中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (32): 5133-5137.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2861
• 脊柱组织构建 spinal tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
内镜下行单、双侧减压修复对侧症状型腰椎间盘突出症的优效性比较
王秋安,袁 峰,吴继彬,孙玛骥,吴东迎,孟 强,郭开今
- 徐州医科大学附属医院骨科,江苏省徐州市 221002
Endoscopic unilateral versus bilateral decompression effects on lumbar disc herniation with contralateral symptoms
Wang Qiuan, Yuan Feng, Wu Jibin, Sun Maji, Wu Dongying, Meng Qiang, Guo Kaijin
- Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
腰椎间盘突出症:是常见的脊柱疾患,主要是因为腰椎间盘各部分在有不同程度退行性改变后,在外力因素或其他因素的作用下,椎间盘的纤维环破裂,髓核等组织从破裂之处突出(或脱出)于后方或椎管内,导致相邻脊神经根受刺激或压迫,从而产生腰部疼痛,以及一侧下肢或双下肢麻木、疼痛等一系列临床症状。
内镜下(经皮椎间孔镜下)腰椎髓核摘除手术:与传统手术相比具有创伤小、恢复快、安全可靠等特点,现已越来越广泛的应用于腰椎间盘突出症的治疗。
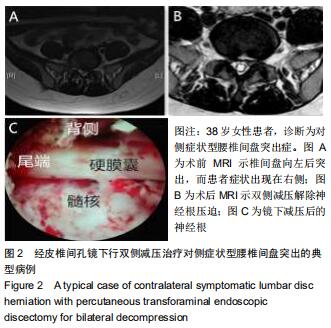
背景:腰椎间盘突出症多为突出部分压迫一侧神经根引起同侧神经根受压症状,一侧腰椎间盘突出而对侧出现症状的病例在临床上并不多见,因此对于此类腰椎间盘突出症目前尚无特定的分型及命名,文中将其称为“对侧症状腰椎间盘突出症”。
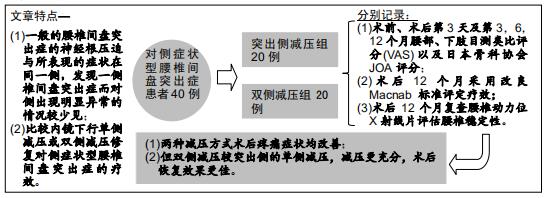
目的:探讨在内镜下椎间孔入路腰椎髓核摘除术治疗对侧症状腰椎间盘突出症患者,行单侧或双侧减压的疗效对比。
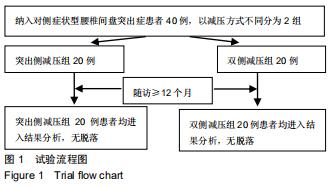
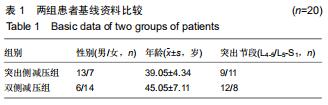
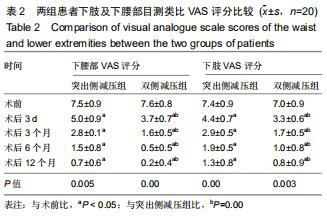
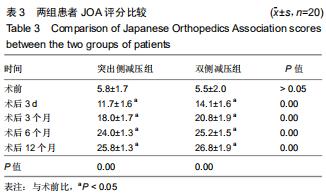
方法:回顾性选取2015年1月至2018年12月收治,并行内镜下椎间孔入路腰椎髓核摘除术的40例对侧症状型腰椎间盘突出症患者,以减压方式不同将患者分为突出侧减压组20例和双侧减压组20例。分别记录两组患者术前、术后第3天及第3,6,12个月腰部、下肢目测类比评分以及日本骨科协会JOA评分;术后12个月采用改良Macnab标准评定疗效,复查腰椎动力位X射线片评估腰椎稳定性。
结果与结论:40例患者均获得随访,随访时间12-20个月,平均16个月。①两组均未出现硬膜囊撕裂、椎间隙感染等并发症;②两组患者术后腰部及下肢疼痛均有明显缓解,且与术前相比,术后JOA评分有明显提高,术后腰部及下肢目测类比评分明显降低,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05);双侧减压组各对应时间点的目测类比评分及JOA评分均优于突出侧减压组(P < 0.05);③术后12个月改良Macnab评估结果示,突出侧减压组优良率为70%,双侧减压组优良率为95%,两组间差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);④术后12个月复查腰椎动力位X射线片,两组均未出现腰椎失稳或滑脱的情况。提示:对于对侧症状腰椎间盘突出症患者采取经皮内镜下椎间孔入路腰椎髓核摘除术治疗,两种减压方式均可改善疼痛症状,但双侧减压较突出侧的单侧减压,减压更充分,术后恢复效果更佳。
ORCID: 0000-0002-7636-0921(王秋安)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: