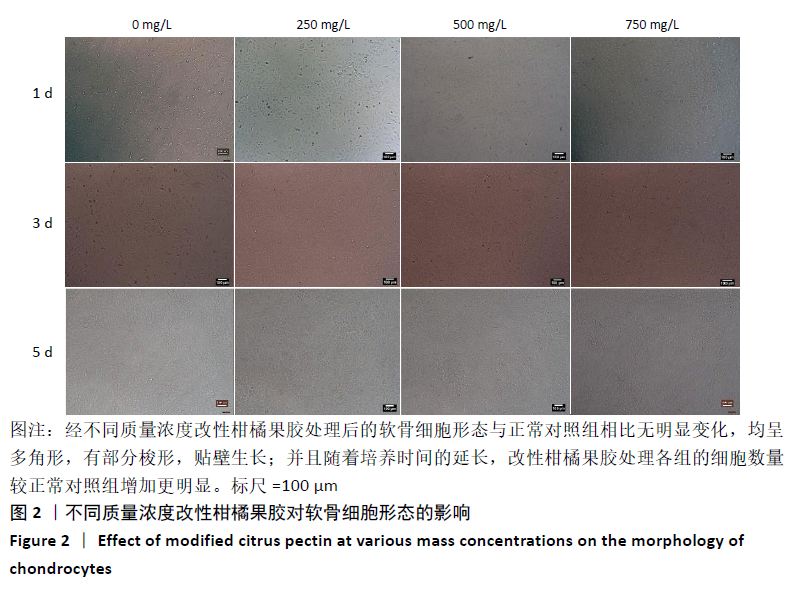
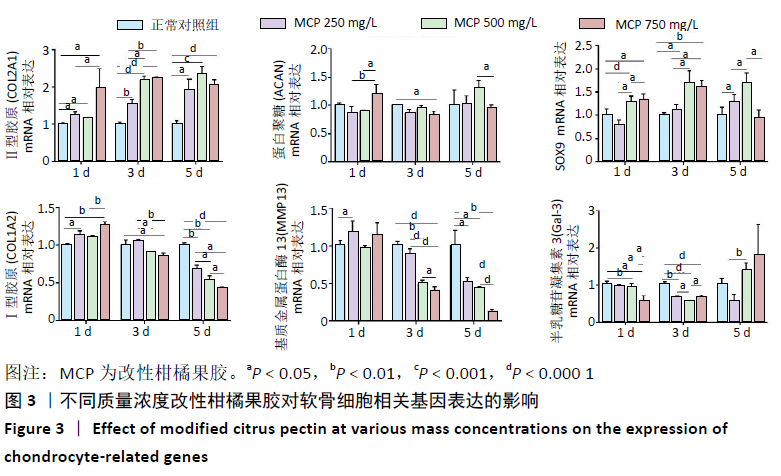
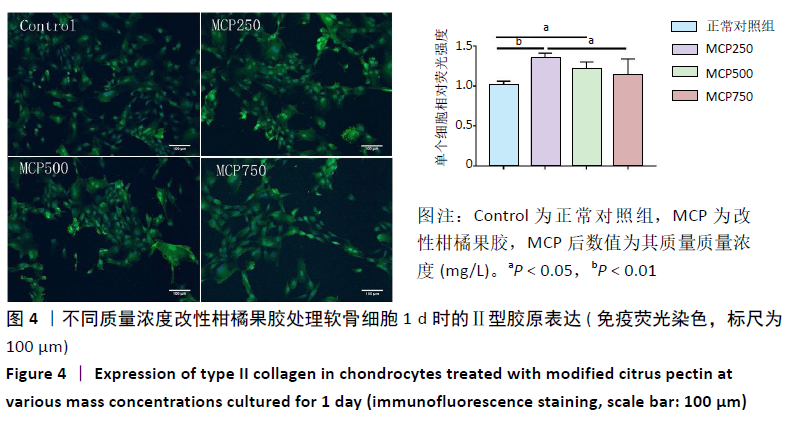
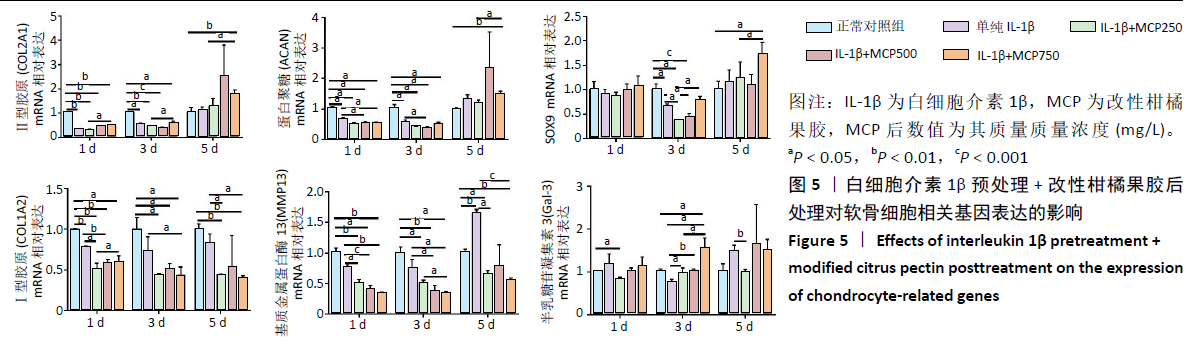
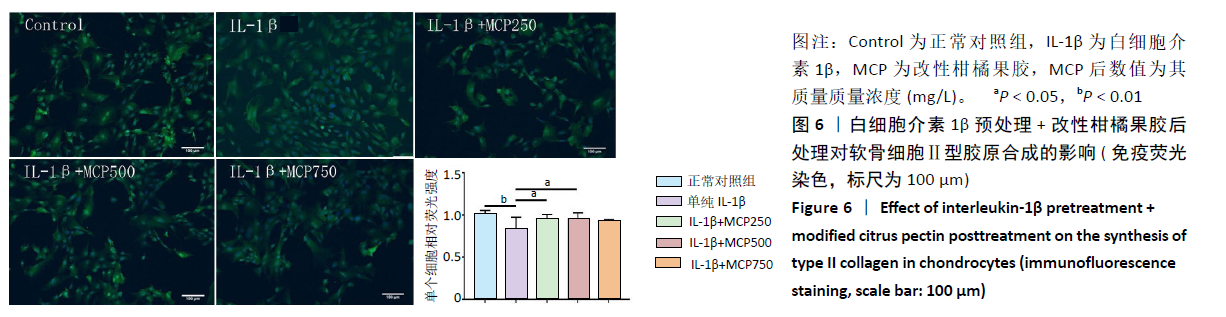
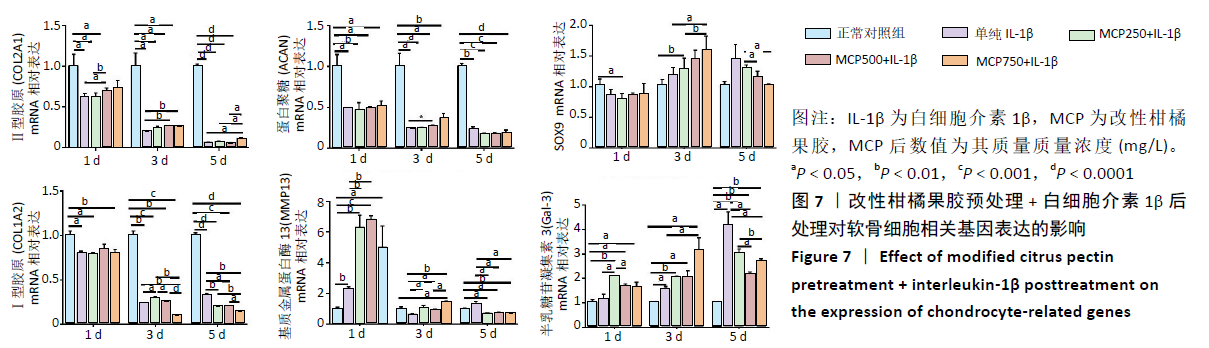
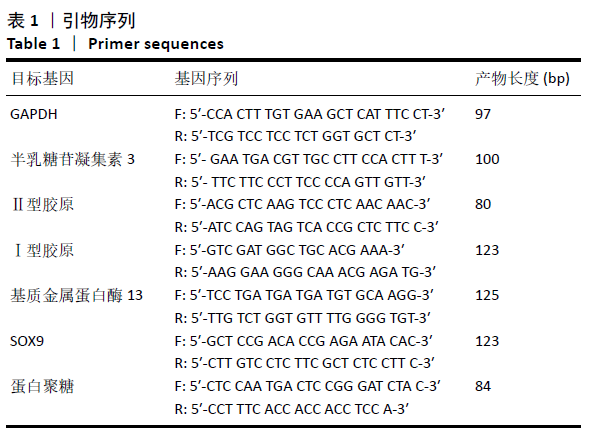
[1] GOLDRING MB. Chondrogenesis, chondrocyte differentiation, and articular cartilage metabolism in health and osteoarthritis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2012;4(4):269-285.
[2] AHSAN T, SAH RL. Biomechanics of integrative cartilage repair. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1999;7(1):29-40.
[3] WARNOCK WR, MARSH CA, HAND DR. Outcome of arthroscopic debridement of cartilage injury in the equine distal interphalangeal joint. Can Vet J. 2019;60(7):731-736.
[4] GIANAKOS AL, YASUI Y, FRASER EJ, et al. The Effect of Different Bone Marrow Stimulation Techniques on Human Talar Subchondral Bone: A Micro-Computed Tomography Evaluation. Arthroscopy. 2016;32(10):2110-2117.
[5] BECHER C, MALAHIAS MA, ALI MM, et al. Arthroscopic microfracture vs. arthroscopic autologous matrix-induced chondrogenesis for the treatment of articular cartilage defects of the talus. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(9):2731-2736.
[6] MERKELY G, OGURA T, BRYANT T, et al. Severe Bone Marrow Edema Among Patients Who Underwent Prior Marrow Stimulation Technique Is a Significant Predictor of Graft Failure After Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(8):1874-1884.
[7] HUANG BJ, HU JC, ATHANASIOU KA. Cell-based tissue engineering strategies used in the clinical repair of articular cartilage. Biomaterials. 2016;98:1-22.
[8] JUNG M, KARAMPINOS D, HOLWEIN C, et al. Quantitative 3-T Magnetic Resonance Imaging After Matrix-Associated Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation With Autologous Bone Grafting of the Knee: The Importance of Subchondral Bone Parameters. Am J Sports Med. 2021:363546520980134.
[9] ARBAB D, REIMANN P, BRUCKER M, et al. Alignment in total knee arthroplasty - A comparison of patient-specific implants with the conventional technique. Knee. 2018;25(5):882-887.
[10] KAMENAGA T, HIRANAKA T, KIKUCHI K, et al. Influence of tibial component rotation on short-term clinical outcomes in Oxford mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2018;25(6):1222-1230.
[11] 赵晨西,刘明远.膝关节骨性关节炎的治疗进展[J].湖南中医杂志,2018, 34(11):197-200.
[12] SCIACCHITANO S, LAVRA L, MORGANTE A, et al. Galectin-3: One Molecule for an Alphabet of Diseases, from A to Z. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(2):379.
[13] SACCON F, GATTO M, GHIRARDELLO A, et al. Role of galectin-3 in autoimmune and non-autoimmune nephropathies. Autoimmun Rev. 2017;16(1):34-47.
[14] SREJOVIC I, SELAKOVIC D, JOVICIC N, et al. Galectin-3: Roles in Neurodevelopment, Neuroinflammation, and Behavior. Biomolecules. 2020;10(5):798.
[15] WEINMANN D, SCHLANGEN K, ANDRé S, et al. Galectin-3 Induces a Pro-degradative/inflammatory Gene Signature in Human Chondrocytes, Teaming Up with Galectin-1 in Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:39112.
[16] HU Y, YéLéHé-OKOUMA M, EA HK, et al. Galectin-3: A key player in arthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2017;84(1):15-20.
[17] ELIAZ I, RAZ A. Pleiotropic Effects of Modified Citrus Pectin. Nutrients. 2019;11(11): 2619.
[18] MERHEB R, ABDEL-MASSIH RM, KARAM MC. Immunomodulatory effect of natural and modified Citrus pectin on cytokine levels in the spleen of BALB/c mice. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;121:1-5.
[19] ABU-ELSAAD NM, ELKASHEF WF. Modified citrus pectin stops progression of liver fibrosis by inhibiting galectin-3 and inducing apoptosis of stellate cells. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016;94(5):554-562.
[20] LU Y, ZHANG M, ZHAO P, et al. Modified citrus pectin inhibits galectin-3 function to reduce atherosclerotic lesions in apoE-deficient mice. Mol Med Rep. 2017; 16(1):647-653.
[21] LI HY, YANG S, LI J C, et al. Galectin 3 inhibition attenuates renal injury progression in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(6):BSR20181803.
[22] TIAN Y, LV W, LU C, et al. Galectin-3 inhibition attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiac dysfunction by upregulating the expression of peroxiredoxin-4. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020;98(10):700-707.
[23] 魏子淏,杨伟,刘夫国,等.改性柑橘果胶研究进展[J].中国食品添加剂, 2014(3):194-200.
[24] SYNYTSYA A, POUČKOVá P, ZADINOVá M, et al. Hydrogels based on low-methoxyl amidated citrus pectin and flaxseed gum formulated with tripeptide glycyl-l-histidyl-l-lysine improve the healing of experimental cutting wounds in rats. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;165:3156-3168.
[25] YIN Q, CHEN J, MA S, et al. Pharmacological Inhibition of Galectin-3 Ameliorates Diabetes-Associated Cognitive Impairment, Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in vivo and in vitro. J Inflamm Res. 2020;13:533-542.
[26] CAO J, YANG J, WANG Z, et al. Modified citrus pectins by UV/HO oxidation at acidic and basic conditions: Structures and in vitro anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative activities. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;247:116742.
[27] RAHMANI DEL BAKHSHAYESH A, BABAIE S, TAYEFI NASRABADI H, et al. An overview of various treatment strategies, especially tissue engineering for damaged articular cartilage. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2020;48(1):1089-1104.
[28] KWON H, PASCHOS NK, HU JC, et al. Articular cartilage tissue engineering: the role of signaling molecules . Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(6):1173-1194.
[29] SZWEDOWSKI D, SZCZEPANEK J, PACZESNY Ł, et al. Genetics in Cartilage Lesions: Basic Science and Therapy Approaches. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(15):5430.
[30] YU Y, WANG S, ZHOU Z. Cartilage Homeostasis Affects Femoral Head Necrosis Induced by Methylprednisolone in Broilers. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(14):4841.
[31] GUILAK F, NIMS RJ, DICKS A, et al. Osteoarthritis as a disease of the cartilage pericellular matrix. Matrix Biol. 2018;71-72:40-50.
[32] LIU C, WANG B, XIAO L, et al. Protective effects of the pericellular matrix of chondrocyte on articular cartilage against the development of osteoarthritis. Histol Histopathol. 2018;33(8):757-764.
[33] DANALACHE M, ERLER AL, WOLFGART JM, et al. Biochemical changes of the pericellular matrix and spatial chondrocyte organization-Two highly interconnected hallmarks of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(10):2170-2180.
[34] GENCOGLU H, ORHAN C, SAHIN E, et al. Undenatured Type II Collagen (UC-II) in Joint Health and Disease: A Review on the Current Knowledge of Companion Animals. Animals (Basel). 2020;10(4):697.
[35] FISCHENICH KM, WAHLQUIST JA, WILMOTH RL, et al. Human articular cartilage is orthotropic where microstructure, micromechanics, and chemistry vary with depth and split-line orientation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(10):1362-1372.
[36] LUO L, CHU J, ESWARAMOORTHY R, et al. Engineering Tissues That Mimic the Zonal Nature of Articular Cartilage Using Decellularized Cartilage Explants Seeded with Adult Stem Cells.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2017;3(9):1933-1943.
[37] LEFEBVRE V, ANGELOZZI M, HASEEB A. SOX9 in cartilage development and disease. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2019;61:39-47.
[38] DAI J, ZHANG Y, CHEN D, et al. Glabridin inhibits osteoarthritis development by protecting chondrocytes against oxidative stress, apoptosis and promoting mTOR mediated autophagy. Life Sci. 2021:118992.
[39] 张煜珅,张普华,刘鑫成,等.丹参酮ⅡA对软骨细胞去分化影响的研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(9):942-945.
[40] MEHANA EE, KHAFAGA AF, EL-BLEHI SS. The role of matrix metalloproteinases in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: An updated review. Life Sci. 2019;234:116786.
[41] LI H, WANG D, YUAN Y, et al. New insights on the MMP-13 regulatory network in the pathogenesis of early osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):248.
[42] XU G, ZHANG C, YANG H, et al. Modified citrus pectin ameliorates myocardial fibrosis and inflammation via suppressing galectin-3 and TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;126:110071.
[43] GOLDRING MB, MARCU KB. Cartilage homeostasis in health and rheumatic diseases . Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(3):224.
[44] ZHANG L, MA S, SU H, et al. Isoliquiritigenin Inhibits IL-1β-Induced Production of Matrix Metalloproteinase in Articular Chondrocytes. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2018;9:153-159.
[45] HE YK, CEN XT, LIU SS, et al. Protective effects of ten oligostilbenes from Paeonia suffruticosa seeds on interleukin-1β-induced rabbit osteoarthritis chondrocytes. BMC Chem. 2019;13(1):72.
[46] YI H, ZHANG W, CUI ZM, et al. Resveratrol alleviates the interleukin-1β-induced chondrocytes injury through the NF-κB signaling pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):424.
[47] ZHENG W, TAO Z, CAI L, et al. Chrysin Attenuates IL-1β-Induced Expression of Inflammatory Mediators by Suppressing NF-κB in Human Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes. Inflammation. 2017;40(4):1143-1154.
[48] SHI S, MAN Z, LI W, et al. Silencing of Wnt5a prevents interleukin-1β-induced collagen type II degradation in rat chondrocytes. Exp Ther Med. 2016;12(5): 3161-3166.
[49] ZENG YF, WANG R, BIAN Y, et al. Catalpol Attenuates IL-1β Induced Matrix Catabolism, Apoptosis and Inflammation in Rat Chondrocytes and Inhibits Cartilage Degeneration. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:6649-6659.
[50] GAO GC, CHENG XG, WEI QQ, et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT-1 inhibits apoptosis and matrix metabolism disorder in interleukin-1β-induced inflammation in articular chondrocytes via the JNK signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(10):17167-17179.
[51] MA C, ZHOU X, XU K, et al. Specnuezhenide Decreases Interleukin-1β-Induced Inflammation in Rat Chondrocytes and Reduces Joint Destruction in Osteoarthritic Rats. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:700. |