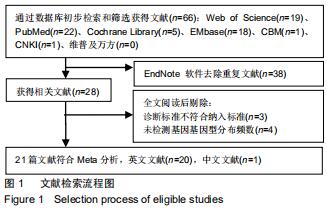
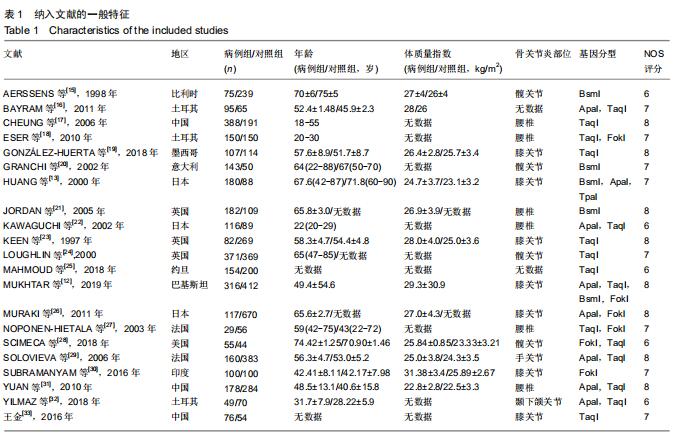
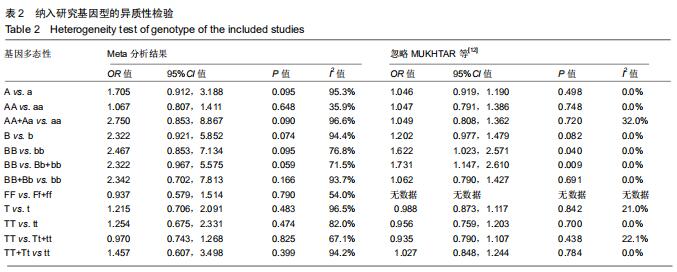
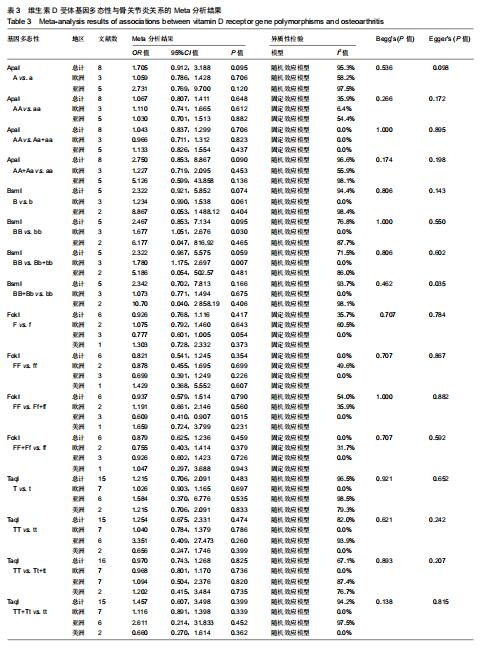
|
[1] KRAUS VB, BLANCO FJ, ENGLUND M, et al. Call for standardized definitions of osteoarthritis and risk stratification for clinical trials and clinical use.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(8): 1233-1241.
[2] CROSS M, SMITH E, HOY D, et al. The global burden of hip and knee osteoarthritis: estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis.2014;73(7):1323-1330.
[3] BORTOLUZZI A, FURINI F. Osteoarthritis and its management Epidemiology, nutritional aspects and environmental factors. Autoimmun Rev.2018;17(11):1097-1104.
[4] O'NEILL TW, MCCABE PS. Update on the epidemiology, risk factors and disease outcomes of osteoarthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2018;32(2):312-326.
[5] GENG R, XU Y, HU W. The association between MMP-1 gene rs1799750 polymorphism and knee osteoarthritis risk.Biosci Rep. 2018;38(5).pii: BSR20181257.
[6] BAI Y, GAO S, LIU Y, et al. Correlation between Interleukin-17 gene polymorphism and osteoarthritis susceptibility in Han Chinese population. BMC Med Genet.2019;20(1):20.
[7] COLOMBINI A, CAUCI S, LOMBARDI G, et al. Relationship between vitamin D receptor gene (VDR) polymorphisms, vitamin D status, osteoarthritis and intervertebral disc degeneration. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.2013;138():24-40.
[8] WANG Y, WACTAWSKI-WENDE J, SUCHESTON-CAMPBELL LE, et al. The influence of genetic susceptibility and calcium plus vitamin D supplementation on fracture riskAm J Clin Nutr. 2017; 105(4):970-979.
[9] IOM. Dietary Refence Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D.The National Academies Press:Washington,DC,USA.2011.
[10] CHRISTAKOS S, DHAWAN P, VERSTUYF A, et al. Vitamin D: Metabolism, Molecular Mechanism of Action, and Pleiotropic Effects. Physiol Rev.2016;96(1):365-408.
[11] Colombini A, Cauci S, Lombardi G, et al. Relationship between vitamin D receptor gene (VDR) polymorphisms, vitamin D status, osteoarthritis and intervertebral disc degeneration.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013; 138:24-40.
[12] MUKHTAR M, SHEIKH N, SUQAINA SK, et al. Vitamin D Receptor Gene Polymorphism: An Important Predictor of Arthritis Development. BioMed Res Int.2019;2019:8326246.
[13] HUANG J, USHIYAMA T, INOUE K, et al. Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and osteoarthritis of the hand,hip,and knee: acase-control study in Japan.Rheumatology(Oxford, England). 2000; 39(1):79-84.
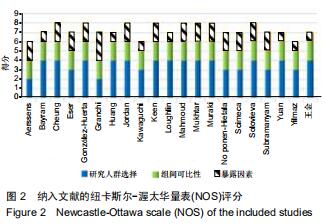
[14] 曾宪涛,刘慧,陈曦,等.Meta分析系列之四:观察性研究的质量评价工具[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2012,4(4):297-299.
[15] AERSSENS J, DEQUEKER J, PEETERS J, et al. Lack of association between osteoarthritis of the hip and gene polymorphisms of VDR, COL1A1, and COL2A1 in postmenopausal women. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41(11):1946-1950.
[16] BAYRAM B, SAYIN BE, TÜRKOĞLU Z, et al. An Investigation Into the Relationship Between Taq1 and Apa1 Polymorphisms of the Vitamin D Receptor Gene and the Development of Osteoarthritis.Turk J Rheumatol. 2011;26(4):303-307.
[17] CHEUNG KM, CHAN D, KARPPINEN J, et al. Association of the Taq I allele in vitamin D receptor with degenerative disc disease and disc bulge in a Chinese population.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(10): 1143-1148.
[18] ESER B, CORA T, ESER O, et al. Association of the polymorphisms of vitamin D receptor and aggrecan genes with degenerative disc disease. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers.2010; 14(3):313-317.
[19] GONZÁLEZ-HUERTA NC, BORGONIO-CUADRA VM, MORALES-HERNÁNDEZ E, et al. Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and susceptibility for primary osteoarthritis of the knee in a Latin American population.Null.2018;58(1):6.
[20] GRANCHI D, STEA S, SUDANESE A, et al. Association of two gene polymorphisms with osteoarthritis secondary to hip dysplasia.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2002;(403):108-117.
[21] JORDAN KM, SYDDALL H, DENNISON EM, et al. Birthweight, vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism, and risk of lumbar spine osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol.2005;32(4):678-683.
[22] KAWAGUCHI Y, KANAMORI M, ISHIHARA H, et al. The association of lumbar disc disease with vitamin-D receptor gene polymorphism. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2002;84-A(11):2022-2028.
[23] KEEN RW, HART DJ, LANCHBURY JS. Association of early osteoarthritis of the knee with a Taq I polymorphism of the vitamin D receptor gene.Arthritis Rheum.1997;40(8):1444-1449.
[24] LOUGHLIN J, SINSHEIMER JS, MUSTAFA Z, et al. Association analysis of the vitamin D receptor gene, the type I collagen gene COL1A1, and the estrogen receptor gene in idiopathic osteoarthritis.J Rheumatol.2000;27(3):779-784.
[25] MAHMOUD SAAH, ATOUM MF, AL-HOURANI HM, et al. Vitamin D deficiency and rs731236(taq1) vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism as possible risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.Acta Medica Mediterranea.2018;34:209.
[26] MURAKI S, DENNISON E, JAMESON K, et al. Association of vitamin D status with knee pain and radiographic knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2011;19(11):1301-1306.
[27] NOPONEN-HIETALA N, KYLLÖNEN E, MÄNNIKKÖ M, et al. Sequence variations in the collagen IX and XI genes are associated with degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2003; 62(12):1208-1214.
[28] SCIMECA M, CENTOFANTI F, CELI M, et al. Vitamin D Receptor in Muscle Atrophy of Elderly Patients: A Key Element of Osteoporosis-Sarcopenia Connection.Aging Dis.2018;9(6): 952-964.
[29] SOLOVIEVA S, HIRVONEN A, SIIVOLA P, et al. Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and susceptibility of hand osteoarthritis in Finnish women.Arthritis Res Ther.2006;8(1):R20.
[30] SUBRAMANYAM K, POORNIMA S, JUTURU KK, et al. Missense FokI variant in the vitamin D receptor gene in primary knee osteoarthritis patients in south Indian population.Gene Rep.2016; 4:118-122.
[31] YUAN HY, TANG Y, LIANG YX, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-3 and vitamin d receptor genetic polymorphisms, and their interactions with occupational exposure in lumbar disc degeneration. J Occup Health. 2010;52(1):23-30.
[32] YILMAZ AD, YAZICIOGLU D, TÜZÜNER ÖNCÜL AM, et al. Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms (Apa1 and Taq1) in temporomandibular joint internal derangement/osteoarthritis in a group of Turkish patients. Mol BiolRep.2018;45(6):1839-1848.
[33] 王金.阳虚质膝骨性关节炎忠者COL2A和VDR基因多态性研究[D].兰州:甘肃中医药大学,2016.
[34] HUNG M, BOUNSANGA J, VOSS MW, et al. Dietary and Supplemental Vitamin C and D on Symptom Severity and Physical Function in Knee Osteoarthritis.J Nutr Gerontol Geriatr. 2017;36(2-3): 121-133.
[35] MANOY P, YUKTANANDANA P, TANAVALEE A, et al. Vitamin D Supplementation Improves Quality of Life and Physical Performance in Osteoarthritis Patients.Nutrients.2017;9(8).pii: E799.
[36] HAUSSLER MR, WHITFIELD GK, HAUSSLER CA, et al. The nuclear vitamin D receptor: biological and molecular regulatory properties revealed.J Bone Miner Res.1998;13(3):325-349.
[37] SANGHI D, SRIVASTAVA RN, RAJ S, et al. Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms modulate the clinicoradiological response to vitamin D supplementation in knee osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014; 22:S235-S236.
[38] LI J, JIN D, FU S, et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 modulates osteoblast differentiation via interaction with vitamin D receptor.Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2013;436(4):632-637.
[39] STARCZAK Y, REINKE DC, BARRATT KR, et al. Absence of vitamin D receptor in mature osteoclasts results in altered osteoclastic activity and bone loss.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2018;177:77-82.
[40] MOSAAD YM, HAMMAD EM, FAWZY Z, et al. Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism as possible risk factor in rheumatoid arthritis and rheumatoid related osteoporosis.Human Immunol. 2014; 75(5):452-461.
[41] ZHANG L, YIN X, WANG J, et al. Associations between VDR Gene Polymorphisms and Osteoporosis Risk and Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women: A systematic review and Meta-Analysis.Sci Rep.2018;8(1):981.
[42] TETLOW LC, WOOLLEY DE. Expression of vitamin D receptors and matrix metalloproteinases in osteoarthritic cartilage and human articular chondrocytes in vitro.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001;9:423-431.
[43] BAHAT G, SAKA B, ERTEN N, et al. BsmI polymorphism in the vitamin D receptor gene is associated with leg extensor muscle strength in elderly men.Aging Clin Exp Res.2010;22(3):198-205.
[44] UITTERLINDEN AG, BURGER H, VAN DUIJN CM, et al. Adjacent genes, for COL2A1 and the vitamin D receptor, are associated with separate features of radiographic osteoarthritis of the knee. Arthritis Rheum.2000;43(7):1456-1464.
[45] LIU H, HE H, LI S, et al. Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and risk of osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis.Exp Biol Med(Maywood). 2014; 239(5):559-567.
[46] ZHU ZH, JIN XZ, ZHANG W, et al. Associations between vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and osteoarthritis: an updated meta-analysis.Rheumatology (Oxford,England). 2014;53(6): 998-1008.
|