[1] HAN Y, LI X, ZHANG Y, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Regenerative Medicine. Cells. 2019;8(8):886.
[2] GALIPEAU J, SENSÉBÉ L. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Clinical Challenges and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;22(6):824-833.
[3] DA COSTA GONÇALVES F, PAZ AH. Cell membrane and bioactive factors derived from mesenchymal stromal cells: Cell-free based therapy for inflammatory bowel diseases. World J Stem Cells. 2019;11(9):618-633.
[4] 李青青,刘建昆,潘兴华.干细胞移植治疗炎症性肠病[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(21):3432-3437.
[5] ZHOU Y, YAMAMOTO Y, XIAO Z, et al. The Immunomodulatory Functions of Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells Mediated via Paracrine Activity. J Clin Med. 2019;8(7):1025.
[6] 王颍翠,潘兴华.间充质干细胞对系统性红斑狼疮T、B细胞的免疫调节机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(29):4734-4741.
[7] GUERROUAHEN BS, SIDAHMED H, AL SULAITI A, et al. Enhancing Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Immunomodulation for Treating Conditions Influenced by the Immune System. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:7219297.
[8] 谢景春,姚观平,余丽梅.间充质干细胞在类风湿性关节炎治疗中的免疫调节作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(29):4722-4727.
[9] SALA E, GENUA M, PETTI L, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reduce Colitis in Mice via Release of TSG6, Independently of Their Localization to the Intestine. Gastroenterology. 2015;149(1):163-176.
[10] YAN Y, ZHAO N, HE X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell expression of interleukin-35 protects against ulcerative colitis by suppressing mucosal immune responses. Cytotherapy. 2018;20(7):911-918.
[11] 杨敏,安国,赵威,等.结肠炎小鼠模型的病理机制研究[J].首都医科大学学报,2018,39(5):704-709.
[12] 陈素傲,金世柱.葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导鼠溃疡性结肠炎模型研究进展[J].中国比较医学杂志,2020,30(4):142-146.
[13] GOODMAN RR, DAVIES JE. Mesenchymal stromal cells and their derivatives - putative therapeutics in the management of autoimmune pancreatitis. FEBS Open Bio. 2020;10(6):969-978.
[14] WHYTE MP. Hypophosphatasia - aetiology, nosology, pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016;12(4):233-246.
[15] WHYTE MP, SIMMONS JH, MOSELEY S, et al. Asfotase alfa for infants and young children with hypophosphatasia: 7 year outcomes of a single-arm, open-label, phase 2 extension trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(2):93-105.
[16] PADIDELA R. Asfotase alfa treatment in perinatal and infantile hypophosphatasia: safe and sustained efficacy. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(2):76-78.
[17] LIU W, ZHANG L, XUAN K, et al. Alpl prevents bone ageing sensitivity by specifically regulating senescence and differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells. Bone Res. 2018;6:27.
[18] ALLAN D, TIEU A, LALU M, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles for regenerative therapy and immune modulation: Progress and challenges toward clinical application. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020;9(1):39-46.
[19] DE CASTRO LL, LOPES-PACHECO M, WEISS DJ, et al. Current understanding of the immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal stromal cells. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019;97(5):605-618.
[20] WANG LT, TING CH, YEN ML, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) for treatment towards immune- and inflammation-mediated diseases: review of current clinical trials. J Biomed Sci. 2016;23(1):76.
[21] GAO L, ZHANG Y, HU B, et al. Phase II Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind Controlled Study of Efficacy and Safety of Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in the Prophylaxis of Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease After HLA-Haploidentical Stem-Cell Transplantation. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(24):2843-2850.
[22] HOSSEINI SHAMILI F, ALIBOLANDI M, RAFATPANAH H, et al. Immunomodulatory properties of MSC-derived exosomes armed with high affinity aptamer toward mylein as a platform for reducing multiple sclerosis clinical score. J Control Release. 2019; 299:149-164.
[23] CEKIC C, LINDEN J. Purinergic regulation of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016;16(3):177-192.
[24] CHEN X, CAI C, XU D, et al. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Treated Regulatory CD23+CD43+ B Cells Alleviate Intestinal Inflammation. Theranostics. 2019;9(16): 4633-4647.
[25] BISWAS A, SHOUVAL DS, GRIFFITH A, et al. WASP-mediated regulation of anti-inflammatory macrophages is IL-10 dependent and is critical for intestinal homeostasis. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1779.
[26] RIEHL TE, ALVARADO D, EE X, et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG protects the intestinal epithelium from radiation injury through release of lipoteichoic acid, macrophage activation and the migration of mesenchymal stem cells. Gut. 2019;68(6):1003-1013.
[27] LI X, WANG Q, DING L, et al. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 enhances the therapeutic effects of MSCs in a dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis models by promoting MSCs homing to murine colons and spleens. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):267.
[28] JIANG B, YAN L, WANG X, et al. Concise Review: Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Human Pluripotent Cells, an Unlimited and Quality-Controllable Source for Therapeutic Applications. Stem Cells. 2019;37(5):572-581.
[29] BLANDER JM. A long-awaited merger of the pathways mediating host defence and programmed cell death. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14(9):601-618.
[30] YANG FY, CHEN R, ZHANG X, et al. Preconditioning Enhances the Therapeutic Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Colitis Through PGE2-Mediated T-Cell Modulation. Cell Transplant. 2018;27(9):1352-1367.
[31] NAJAR M, BOUHTIT F, MELKI R, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Based Therapy: New Perspectives and Challenges. J Clin Med. 2019;8(5):626.
[32] MÉNARD C, DULONG J, ROULOIS D, et al. Integrated transcriptomic, phenotypic, and functional study reveals tissue-specific immune properties of mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cells. 2020;38(1):146-159.
[33] ANKRUM JA, ONG JF, KARP JM. Mesenchymal stem cells: immune evasive, not immune privileged. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32(3):252-260.
[34] ALONSO N, LARRAZ-PRIETO B, BERG K, et al. Loss-of-Function Mutations in the ALPL Gene Presenting with Adult Onset Osteoporosis and Low Serum Concentrations of Total Alkaline Phosphatase. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(4): 657-661.
[35] MACGREGOR GR, ZAMBROWICZ BP, SORIANO P. Tissue non-specific alkaline phosphatase is expressed in both embryonic and extraembryonic lineages during mouse embryogenesis but is not required for migration of primordial germ cells. Development. 1995;121(5):1487-1496.
[36] LIU CH, RAJ S, CHEN CH, et al. HLA-B27-mediated activation of TNAP phosphatase promotes pathogenic syndesmophyte formation in ankylosing spondylitis. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(12):5357-5373.
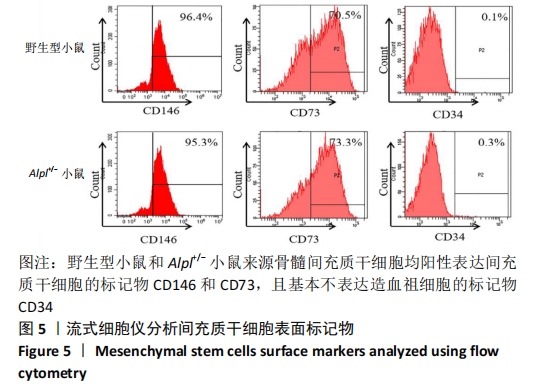
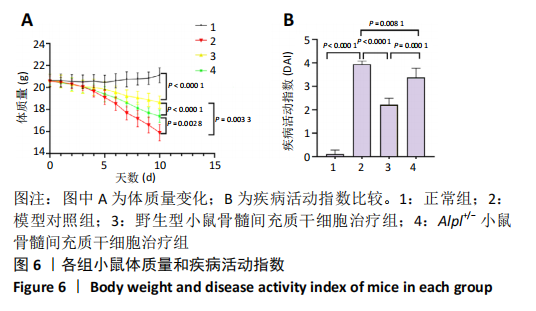
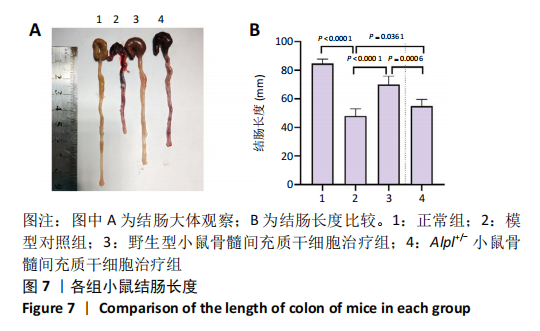
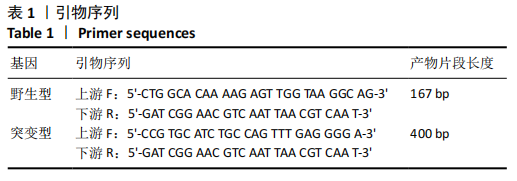
|