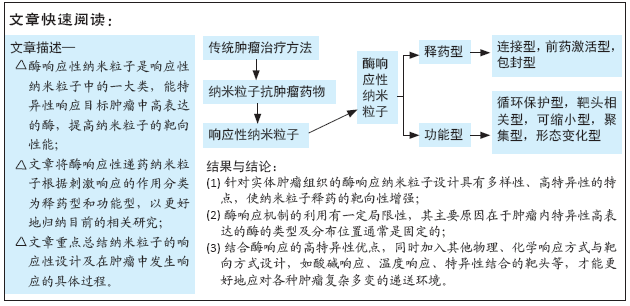
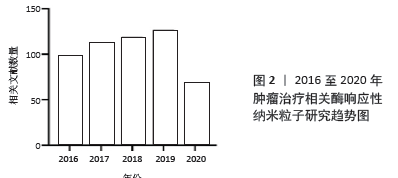
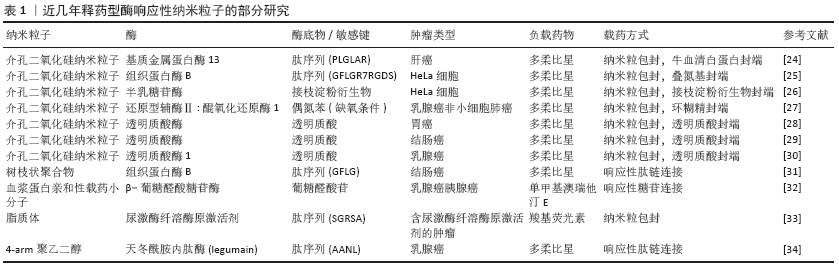
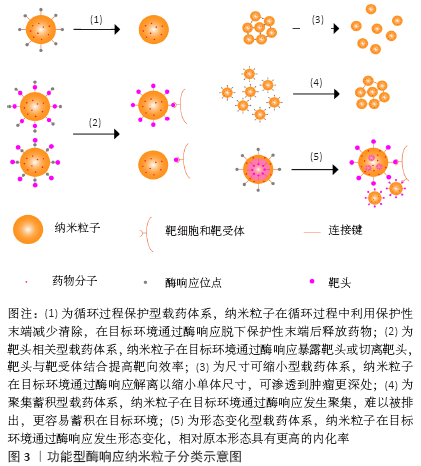
[1] WILD CP, WEIDERPASS E, STEWART BW. World cancer report: cancer research for cancer prevention. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2020.
[2] 姚梦欢,王铁梅,林梓桐.纳米靶向给药系统在口腔鳞状细胞癌诊断与治疗的研究进展[J].口腔医学研究,2018,34(12):1277-1280.
[3] 魏常博.纳米材料和纳米技术在肿瘤放疗增敏中的研究进展[J].口腔疾病防治,2017,25(11):744-748.
[4] PRABHAKAR U, MAEDA H, JAIN K, et al. Challenges and key considerations of the enhanced permeability and retention effect for nanomedicine drug delivery in oncology. Cancer Res. 2013;73(8):2412-2417.
[5] 刘艳红,周建平,霍美蓉.肿瘤微环境响应型智能纳米药物载体的研究进展[J].中国药科大学学报,2016,47(2):4-12.
[6] 贺瑞,甘杨子,钟克焱,等.纳米抗肿瘤药物及其研究进展[J].现代养生(下半月版),2019(2):109-110.
[7] AMREDDY N, BABU A, MURALIDHARAN R, et al. Recent Advances in Nanoparticle-Based Cancer Drug and Gene Delivery. Adv Cancer Res. 2018; 137:115-170.
[8] BEHZADI S, SERPOOSHAN V, TAO W, et al. Cellular uptake of nanoparticles: journey inside the cell. Chem Soc Rev. 2017;46(14):4218-4244.
[9] Chen B, Dai W, He B, et al. Current Multistage Drug Delivery Systems Based on the Tumor Microenvironment. Theranostics, 2017;7(3):538-558.
[10] ZHANG H, LIU XL, ZHANG YF, et al. Magnetic nanoparticles based cancer therapy: current status and applications. Sci China Life Sci. 2018;61(4): 400-414.
[11] 刘耀阳,王荣梅.酶响应纳米粒子共输送地西他滨阿霉素逆转乳腺癌多药耐药[J].药物生物技术,2018,25(4):288-293.
[12] KUMAR B, KULANTHAIVEL S, MONDAL A, et al. Mesoporous silica nanoparticle based enzyme responsive system for colon specific drug delivery through guar gum capping. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;150: 352-361.
[13] 刘新,马铭怿.基质金属蛋白酶响应的紫杉醇-二氢卟吩e6纳米粒子诱导结肠癌细胞凋亡[J].药物生物技术,2019,26(3):211-216.
[14] JIANG H, SHI X, YU X, et al. Hyaluronidase Enzyme-responsive Targeted Nanoparticles for Effective Delivery of 5-Fluorouracil in Colon Cancer. Pharm Res. 2018;35(4):73.
[15] 李辉盛,苏子桓,王冠海.酶刺激响应纳米载体的制备与负载姜黄素体外释放研究[J].山东化工,2018,47(20):18-19.
[16] ZHANG C, PAN D, LUO K, et al. Peptide Dendrimer–doxorubicin Conjugate-Based Nanoparticles as an Enzyme-Responsive Drug Delivery System for Cancer Therapy. Adv Healthc Mater. 2014;3(8):1299-1308.
[17] BEN-NUN Y, FICHMAN G, ADLER-ABRAMOVICH L, et al. Cathepsin nanofiber substrates as potential agents for targeted drug delivery. J Control Release. 2017;257:60-67.
[18] DE LA TORRE C, MONDRAGÓN L, COLL C, et al. Cathepsin-B induced controlled release from peptide-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chemistry. 2014;20(47):15309-15314.
[19] VAN RIJT SH, BÖLÜKBAS DA, ARGYO C, et al. Protease-Mediated Release of Chemotherapeutics from Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles to ex Vivo Human and Mouse Lung Tumors. ACS Nano. 2015;9(3):2377-2389.
[20] SHI L, HU Y, LIN A, et al. Matrix Metalloproteinase Responsive Nanoparticles for Synergistic Treatment of Colorectal Cancer via Simultaneous Anti-Angiogenesis and Chemotherapy. Bioconjug Chem. 2016;27(12):2943-2953.
[21] ZHOU Y, ZHANG S, CHEN Z, et al. Targeted Delivery of Secretory Promelittin via Novel Poly(lactone-co-β-amino ester) Nanoparticles for Treatment of Breast Cancer Brain Metastases. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7(5):1901866.
[22] JALLOUK AP, PALEKAR RU, MARSH JN, et al. Delivery of a Protease-Activated Cytolytic Peptide Prodrug by Perfluorocarbon Nanoparticles. Bioconjug Chem. 2015;26(8):1640-1650.
[23] YE M, HAN Y, TANG J, et al. A Tumor-Specific Cascade Amplification Drug Release Nanoparticle for Overcoming Multidrug Resistance in Cancers. Adv Mater. 2017;29(38):1702342.
[24] LIU Y, DING X, LI J, et al. Enzyme responsive drug delivery system based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles for tumor therapyin vivo. Nanotechnology. 2015;26(14):145102.
[25] CHENG YJ, LUO GF, ZHU JY, et al. Enzyme-induced and tumor-targeted drug delivery system based on multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(17):9078-9087.
[26] BERNARDOS A, MONDRAGON L, AZNAR E, et al. Enzyme-responsive intracellular controlled release using nanometric silica mesoporous supports capped with “saccharides”. ACS Nano. 2010;4(11):6353-6368.
[27] LEE J, OH ET, YOON H, et al. Mesoporous nanocarriers with a stimulus-responsive cyclodextrin gatekeeper for targeting tumor hypoxia. Nanoscale. 2017;9(20):6901-6909.
[28] NAZ S, WANG M, HAN Y, et al. Enzyme-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for tumor cells and mitochondria multistage-targeted drug delivery. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:2533-2542.
[29] ZHANG M, XU C, WEN L, et al. A Hyaluronidase-Responsive Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery System for Targeting Colon Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2016;76(24):7208-7218.
[30] CHEN Z, LI Z, LIN Y, et al. Bioresponsive hyaluronic acid-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. Chemistry. 2013;19(5): 1778-1783.
[31] LEE SJ, JEONG YI, PARK HK, et al. Enzyme-responsive doxorubicin release from dendrimer nanoparticles for anticancer drug delivery. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;10:5489-5503.
[32] RENOUX B, RAES F, LEGIGAN T, et al. Targeting the tumour microenvironment with an enzyme-responsive drug delivery system for the efficient therapy of breast and pancreatic cancers. Chem Sci. 2017;8(5):3427-3433.
[33] BASEL MT, SHRESTHA TB, TROYER DL, et al. Protease-sensitive, polymer-caged liposomes: a method for making highly targeted liposomes using triggered release. ACS Nano. 2011;5(3):2162-2175.
[34] 王丁丁,孙中洋,南军,等.胞内酶敏感肿瘤靶向递药体系的合成及应用[J].西北药学杂志,2019,34(2):203-208.
[35] CALLMANN CE, BARBACK CV, THOMPSON MP, et al. Therapeutic Enzyme-Responsive Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery and Accumulation in Tumors. Adv Mater. 2015;27(31):4611-4615.
[36] FENG Q, ZHANG Y, ZHANG W, et al. Tumor-targeted and multi-stimuli responsive drug delivery system for near-infrared light induced chemo-phototherapy and photoacoustic tomography. Acta Biomater. 2016;38: 129-142.
[37] CABRAL H, MATSUMOTO Y, MIZUNO K, et al. Accumulation of sub-100 nm polymeric micelles in poorly permeable tumours depends on size. Nat Nanotechnol. 2011;6(12):815-823.
[38] CHOI KY, SARAVANAKUMAR G, PARK JH, et al. Hyaluronic acid-based nanocarriers for intracellular targeting: interfacial interactions with proteins in cancer. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2012;99:82-94.
[39] HAN M, HUANG-FU MY, GUO WW, et al. MMP-2-Sensitive HA End-Conjugated Poly(amidoamine) Dendrimers via Click Reaction To Enhance Drug Penetration into Solid Tumor. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(49):42459-42470.
[40] FERNANDES C, SUARES D, YERGERI MC. Tumor Microenvironment Targeted Nanotherapy. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1230.
[41] LI H, MITEVA M, KIRKBRIDE KC, et al. Dual MMP7-proximity-activated and folate receptor-targeted nanoparticles for siRNA delivery. Biomacromolecules. 2015;16(1):192-201.
[42] GUO F, WU J, WU W, et al. PEGylated self-assembled enzyme-responsive nanoparticles for effective targeted therapy against lung tumors. J Nanobiotechnology. 2018;16(1):57.
[43] PENG ZH, KOPEČEK J. Enhancing Accumulation and Penetration of HPMA Copolymer-Doxorubicin Conjugates in 2D and 3D Prostate Cancer Cells via iRGD Conjugation with an MMP-2 Cleavable Spacer. J Am Chem Soc. 2015;137(21):6726-6729.
[44] POPOVIĆ Z, LIU W, CHAUHAN VP, et al. A nanoparticle size series for in vivo fluorescence imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2010;49(46):8649-8652.
[45] ZHANG S, DENG G, LIU F, et al. Autocatalytic Delivery of Brain Tumor-targeting, Size-shrinkable Nanoparticles for Treatment of Breast Cancer Brain Metastases. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(14):1910651.
[46] SECRET E, KELLY SJ, CRANNELL KE, et al. Enzyme-responsive hydrogel microparticles for pulmonary drug delivery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(13):10313-10321.
[47] ZHANG X, WANG X, ZHONG W, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases-2/9-sensitive peptide-conjugated polymer micelles for site-specific release of drugs and enhancing tumor accumulation: preparation and in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11:1643-1661.
[48] RUAN S, CAO X, CUN X, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-sensitive size-shrinkable nanoparticles for deep tumor penetration and pH triggered doxorubicin release. Biomaterials. 2015;60:100-110.
[49] RUAN S, HU C, TANG X, et al. Increased Gold Nanoparticle Retention in Brain Tumors by in Situ Enzyme-Induced Aggregation. ACS Nano. 2016;10(11):10086-10098.
[50] PROETTO MT, CALLMANN CE, CLIFF J, et al. Tumor Retention of Enzyme-Responsive Pt(II) Drug-Loaded Nanoparticles Imaged by Nanoscale Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry and Fluorescence Microscopy. ACS Cent Sci. 2018;4(11):1477-1484.
[51] LI J, XIAO S, XU Y, et al. Smart Asymmetric Vesicles with Triggered Availability of Inner Cell-Penetrating Shells for Specific Intracellular Drug Delivery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(21):17727-17735.
[52] RUAN S, QIN L, XIAO W, et al. Acid-Responsive Transferrin Dissociation and GLUT Mediated Exocytosis for Increased Blood–Brain Barrier Transcytosis and Programmed Glioma Targeting Delivery. Adv Funct Mater, 2018;28(30):1802227.
[53] ANSELMO AC, MITRAGOTRI S. Nanoparticles in the clinic. Bioeng Transl Med. 2016;1(1):10-29.
[54] CHATTERJEE N, BIVONA TG. Polytherapy and Targeted Cancer Drug Resistance. Trends Cancer. 2019;5(3):170-182.
|