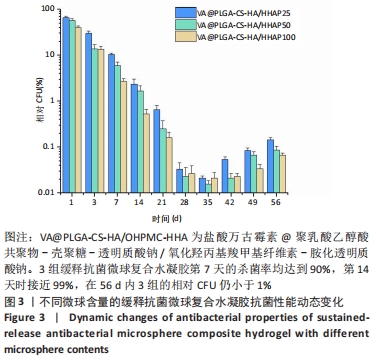
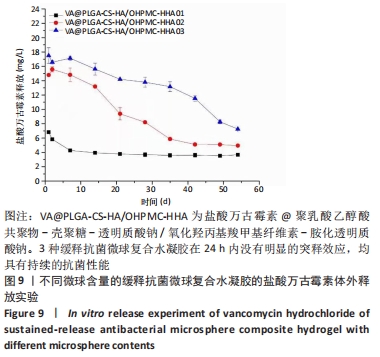
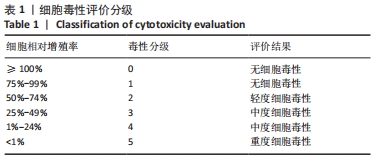
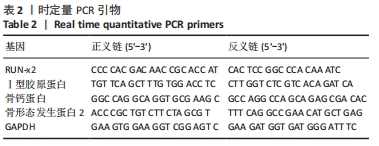
[1] LÁZARO MARTÍNEZ JL, GARCÍA ÁLVAREZ Y, TARDÁGUILA-GARCÍA A,
et al. Optimal management of diabetic foot osteomyelitis: challenges and solutions. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2019;12:947-959.
[2] STEFFENS E, QUINTENS C, DERDELINCKX I, et al. Outpatient parenteral antimicrobial therapy and antibiotic stewardship: opponents or teammates? Infection. 2019;47(2):169-181.
[3] PFÖRRINGER D, HARRASSER N, BEIRER M, et al. Influence of Absorbable Calcium Sulfate-Based Bone Substitute Materials on Human Haemostasis-In Vitro Biological Behavior of Antibiotic Loaded Implants. Materials (Basel). 2018;11(6):935.
[4] NEYISCI C, ERDEM Y, BILEKLI AB, et al. Treatment of implant-related methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis with vancomycin-loaded VK100 silicone cement: An experimental study in rats. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2018;26(1):2309499017754093.
[5] YOUNG SW, ZHANG M, FREEMAN JT, et al. Higher cefazolin concentrations with intraosseous regional prophylaxis in TKA[J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(1):244-249.
[6] 张永红,秦泗河,王栋,等.骨搬运治疗胫骨慢性骨髓炎,是否需要加用抗生素骨水泥?[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(4):331-335.
[7] MOOJEN DJ, HENTENAAR B, CHARLES VOGELY H, et al. In vitro release of antibiotics from commercial PMMA beads and articulating hip spacers. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23(8):1152-1156.
[8] 范少地,刘志恒,吴国忠,等.抗生素骨水泥结合膜诱导技术治疗胫骨骨髓炎的临床研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2017,14(4): 54-57.
[9] 桂雪洋,郑欣,陈一心.可降解抗生素缓释系统的应用进展[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015,30(8):894-896.
[10] BARBER FA, HRNACK SA. Poly L-lactide co-glycolide/β-tricalcium phosphate interference screw fixation for bone-patellar tendon bone anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Knee Surg. 2013;26(6):423-428.
[11] SAHMANI S, SABER-SAMANDARI S, SHAHALI M, et al. Mechanical and biological performance of axially loaded novel bio-nanocomposite sandwich plate-type implant coated by biological polymer thin film. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;88:238-250.
[12] JIANG Z, DONG X, SUN Y. Charge effects of self-assembled chitosan-hyaluronic acid nanoparticles on inhibiting amyloid β-protein aggregation. Carbohydr Res. 2018; 461:11-18.
[13] YAMANE S, IWASAKI N, MAJIMA T, et al. Feasibility of chitosan-based hyaluronic acid hybrid biomaterial for a novel scaffold in cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2005; 26(6):611-619.
[14] JIANG Z, DONG X, SUN Y. Charge effects of self-assembled chitosan-hyaluronic acid nanoparticles on inhibiting amyloid β-protein aggregation. Carbohydr Res. 2018;461:11-18.
[15] YAMANE S, IWASAKI N, MAJIMA T, et al. Feasibility of chitosan-based hyaluronic acid hybrid biomaterial for a novel scaffold in cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2005;26(6):611-619.
[16] 刘永龙,黄江鸿,熊建义,等.胶原水凝胶在软骨与骨组织工程中的研究进展[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2019,16(2):62-66.
[17] FERLIN KM, KAPLAN DS, FISHER JP. Separation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through a Strategic Centrifugation Protocol. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2016;22(4):348-359.
[18] MENZIES DJ, CAMERON A, MUNRO T, et al. Tailorable cell culture platforms from enzymatically cross-linked multifunctional poly(ethylene glycol)-based hydrogels. Biomacromolecules. 2013;14(2):413-423.
[19] 刘宸.仿贻贝nHA/OSA可注射水凝胶的构建及促骨修复的效果研究[D].成都:成都医学院,2018.
[20] MESDAGHINIA A, POURPAK Z, NADDAFI K, et al. An in vitro method to evaluate hemolysis of human red blood cells (RBCs) treated by airborne particulate matter (PM10). MethodsX. 2019;6:156-161.
[21] LEE J, BYUN H, MADHURAKKAT PERIKAMANA SK, et al. Current Advances in Immunomodulatory Biomaterials for Bone Regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(4):e1801106.
[22] 梁嘉碧,李汪婷,梁雨虹,等.原位交联透明质酸水凝胶的制备及体外生物相容性研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2016,30(6):767-771.
[23] CHAKRABORTY S, NANDI S, BHATTACHARYYA K, et al. Time Evolution of Local pH Around a Photo-Acid in Water and a Polymer Hydrogel: Time Resolved Fluorescence Spectroscopy of Pyranine. Chemphyschem. 2019;20(23):3221-3227.
[24] HASHEMNEJAD SM, KUNDU S. Rheological properties and failure of alginate hydrogels with ionic and covalent crosslinks. Soft Matter. 2019;15(39):7852-7862.
[25] 魏娟,刘怀阳,张影,等.载壳聚糖微球PVA/SA水凝胶的制备及其在药物缓释中的应用[J].军事医学,2018,42(4):289-294.
[26] RAVANBAKHSH H, BAO G, LATIFI N, et al. Carbon nanotube composite hydrogels for vocal fold tissue engineering: Biocompatibility, rheology, and porosity. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;103:109861.
[27] ZHANG Y, ZHANG K, WANG Z, et al. Transcutol® P/Cremophor® EL/Ethyl Oleate-Formulated Microemulsion Loaded into Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogel for Improved Transdermal Delivery and Biosafety of Ibuprofen. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019;21(1):22.
[28] ZERBINATI N, LOTTI T, MONTICELLI D, et al. In Vitro Evaluation of the Biosafety of Hyaluronic Acid PEG Cross-Linked with Micromolecules of Calcium Hydroxyapatite in Low Concentration. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2018;6(1):15-19.
[29] 蔡玉辉,胡克甦,张逸.乳酸化壳聚糖/透明质酸复合海绵的生物安全性评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(10):1558-1563.
[30] 徐斌,卢文宁,刘涛,等.心肌梗死局部注射壳聚糖水凝胶材料的存留和降解[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(12):2157-2160.
[31] HASSANI BESHELI N, MOTTAGHITALAB F, ESLAMI M, et al. Sustainable Release of Vancomycin from Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles for Treating Severe Bone Infection in Rat Tibia Osteomyelitis Model. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(6):5128-5138.
[32] MAKAROV C, BERDICEVSKY I, RAZ-PASTEUR A, et al. In vitro antimicrobial activity of vancomycin-eluting bioresorbable β-TCP-polylactic acid nanocomposite material for load-bearing bone repair. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013;24(3):679-687.
[33] EDIN ML, MICLAU T, LESTER GE, et al. Effect of cefazolin and vancomycin on osteoblasts in vitro. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(333): 245-251.
[34] 袁宝明.PLGA-PEG-PLGA温度敏感水凝胶的制备及在骨科应用基础研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2015.
[35] 李鑫平,崔秋菊,曾曙光,等.β-磷酸三钙/壳聚糖水凝胶改性对牙髓干细胞生长与矿化的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(22): 3493-3499.
[36] 王雅倩,洪莹莹,周小莉,等.壳聚糖-氧化石墨烯复合水凝胶在骨缺损中的应用[J].生物医学工程研究,2020,39(2):214-218.
[37] 陈明姣,范先群.透明质酸-明胶双网络水凝胶促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的作用[J].上海交通大学学报,2018,38(7):722-731.
|