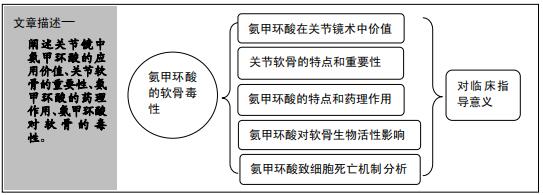
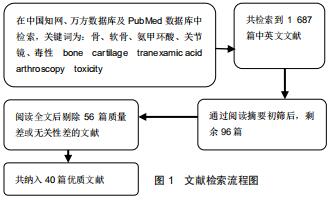
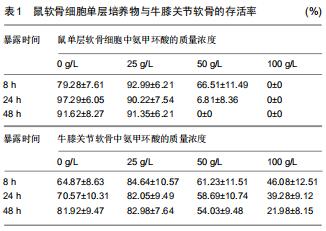
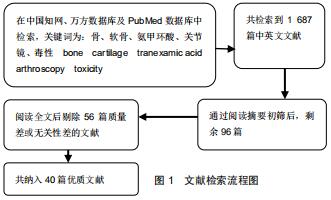
|
[1] CAI J, RIBKOFF J, OLSON S, et al. The many roles of tranexamic acid: An overview of the clinical indications for TXA in medical and surgical patients.Eur J Haematol. 2020; 104(2):79-87.
[2] 王鑫瑞,王涛,张志强.全膝关节置换围置换期氨甲环酸的临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(44):7188-7192.
[3] CHEN TP, CHEN YM, JIAO JB, et al. Comparison of the effectiveness and safety of topical versus intravenous tranexamic acid in primary total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Orthop Surg Res.2017;12(1):11-13.
[4] ZHANG P, LIANG Y, CHEN P, et al. Intravenous versus topical tranexamic acid in primary total hip replacement: A meta-analysis.Medicine.2016;95(50):5573-5576.
[5] 陈廷玉,蔡霖,王春风,等.老年人全膝关节置换围术期使用氨甲环酸对术后深静脉血栓形成发生率的影响[J].中国老年学杂志, 2019,39(14):3425-3428.
[6] 毕建静,唐晨.玻璃酸钠关节腔注射配合物理疗法治疗部队训练致急性期半月板损伤疗效观察[J].中国疗养医学,2017,26(9): 920-921.
[7] 殷铭.玻璃酸钠用于膝关节半月板损伤关节镜治疗术后近期疗效分析[J].中外医学研究,2017,15(31):16-17.
[8] 李飞龙,秦磊磊,胡宁,等.前交叉韧带重建的研究进展[J].骨科, 2018,9(1):79-84.
[9] 曾昭池,郭中凯,朱志勇,等.关节镜辅助内侧副韧带浅层松解联合玻璃酸钠注射液对内侧半月板损伤修复效果分析[J].中国医学前沿杂志,2017,9(12):84-88.
[10] CHIANG ER, CHEN KH, WANG ST, et al. Intra-articular Injection of Tranexamic Acid Reduced Postoperative Hemarthrosis in Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Prospective Randomized Study. Arthroscopy. 2019;35(7):2127-2132.
[11] 李明晋,陈小华,唐晓莉,等.膝关节腔注射氨甲环酸对单纯半月板损伤患者关节肿胀、疼痛、关节功能恢复的影响[J].中国药房, 2018,29(8):1098-1101.
[12] CHOI E, LEE J, LEE S, et al. Potential therapeutic application of small molecule with sulfonamide for chondrogenic differentiation and articular cartilage repair.Bioorg Med Chem Lett.2016;26(20):5098-5102.
[13] LIU C, MA X, LI T, et al. Kartogenin, transforming growth factor-beta1 and bone morphogenetic protein-7 coordinately enhance lubricin accumulation in bone-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Biol Int.2015;39(9):1026-1035.
[14] CARBALLO CB, NAKAGAWA Y, SEKIYA I, et al. Basic Science of Articular Cartilage.Clin Sports Med.2017;36: 413-425.
[15] HALL AC.The Role of Chondrocyte Morphology and Volume in Controlling Phenotype-Implications for Osteoarthritis, Cartilage Repair, and Cartilage Engineering.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2019;21(8):38-40.
[16] HUEY DJ, HU JC, ATHANASIOU KA. Unlike bone, cartilage regeneration remains elusive.Science. 2012;338(6109): 917-921.
[17] ROSOWSKI M, FALB M, TSCHIRSCHMANN M, et al. Initiation of mesenchymal condensation in alginate hollow spheres--a useful model for understanding cartilage repair. Artif Organs. 2006;30(10):775-784.
[18] OKAMOTO S, OKAMOTO U. Amino-methyl-cyclohexane- carboxylic acid: AMCHA. A new potent inhibitor of the fibrinolysis Keio.J Med. 1962;26(8):105-115.
[19] MAHDY AM, WEBSTER NR. Perioperative systemic haemostatic agents.Br J Anaesth.2004;93(6):842-858.
[20] GANDHI R, EVANS HM, MAHOMED SR, et al. Tranexamic acid and the reduction of blood loss in total knee and hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis.BMC Res Notes. 2013;6: 184-187.
[21] FILLINGHAM YA, RAMKUMAR DB, JEVSEVAR DS, et al. The Safety of Tranexamic Acid in Total Joint Arthroplasty: A Direct Meta-Analysis.J Arthroplasty.2018;33(10):3070-3082.
[22] GIANAKOS AL, HURLEY ET, HARING RS, et al. Reduction of Blood Loss by Tranexamic Acid Following Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty: A Meta-Analysis.JBJS Rev.2018;6(5):748-754.
[23] CHUNG LH, CHEN WM, CHEN CF. Deep vein thromhosis after total kneearthroplasty in asian patients without prophylactic anticoagulation.Orthopedics.2011;34(1):15-19.
[24] COLWELL CW JR. Rationale for thromboprophylaxis in lower joint arthroplasty.Am J Orthop. 2007;36(9):11-13.
[25] PARKER MJ. Iron supplementation for anemia after hip fracture surgery: a randomized trial of 300 patients.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2010;92(2):265-269.
[26] KALAVROUZIOTIS D, VOISINE P, MOHAMMADI S, et al. High-dose tranexamic acid is an independent predictor of early seizure after cardiopulmonary bypass.Ann Thorac Surg. 2012;93(1):148-154.
[27] MURKIN JM, FALTER F, GRANTON J, et al. High-dose tranexamic Acid is associated with nonischemic clinical seizures in cardiac surgical patients.Anesth Analg.2010; 110(2):350-353.
[28] KOSTER A, BÖRGERMANN J, ZITTERMANN A, et al. Moderate dosage of tranexamic acid during cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass and convulsive seizures: incidence and clinical outcome.Br J Anaesth.2013;110(1): 34-40.
[29] BREUER T, MARTIN K, WILHELM M, et al. The blood sparing effect and the safety of aprotinin compared to tranexamic acid in paediatric cardiac surgery.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2009; 35(1):167-171.
[30] 张少云,肖聪,裴福兴.氨甲环酸在创伤骨科手术中应用的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2019,33(11):1457-1461.
[31] 施林军,曹扬,姜丹生.不同剂量氨甲环酸对初次全髋关节置换失血量的影响[J].临床骨科杂志,2015,18(4):437-439.
[32] 徐飞,杨阳,王合围,等.氨甲环酸关节腔内注射对全膝关节置换患者治疗效果的影响[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2019,18(21): 2316-2319.
[33] FELLI L, REVELLO S, BURASTERO G, et al. Single Intravenous Administration of Tranexamic Acid in Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction to Reduce Postoperative Hemarthrosis and Increase Functional Outcomes in the Early Phase of Postoperative Rehabilitation: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Arthroscopy.2019;35(1):149-157.
[34] SIEGEL MG. The Dangers and Concerns of Intra-articular Tranexamic Acid.Arthroscopy. 2019;35(11):2973-2974.
[35] GOBBI RG, GIGLIO PN, HELITO CP, et al. Regarding "Intra-articular Injection of Tranexamic Acid Reduced Postoperative Hemarthrosis in Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Prospective Randomized Study". Arthroscopy.2019;35(11):2974-2975.
[36] TUTTLE JR, FELTMAN PR, RITTERMAN SA, et al. Effects of Tranexamic Acid Cytotoxicity on In Vitro Chondrocytes.Am J Orthop.2015;44(12):497-502.
[37] AMBRA LF, DE GIROLAMO L, NIU W, et al. No effect of topical application of tranexamic acid on articular cartilage. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2019;27(3):931-935.
[38] PARKER JD, LIM KS, KIESER DC, et al. Is tranexamic acid toxic to articular cartilage when administered topically? What is the safe dose?Bone Joint J.2018;100(3):404-412.
[39] GODERECCI R, GIUSTI I, NECOZIONE S, et al. Short exposure to tranexamic acid does not affect, in vitro, the viability of human chondrocytes.Eur J Med Res. 2019;24(1): 15-17.
[40] MCLEAN M, MCCALL K, SMITH IDM, et al. Tranexamic acid toxicity in human periarticular tissues. Bone Joint Res. 2019; 8(1):11-18.
|