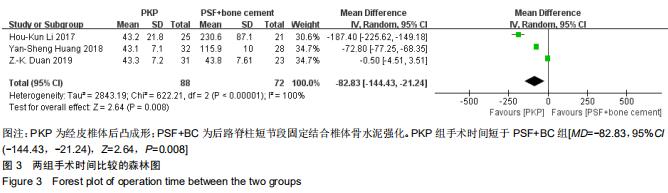
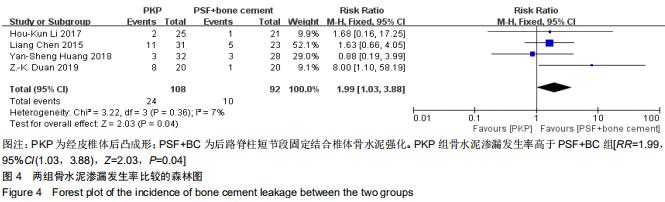
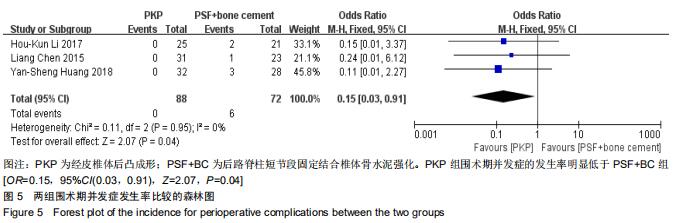
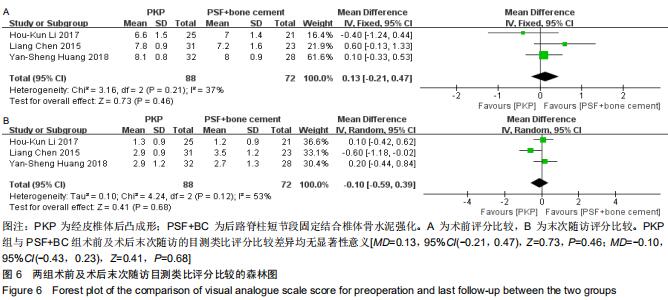
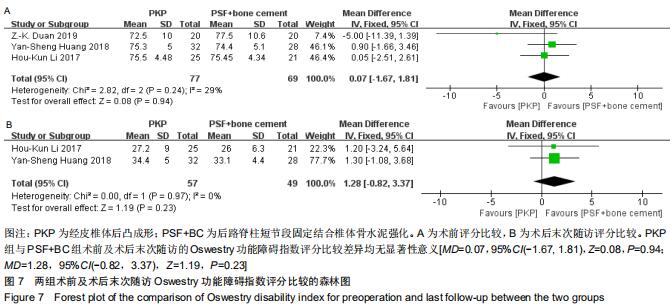
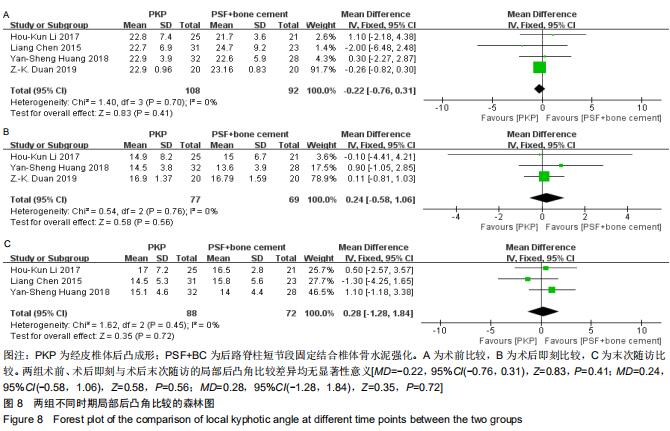
|
[1] KIM YC, KIM YH, HA KY. Pathomechanism of intravertebral clefts in osteoporotic compression fractures of the spine.Spine J. 2014;14:659-666.
[2] WANG G, YANG H, CHEN K. Osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with an intravertebral cleft treated by percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2010;92:1553-1557.
[3] FORMICA M, BASSO M, CAVAGNARO L,et al. Kümmell disease: illustrative case for definition criteria.Spine J. 2016;16(10):e707-e708.
[4] CHOU LH, KNIGH RQ. Idiopathic avascular necrosis of a vertebral body.Case report and literature review.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997; 22(16):1928-1932.
[5] FREEDMAN BA, HELLER JG. Kummel disease:a not-so-rare complication of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.J Am Board Fam Med.2009;22(1):75-78.
[6] JANG JS, KIM DY, LEE SH. Efficacy of percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of intravertebral pseudarthrosis associated with noninfected avascular necrosis of the vertebral body.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2003;28(14):1588-1592.
[7] PARK JW, PARK JH, JEON HJ, et al. Kümmell's Disease Treated with Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: Minimum 1 Year Follow-Up.Korean J Neurotrauma.2017;13(2):119-123.
[8] LI H, LIANG CZ, CHEN QX. Kümmell’s disease,an uncommon and complicated spinal disorder:a review.J Int Med Res. 2012;40(2):406-414.
[9] LU W, WANG L, XIE C, et al. Analysis of percutaneous kyphoplasty or short-segmental fixation combined with vertebroplasty in the treatment of Kummell disease.J Orthop Surg Res.2019;14(1):311.
[10] ZHANG X, HU W, YU J, et al. An effective treatment option for kümmell disease with neurological deficits:Modified transpedicular subtraction and disc osteotomy combined with long‑segment fixation.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2016;41(15):E923-930.
[11] RUAN J, GONG X, KONG J, et al. Effect of B vitamin (folate, B6, and B12) supplementation on osteoporotic fracture and bone turnover markers:A meta-analysis.Med Sci Monit.2015;21:875-881.
[12] CHEN GD, LU Q, WANG GL, et al. Percutaneous kyphoplasty for kümmell disease with severe spinal canal stenosis. Pain Physician. 2015;18(6):E1021-1028.
[13] MATZAROGLOU C, GEORGIOU CS, PANAGOPOULOS A, et al. Kümmell's disease:Clarifying the mechanisms and patients' inclusion criteria.Open Orthop J.2014;8:288-297.
[14] CHEN F, XIA YH, CAO WZ, et al. Percutaneous kyphoplasty for the treatment of spinal metastases.Oncol Lett.2016;11(3):1799-1806.
[15] LIU H, ZHANG J, LIANG X, et al. Distribution Pattern Making Sense:Patients Achieve Rapider Pain Relief with Confluent Rather Than Separated Bilateral Cement in Percutaneous Kyphoplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures.World Neurosurg. 2019;126:e1190-e1196.
[16] ZHANG Y, LIU H, HE F, et al. Safety and efficacy of percutaneous kyphoplasty assisted with O-arm navigation for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures at T6 to T9 vertebrae.Int Orthop.2020;44(2):349-355.
[17] NIU J, SONG D, ZHOU H, et al. Percutaneous Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures With Intravertebral Fluid or Air.Clin Spine Surg.2017;30(8):367-373.
[18] KAWAGUCHI S,HORIGOME K,YAJIMA H,et al.Symptomatic relevance of intravertebral cleft in patients with osteoporotic vertebral fracture.J Neurosurg Spine.2010;13(2):267-275.
[19] WEI P, YAO Q, XU Y, et al. Percutaneous kyphoplasty assisted with/without mixed reality technology in treatment of OVCF with IVC:a prospective study.J Orthop Surg Res.2019;14(1):255.
[20] SUDO H, ITO M, KANEDA K, et al. Anterior decompression and strut graft versus posterior decompression and pedicle screw fixation with vertebroplasty for osteoporotic thoracolumbar vertebral collapse with neurologic deficits.Spine J.2013;13(12):1726-1732.
[21] UCHIDA K, NAKAJIMA H, YAYAMA T, et al. Vertebroplasty-augmented short-segment posterior fixation of osteoporotic vertebral collapse with neurological deficit in the thoracolumbar spine: comparisons with posterior surgery without vertebroplasty and anterior surgery.J Neurosurg Spine.2010;13(5):612-621.
[22] WAGNER AL, BASKURT E. Refracture with cement extrusion following percutaneous vertebroplasty of large interbody cleft.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.2006;27(1):230-231.
[23] HUANG YS, HAO DJ, FENG H, et al. Comparison of Percutaneous Kyphoplasty and Bone Cement-Augmented Short-Segment Pedicle Screw Fixation for Management of Kümmell Disease.Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:1072-1079.
[24] LI HK, HAO DJ, YANG JS, et al. Percutaneous kyphoplasty versus posterior spinal fixation with vertebroplasty for treatment of Kümmell disease.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(51):e9287.
[25] DUAN ZK, ZOU JF, HE XL, et al. Bone-filling mesh container versus percutaneous kyphoplasty in treating Kümmell’s disease.Arch Osteoporos.2019;14(1):109.
[26] CHEN L, DONG R, GU Y, et al. Comparison between Balloon Kyphoplasty and Short Segmental Fixation Combined with Vertebroplasty in the Treatment of Kümmell’s Disease.Pain Physician. 2015;18(4):373-381.
[27] WANG G, YANG H, MENG B, et al. Post-traumatic osteoporotic vertebral osteonecrosis treated using balloon kyphoplasty.Clin Neurosci. 2011;18(5):664-668.
[28] WU AM, CHI YL, NI WF. Vertebral compression fracture with intravertebral vacuum cleft sign: Pathogenesis,image,and surgical intervention.Asian Spine J.2013;7(2):148-155.
[29] PFLUGMACHER R, SCHROEDER RJ, KLOSTERMANN CK. Incidence of adjacent vertebral fractures in patients treated with balloon kyphoplasty:Two years' prospective follow-up.Acta Radiol. 2006;47(8):830-840.
[30] XIA YH, CHEN F, ZHANG L, et al. Percutaneous kyphoplasty treatment evaluation for patients with Kümmell disease based on a two‑year follow‑up.Exp Ther Med.2018;16(4):3617-3622.
[31] PIAO M, DARWONO AB, ZHU K, et al. Extrapendicular Approach of Unilateral Percutaneous Vesselplasty for the Treatment of Kummell Disease.Int J Spine Surg.2019;13(2):199-204.
[32] 王小刚,杨 彬,王亚寒,等.单侧穿刺椎体成形术治疗Kummell病的疗效观察[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(1):86-88.
[33] 蒋杰,张勇.单侧穿刺经皮椎体后凸成形与椎体成形骨水泥注射治疗Kummell病的对比[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(22):3481-3487.
[34] WANG H, DING W. Posterior Vertebral Column Resection Through Unilateral Osteotomy Approach for Old Lumbar Fracture Combined with Kummell Disease.World Neurosurg.2018;109:147-151.
[35] LEE SH, CHO DC, SUNG JK. Catastrophic intramedullary hematoma following Kümmell’s disease with large intravertebral cleft.Spine J. 2008;8(6):1007-1010.
[36] LEE SH, KIM ES, EOH W. Cement augmented anterior reconstruction with short posterior instrumentation:A less invasive surgical option for Kümmell’s disease with cord compression.J Clin Neurosci. 2011;18(4): 509-514.
[37] HUANG YS, GE CY, FENG H, et al. Bone Cement-Augmented Short-Segment Pedicle Screw Fixation for Kümmell Disease with Spinal Canal Stenosis.Med Sci Monit.2018;24:928-935.
[38] HUANG Y, PENG M, HE S, et al. Clinical efficacy of percutaneous kyphoplasty at the hyperextension position for the treatment of osteoporotic Kümmell disease.Clin Spine Surg.2016;29(4):161-166.
[39] WANG W, LIU Q, LIU WJ, et al. Different Performance of Intravertebral Vacuum Clefts in Kümmell's Disease and Relevant Treatment Strategies. Orthop Surg.2020;12(1):199-209.
[40] ZHANG GQ, GAO YZ, ZHENG J, et al. Posterior decompression and short segmental pedicle screw fixation combined with vertebroplasty for Kümmell’s disease with neurological deficits. Exp Ther Med. 2013; 5(2):517-522.
[41] YANG DL, YANG SD, CHEN Q, et al. The treatment evaluation for osteoporotic Kümmell disease by modified posterior vertebral column resection:Minimum of one-year follow-up.Med Sci Monit. 2017;23: 606-612.
[42] WANG F, WANG D, TAN B, et al. Comparative study of modified posterior operation to treat Kümmell’s disease.Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(39):e1595.
[43] LIM J, CHOI SW, YOUM JY, et al. Posttraumatic Delayed Vertebral Collapse:Kummell’s Disease.J Korean Neurosurg Soc.2018;61(1):1-9.
|