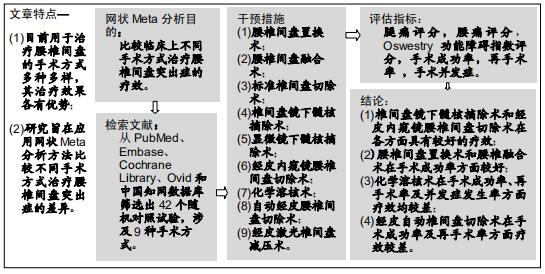
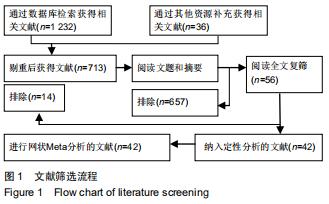
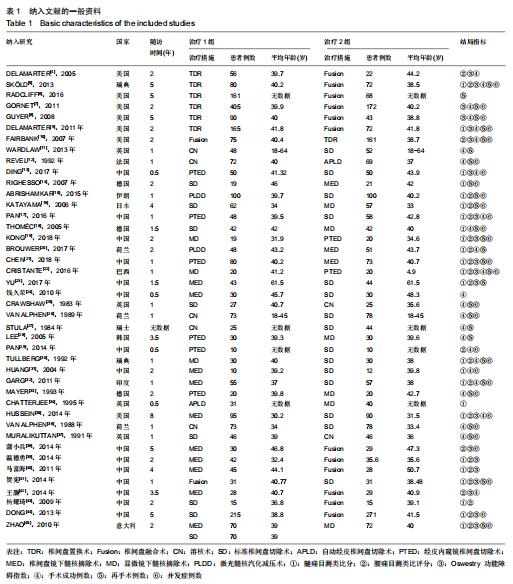
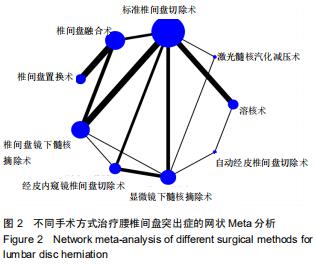
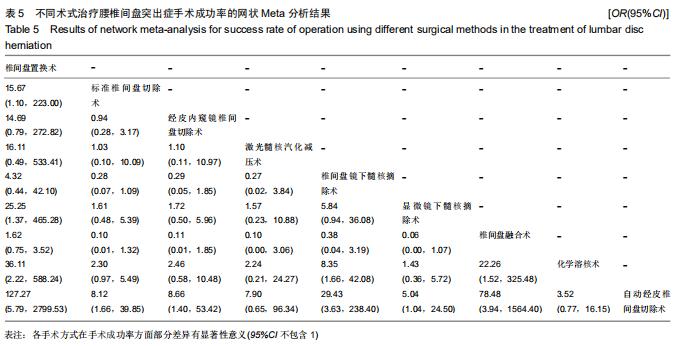
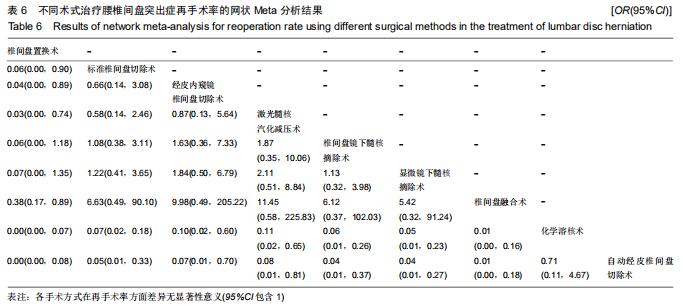
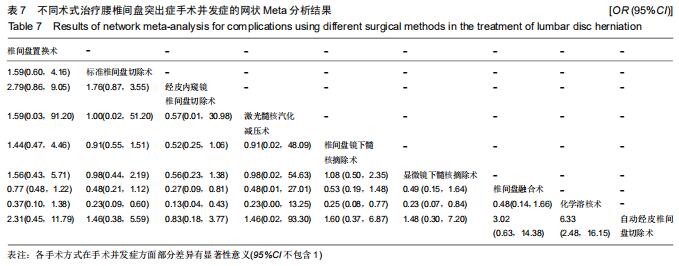
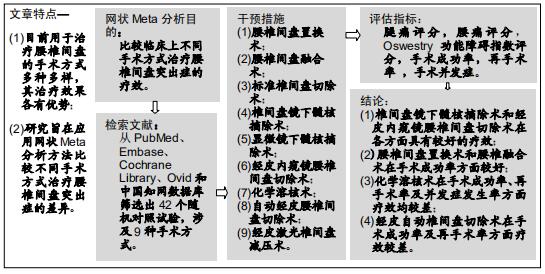
|
[1] 易军飞,陈通,刘友军.腰椎间盘突出手术治疗的进展[J].现代医学与健康研究电子杂志,2017,1(9):135-137.
[2] 冯帆,蔡毅,李颖波,等.腰椎间盘突出症7种手术修复方式差异的网络Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(3):453-459.
[3] 刘国伟,于莉莉,贾洪霞,等.系统评价中的间接比较与网状Meta分析方法研究进展[J].中国循证医学杂志,2014,14(10):1276-1280.
[4] DELAMARTER RB, BAE HW, PRADHAN BB. Clinical results of ProDisc-II lumbar total disc replacement: Report from the United States clinical trial.Orthop Clin North Am.2005;36(3):301-313.
[5] SKÖLD C, TROPP H, BERG S. Five-year follow-up of total disc replacement compared to fusion: A randomized controlled trial.Eur Spine J.2013;22(10):2288-2295.
[6] RADCLIFF K, SPIVAK J, DARDEN B, et al. Five-Year Reoperation Rates of 2-Level Lumbar Total Disk Replacement Versus Fusion.Clin Spine Surg.2018;31(1):37-42.
[7] GORNET MF, BURKUS JK, DRYER RF, et al. Lumbar disc arthroplasty with MAVERICK disc versus stand-alone interbody fusion: A prospective, randomized, controlled, multicenter investigational device exemption trial.Spine.2011;36(25):E1600-E1611.
[8] GUYER RD, MCAFEE PC, BANCO RJ, et al.Prospective, randomized, multicenter Food and Drug Administration investigational device exemption study of lumbar total disc replacement with the CHARITÉ artificial disc versus lumbar fusion: Five-year follow-up.Spine J. 2009;9(5):374-386.
[9] DELAMARTER R, ZIGLER JE, BALDERSTON RA, et al. Prospective, randomized, multicenter food and drug administration investigational device exemption study of the ProDisc-L total disc replacement compared with circumferential arthrodesis for the treatment of two-level lumbar degenerative disc disease: Results at twenty-four months.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2011;93(8):705-715.
[10] ZIGLER J, DELAMARTER R, SPIVAK JM, et al. Results of the prospective, randomized, multicenter Food and Drug Administration investigational device exemption study of the ProDisc-L total disc replacement versus circumferential fusion for the treatment of 1-level degenerative disc disease.Spine.2007;32:1155-1162.
[11] WARDLAW D, RITHCHIE IK, SABBOUBEH AF, et al. Prospective randomized trial of chemonucleolysis compared with surgery for soft disc herniation with 1-year, intermediate, and long-term outcome: part I: the clinical outcome.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2013;38(17):E1051-1057.
[12] REVEL M, PAYAN C, VALLEE C, et al.Automated percutaneous lumbar discectomy versus chemonucleolysis in the treatment of sciatica.A randomized multicenter trial.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1993;18(1):1-7.
[13] DING ZM, TAO YQ. Clinical outcomes of percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy versus fenestration discectomy in patients with lumbar disc herniation. J Transl Med.2017;5(1):29-33.
[14] RIGHESSO O, FALAVIGNA A, AVANZI O. Comparison of open discectomy with microendoscopic discectomy in lumbar disc herniations: results of a randomized controlled trial. Neurosurgery. 2007;61(3):545-549; discussion 549.
[15] ABRISHAMKAR S, KOUCHAKZADEH M, MIRHOSSEINI A, et al. Comparison of open surgical discectomy versus plasma-laser nucleoplasty in patients with single lumbar disc herniation. J Res Med Sci.2015;20(12):1133-1137.
[16] KATAYAMA Y, MATSUYAMA Y, YOSHIHARA H, et al. Comparison of surgical outcomes between macro discectomy and micro discectomy for lumbar disc herniation: a prospective randomized study with surgery performed by the same spine surgeon.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2006;19(5):344-347.
[17] PAN Z, HA Y, YI S, et al. Efficacy of Transforaminal Endoscopic Spine System (TESSYS) Technique in Treating Lumbar Disc Herniation.Med Sci Monit.2016;22:530-539.
[18] THOMÉC, BARTH M, SCHARF J, et al. Outcome after lumbar sequestrectomy compared with microdiscectomy: a prospective randomized study.J Neurosurg Spine.2005;2(3):271-278.
[19] KONG L, SHANG XF, ZHANG WZ, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy and microsurgical laminotomy : a prospective, randomized controlled trial of patients with lumbar disc herniation and lateral recess stenosis.Orthopade.2019;48(2):157-164.
[20] BROUWER PA, BRAND R, VAN DEN AKKER-VAN MARLE ME, et al. Percutaneous laser disc decompression versus conventional microdiscectomy for patients with sciatica: Two-year results of a randomised controlled trial.Interv Neuroradiol.2017;23(3):313-324.
[21] CHEN Z, ZHANG L, DONG J, et al. Percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy compared with microendoscopic discectomy for lumbar disc herniation: 1-year results of an ongoing randomized controlled trial.J Neurosurg Spine.2018;28(3):300-310.
[22] CRISTANTE AF, ROCHA ID, MARTUSMARCON R, et al.Randomized clinical trial comparing lumbar percutaneous hydrodiscectomy with lumbar open microdiscectomy for the treatment of lumbar disc protrusions and herniations.Clinics(Sao Paulo).2016;71(5):276-280.
[23] YU D, WANG G, WEI Y, et al. The effect of posterior microendoscopy discectomy and open surgery on lumbar disc herniation.BIOMED RES-INDIA.2017;28(20):8874-8877.
[24] 钱久荣,华锦明,钱忠来,等.微创与椎板开窗技术治疗腰椎间盘突出症临床疗效比较[J].中国全科医学,2010,13(30):3431-3433.
[25] CRAWSHAW C, FRAZER AM, MERRIAM WF. A comparison of surgery and chemonucleolysis in the treatment of sciatica. A prospective randomized trial.Spine.1984;9(2):195-198.
[26] VAN ALPHEN HAM, BRAAKMAN R, BEZEMER PD, et al. Chemonucleolysis versus discectomy: a randomized multicenter trial.J Neurosurg.1989;70(6):869-875.
[27] STULA D. Chemonucleolysis with chymopapain in intervertebral disc hernia. A randomised comparative study of patients following surgery.Neurochirurgia(Stuttg).1990;33(5):169-172.
[28] LEE SH, CHUNG SE, AHN Y, et al. Comparative radiologic evaluation of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy and open microdiscectomy: A matched cohort analysis. Mt Sinai J Med. 2006; 73(5):795-801.
[29] PAN L. Comparison of tissue damages caused by endoscopic lumbar discectomy and traditional lumbar discectomy: a randomised controlled trial. Int J Surg.2014;12(5):534-537.
[30] TULLBERG T, ISACSON J, WEIDENHIELM L. Does microscopic removal of lumbar disc herniation lead to better results than the standard procedure? Results of a one-year randomized study.Spine. 1993;18(1):24-27.
[31] HUANG TJ, HSU RWW, LI YY, et al. Less systemic cytokine response in patients following microendoscopic versus open lumbar discectomy. J Orthop Res.2005;23(2):406-411.
[32] GARG B, NAGRAJA UB, JAYASWAL A. Microendoscopic versus open discectomy for lumbar disc herniation: a prospective randomised study. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong).2011;19(1):30-34.
[33] MAYER HM, BROCK M. Percutaneous endoscopic discectomy: surgical technique and preliminary results compared to microsurgical discectomy.J Neurosurg.1993;78(2):216-225.
[34] CHATTERJEE S, FOY P, FINDLAY G.. Report of a Controlled Clinical Trial Comparing Automated Percutaneous Lumbar Discectomy and Microdiscectomy in the Treatment of Contained Lumbar Disc Herniation. Spine.1995;20(6):734-738.
[35] HUSSEIN M, ABDELDAYEM A, MATTAR MMM. Surgical technique and effectiveness of microendoscopic discectomy for large uncontained lumbar disc herniations: A prospective, randomized, controlled study with 8 years of follow-up.Eur Spine J.2014;23(9):1992-1999.
[36] VAN ALPHEN HA, BRAAKMAN R, BERFELO MW, et al. Chemonucleolysis or discectomy? Results of a randomized multicentre trial in patients with a herniated lumbar intervertebral disc (a preliminary report). Acta Neurochir Suppl(Wien). 1988;43:35-38.
[37] MURALIKUTTAN KP, HAMILTON A, KERNOHAN WG, et al. A prospective randomized trial of chemonucleolysis and conventional disc surgery in single level lumbar disc herniation.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1992;17(4):381-387.
[38] 蒲小兵,周强,杨双石,等.MED与微创TLIF治疗伴Modic改变的腰椎间盘突出症的对比研究[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2014,6(2):79-83.
[39] 温德勇.不同手术方式治疗腰椎间盘突出伴Modic改变的临床疗效研究[J].中国实用医药,2014,9(23):18-19.
[40] 马富海,吴小涛,洪鑫,等.不同术式治疗伴终板Modic改变的腰椎椎间盘突出症的疗效分析[J].脊柱外科杂志,2011,9(2):69-73.
[41] 贺宪,黄东生,梁安靖,等.椎体间融合术与单纯髓核摘除术治疗合并Modic Ⅱ型改变的单节段腰椎间盘突出症的疗效比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2014,24(11):1007-1012.
[42] 王灏.伴终板Modic改变腰椎间盘突出症术式选择及其对疗效的影响研究[J].长治医学院学报,2014,28(3):210-212.
[43] 杨耀琦,曹鹏,潘玉涛,等.伴终板改变的腰椎间盘突出症的手术方式选择[J].中华医学杂志,2009,89(27):1902-1906.
[44] DONG Z, DENG SC, YI M, et al. Surgical options and clinical outcomes in patients of lumbar disc herniation with Modic changes. Zhonghua yi xue za zhi.2013;93(39):3111-3115.
[45] ZHAO D, DENG SC, MA Y, et al. Higher risk of dural tears and recurrent herniation with lumbar micro-endoscopic discectomy.Eur Spine J.2010;19(3):443-450.
[46] 黄振强,罗玉琛.腰椎间盘突出与下腰痛的关系[J].海南医学,2003,14(8): 12-13.
[47] SHI R, WANG F, HONG X, et al. Comparison of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy versus microendoscopic discectomy for the treatment of lumbar disc herniation: a meta-analysis.Int Orthop. 2019;43(4):923-937.
[48] ZIGLER J, FERKO N, CAMERON C, et al. Comparison of therapies in lumbar degenerative disc disease: A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Comp Eff Res.2018;7(3):233-246.
[49] JENNER JR, BUTTLE DJ, DIXON AK. Mechanism of action of intradiscal chymopapain in the treatment of sciatica: A clinical, biochemical, and radiological study.Ann Rheum Dis. 1986;45(6): 441-449.
|