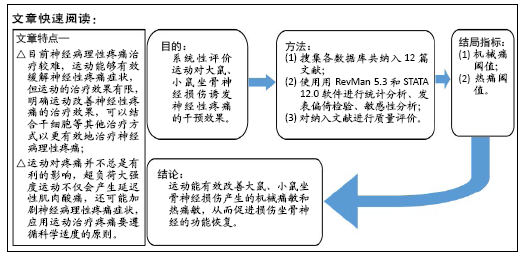
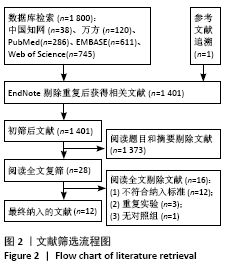
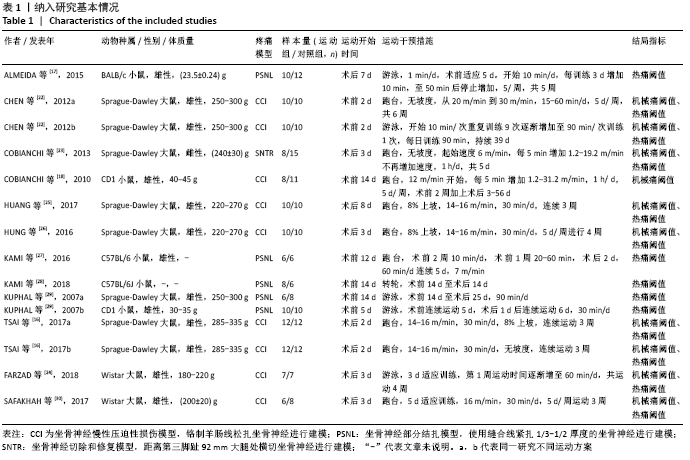
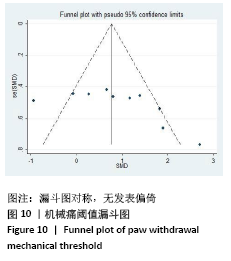
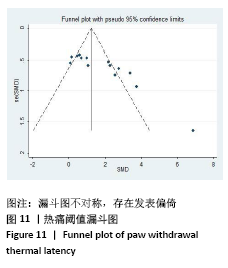
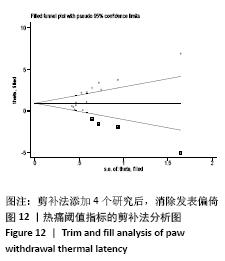
[1] Sá KN, MOREIRA L, BAPTISTA AF, et al. Prevalence of chronic pain in developing countries: systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain Rep. 2019;4:e779.
[2] BREIVIK H, COLLETT B, VENTAFRIDDA V, et al. Survey of chronic pain in Europe: prevalence, impact on daily life, and treatment. Eur J Pain. 2006;10:287.
[3] ZHOU W, JIN Y, MENG Q, et al. A neural circuit for comorbid depressive symptoms in chronic pain. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22:1649.
[4] GOLDBERG DS, MCGEE SJ. Pain as a global public health priority. BMC public health. 2011;11:770.
[5] VAN HECKE O, AUSTIN SK, KHAN RA, et al. Neuropathic pain in the general population: a systematic review of epidemiological studies. Pain. 2014;155:654.
[6] COHEN SP, MAO J. Neuropathic pain: mechanisms and their clinical implications. BMJ. 2014;348:f7656.
[7] ATTAL N. Pharmacological treatments of neuropathic pain: the latest recommendations. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2019; 175:46.
[8] HYLANDS-WHITE N, DUARTE RV, RAPHAEL JH. An overview of treatment approaches for chronic pain management. Rheumatol Int. 2017;37:29.
[9] 孙宁,张娜,林璐璐,等.针刺改善慢性疼痛患者情绪障碍的Meta分析[J].中国针灸,2020,40(6):657-663.
[10] 邓默,赵峰.神经干细胞移植治疗坐骨神经半切断神经病理性疼痛的最佳剂量[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(45):7314-7319.
[11] PEDERSEN BK, SALTIN B. Exercise as medicine-evidence for prescribing exercise as therapy in 26 different chronic diseases. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2015;25 Suppl 3:1-72.
[12] TERKELSEN AJ, BACH FW, JENSEN TS. Experimental forearm immobilization in humans induces cold and mechanical hyperalgesia. Anesthesiology. 2008;109: 297.
[13] TRIERWEILER J, GöTTERT DN, GEHLEN G. Evaluation of mechanical allodynia in an animal immobilization model using the von frey method. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2012;35:18.
[14] GUO JB, CHEN BL, WANG Y, et al. Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Exercise on Neuropathic Pain Induced by Peripheral Nerve Injury in Rat Models. Front Neurol. 2019;10:636.
[15] 吴志伟,宋朋飞,朱清广,等.神经病理性疼痛动物模型研究进展[J].中华中医药学刊,2019,37(5):1083-1087.
[16] TSAI KL, HUANG PC, WANG LK, et al. Incline treadmill exercise suppresses pain hypersensitivity associated with the modulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and anti-inflammatory cytokine in rats with peripheral nerve injury. Neurosci Lett. 2017;643:27.
[17] ALMEIDA C, DEMAMAN A, KUSUDA R, et al. Exercise therapy normalizes BDNF upregulation and glial hyperactivity in a mouse model of neuropathic pain. Pain. 2015;156:504.
[18] COBIANCHI S, MARINELLI S, FLORENZANO F, et al. Short- but not long-lasting treadmill running reduces allodynia and improves functional recovery after peripheral nerve injury. Neuroscience. 2010;168:273.
[19] PITCHER MH. The impact of exercise in rodent models of chronic pain. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2018;16:344.
[20] MOHER D, LIBERATI A, TETZLAFF J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62:1006.
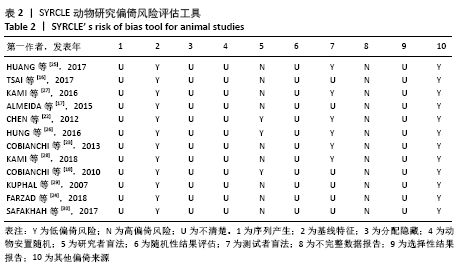
[21] HOOIJMANS CR, ROVERS MM, DE VRIES RBM, et al. SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014;14:43.
[22] CHEN YW, LI YT, CHEN YC, et al. Exercise training attenuates neuropathic pain and cytokine expression after chronic constriction injury of rat sciatic nerve. Anesth Analg. 2012;114:1330.
[23] COBIANCHI S, CASALS-DIAZ L, JARAMILLO J, et al. Differential effects of activity dependent treatments on axonal regeneration and neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve injury. Exp Neurol. 2013; 240:157.
[24] FARZAD B, RAJABI H, GHARAKHANLOU R, et al. Swimming training attenuates allodynia and hyperalgesia induced by peripheral nerve injury in an adult male rat neuropathic model: effects on irisin and GAD65. Pain Med. 2018;19:2236.
[25] HUANG PC, TSAI KL, CHEN YW, et al. Exercise combined with ultrasound attenuates neuropathic pain in rats associated with downregulation of il-6 and tnf-α, but with upregulation of IL-10. Anesth Analg. 2017;124:2038.
[26] HUNG CH, HUANG PC, TZENG JI, et al. Therapeutic ultrasound and treadmill training suppress peripheral nerve injury-induced pain in rats. Phys Ther. 2016;96: 1545.
[27] KAMI K, TAGUCHI MS, TAJIMA F, et al. Improvements in impaired GABA and GAD65/67 production in the spinal dorsal horn contribute to exercise-induced hypoalgesia in a mouse model of neuropathic pain. Mol Pain. 2016. doi: 10.1177/1744806916629059.
[28] KAMI K, TAJIMA F, SENBA E. Activation of mesolimbic reward system via laterodorsal tegmental nucleus and hypothalamus in exercise-induced hypoalgesia. Sci Rep. 2018; 8:11540.
[29] KUPHAL KE, FIBUCH EE, TAYLOR BK. Extended swimming exercise reduces inflammatory and peripheral neuropathic pain in rodents. J Pain. 2007;8:989.
[30] SAFAKHAH HA, MORADI KOR N, BAZARGANI A, et al. Forced exercise attenuates neuropathic pain in chronic constriction injury of male rat: an investigation of oxidative stress and inflammation. J Pain Res. 2017;10:1457.
[31] GRACE PM, FABISIAK TJ, GREEN-FULGHAM SM, et al. Prior voluntary wheel running attenuates neuropathic pain. Pain. 2016; 157:2012.
[32] 王群,吕岩.疼痛特异性学说与闸门控制学说:争论还在持续[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2014,20(9):609-613.
[33] 陈明,武丽娟,吴雪琼.人类Mas相关基因及其G蛋白偶联受体研究进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2016,16(35):6993-6997.
[34] 张瑛,王韵.TRPV1:一种同时参与慢性痛外周敏化和疼痛中枢调制的重要分子[J].生理学报,2017,69(5):677-684.
[35] CAVANAUGH DJ, LEE H, LO L, et al. Distinct subsets of unmyelinated primary sensory fibers mediate behavioral responses to noxious thermal and mechanical stimuli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:9075.
[36] 颜冰,戴文玲,刘吉华.神经病理性疼痛中神经生长因子的作用及其相关镇痛药物研发进展[J]. 药学进展,2019,43(2): 111-117.
[37] CHAUMETTE T, DELAY L, BARBIER J, et al. c-Jun/p38MAPK/ASIC3 pathways specifically activated by nerve growth factor through TrkA are crucial for mechanical allodynia development. Pain. 2020;161:1109.
[38] 吴志伟,宋朋飞,朱清广,等.神经病理性疼痛机制研究进展[J].河北医科大学学报,2018,39(9):1095-1100.
[39] 贾书冰,赵明沂,梁露花,等.漏斗图在Meta分析中的正确使用研究[J].数理医药学杂志,2013,26(4):402-405.
[40] LI WC, GAO G, LUN ZJ, et al. Proceedings of 2018 5th International Symposium on Computer, Communication, Control and Automation (3CA 2018). Information Engineering Research Institute, USA. Singapore Management and Sports Science Institute, Singapore, 2018.
[41] MOGIL JS. Sex differences in pain and pain inhibition: multiple explanations of a controversial phenomenon. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012;13:859. |