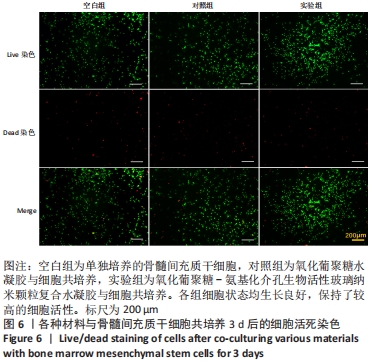
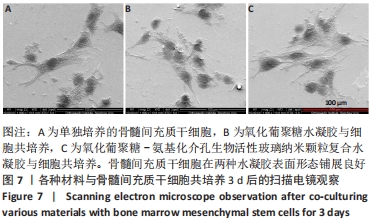
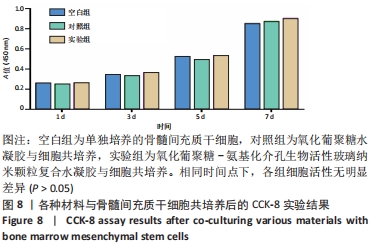
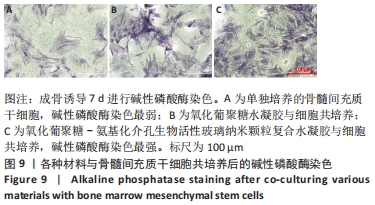
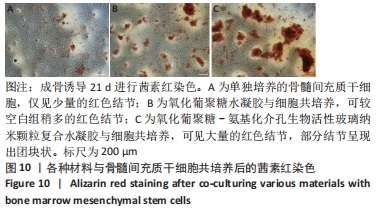
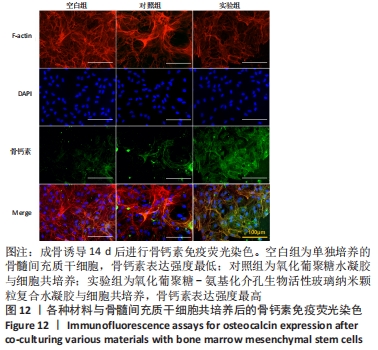
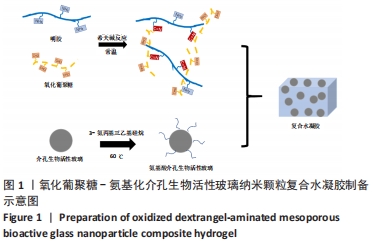
[1] WANG W, YEUNG KWK. Bone grafts and biomaterials substitutes for bone defect repair: A review. Bioact Mater. 2017;2(4):224-247.
[2] TURNBULL G, CLARKE J, PICARD F, et al. 3D bioactive composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Bioact Mater. 2018;3(3):278-314.
[3] 于明琨.自体骨移植修补颅骨缺损的材料与方法 [J].中国临床康复, 2006,10(41):126-129.
[4] 张贝利,张伟滨,邓廉夫.同种异体骨移植研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2005,26(3):164-167.
[5] BAO X, ZHU L, HUANG X, et al. 3D biomimetic artificial bone scaffolds with dual-cytokines spatiotemporal delivery for large weight-bearing bone defect repair. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):1-13.
[6] RAPOSO-AMARAL CE, BUENO DF, ALMEIDA AB, et al. Is bone transplantation the gold standard for repair of alveolar bone defects? J Tissue Eng. 2014;5:2041731413519352.
[7] SHEGARFI H, REIKERAS O. Review article: bone transplantation and immune response. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2009;17(2):206-211.
[8] TOOSI S, BEHRAVAN N, BEHRAVAN J. Nonunion fractures, mesenchymal stem cells and bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018; 106(9):2552-2562.
[9] QIAO C, MA X, ZHANG J, et al. Molecular interactions in gelatin/chitosan composite films. Food Chem. 2017;235:45-50.
[10] 林艳房,霍丹.葡聚糖基水凝胶的制备及其应用的研究进展[J].林产化学与工业,2015,35(6):148-52.
[11] 李丹丹,莫秀梅.基于席夫碱反应的氧化葡聚糖/胺化羧甲基壳聚糖双组分水凝胶粘合剂[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(22):3527-3532.
[12] KUNDU B, RAJKHOWA R, KUNDU SC, et al. Silk fibroin biomaterials for tissue regenerations. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(4):457-470.
[13] 刘冬,秦虎,汪永新,等. 3D打印羟基磷灰石/聚乳酸网状复合物修复颅骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(6):833-837.
[14] XIN T, MAO J, LIU L, et al. Programmed Sustained Release of Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 and Inorganic Ion Composite Hydrogel as Artificial Periosteum. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(6):6840-6851.
[15] HUANG K, WU J, GU Z. Black Phosphorus Hydrogel Scaffolds Enhance Bone Regeneration via a Sustained Supply of Calcium-Free Phosphorus. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(3):2908-2916.
[16] XU T, YANG H, YANG D, et al. Polylactic Acid Nanofiber Scaffold Decorated with Chitosan Islandlike Topography for Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(25):21094-21104.
[17] SHARIFI F, ATYABI SM, NOROUZIAN D, et al.Polycaprolactone/carboxymethyl chitosan nanofibrous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering application. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;115:243-248.
[18] JAIPAN P, NGUYEN A, NARAYAN RJ. Gelatin-based hydrogels for biomedical applications. MRS Commun. 2017;7(3):416-426.
[19] EICHELE DD, KHARBANDA KK. Dextran sodium sulfate colitis murine model: An indispensable tool for advancing our understanding of inflammatory bowel diseases pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23(33):6016.
[20] NONSUWAN P, MATSUGAMI A, HAYASHI F, et al. Controlling the degradation of an oxidized dextran-based hydrogel independent of the mechanical properties. Carbohydr Polym. 2019;204:131-141.
[21] HENCH LL. The story of Bioglass. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2006;17(11): 967-978.
[22] VALLET‐REGÍ M, RUIZ‐HERNÁNDEZ E. Bioceramics: from bone regeneration to cancer nanomedicine. Adv Mater. 2011;23(44):5177-5218.
[23] ZHENG K, BALASUBRAMANIAN P, PATERSON TE, et al. Ag modified mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles for enhanced antibacterial activity in 3D infected skin model. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;103:109764.
[24] XIN T, GU Y, CHENG R, et al. Inorganic Strengthened Hydrogel Membrane as Regenerative Periosteum. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(47):41168-41180.
[25] LENG Y, YANG F, WANG Q, et al. Material-based therapy for bone nonunion. Mater Des.2019;183:108161.
[26] WINKLER T, SASS FA, DUDA GN, et al. A review of biomaterials in bone defect healing, remaining shortcomings and future opportunities for bone tissue engineering: The unsolved challenge. Bone Joint Res. 2018; 7(3):232-243.
[27] LIU L, LI X, SHI X, et al. Injectable alendronate-functionalized GelMA hydrogels for mineralization and osteogenesis. RSC advances. 2018; 8(40):22764-22776.
[28] PAN J, YUAN H, GUO C, et al. One-step cross-linked injectable hydrogels with tunable properties for space-filling scaffolds in tissue engineering. RSC Adv. 2015;5(51):40820-40830.
[29] CHEN QZ, THOMPSON ID, BOCCACCINI AR. 45S5 Bioglass®-derived glass–ceramic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2006;27(11):2414-2425.
[30] FRAYSSINET P, TROUILLET JL, ROUQUET N, et al. Osseointegration of macroporous calcium phosphate ceramics having a different chemical composition. Biomaterials. 1993;14(6):423-429.
[31] VUKAJLOVIC D, PARKER J, BRETCANU O, et al. Chitosan based polymer/bioglass composites for tissue engineering applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;96:955-967.
[32] NARUPHONTJIRAKUL P, PORTER AE, JONES JR. In vitro osteogenesis by intracellular uptake of strontium containing bioactive glass nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2018;66:67-80.
[33] HAO Z, SONG Z, HUANG J, et al. The scaffold microenvironment for stem cell based bone tissue engineering. Biomater Sci. 2017;5(8): 1382-1392.
[34] WEISS S, BAUMGART R, JOCHUM M, et al. Systemic regulation of distraction osteogenesis: a cascade of biochemical factors. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17(7):1280-1289.
[35] LI Y, XIAO Y, LIU C. The Horizon of Materiobiology: A Perspective on Material-Guided Cell Behaviors and Tissue Engineering. Chem Rev. 2017;117(5):4376-4421.
[36] ZHU D, SU Y, YOUNG ML, et al. Biological Responses and Mechanisms of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Zn and Mg Biomaterials. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(33):27453-27461.
[37] WU T, CHENG N, XU C, et al. The effect of mesoporous bioglass on osteogenesis and adipogenesis of osteoporotic BMSCs. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(12):3004-3014.
[38] KAWAGUCHI J, MEE PJ, SMITH AG. Osteogenic and chondrogenic differentiation of embryonic stem cells in response to specific growth factors. Bone. 2005;36(5):758-769.
[39] AUBIN JE, LIU F, MALAVAL L, et al. Osteoblast and chondroblast differentiation. Bone. 1995;17(2):S77-S83.
[40] ICER MA, GEZMEN-KARADAG M. The multiple functions and mechanisms of osteopontin. Clin Biochem. 2018;59:17-24. |