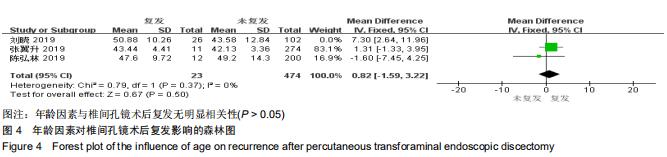
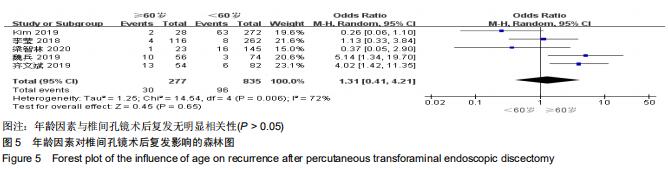
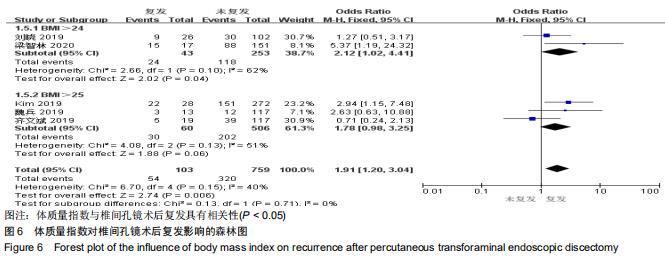
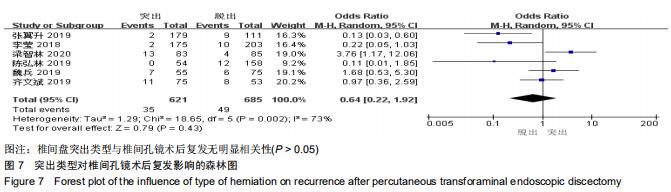
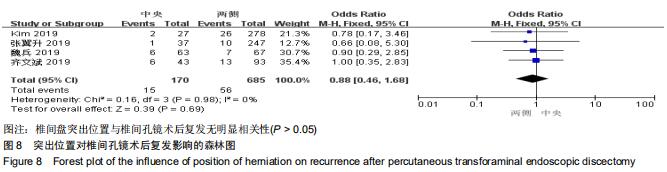
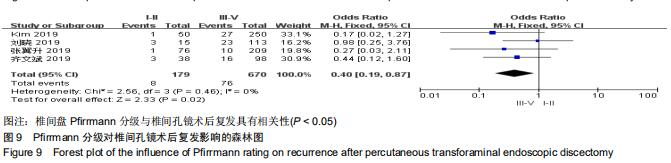
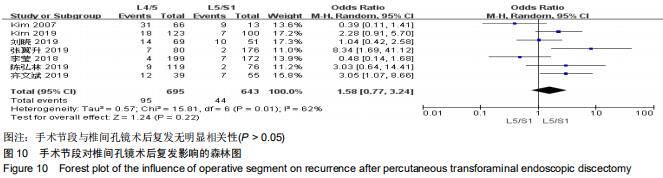
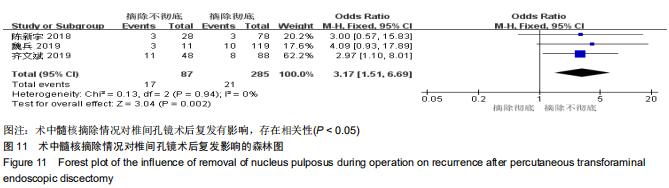
|
[1] DEYO RA, MIRZA SK. Herniated lumbar intervertebral disk. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(18):1763-1772.
[2] BLAMOUTIER A. Surgical discectomy for lumbar disc herniation: surgical techniques. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99(1 Suppl):S187-196.
[3] SNYDER LA, O'TOOLE J, EICHHOLZ KM, et al. The technological development of minimally invasive spine surgery. Biomed Res Int. 2014;(4):2014.
[4] MINAMIDE A, YOSHIDA M, YAMADA H, et al. Endoscope- assisted spinal decompression surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2013;19(6):644-671.
[5] HOOGLAND T, SCHUBERT M, MIKLITZ B, et al. Transforminal posterolateral endoscopic discectomy with or without the combination of a low-dose chymopapain: a prospective randomized study in 280 consecutive cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(24):890-897.
[6] BAI J, ZHANG W, LIU X, et al. Percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy in the treatment of senior patients with lumbar degenerative disc disease. Exp Ther Med. 2018; 17(1):874-882.
[7] 冯帆,蔡毅,李颖波,等.腰椎间盘突出症7种手术修复方式差异的网络Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(3):453-459.
[8] STANG A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25(9):603-605.
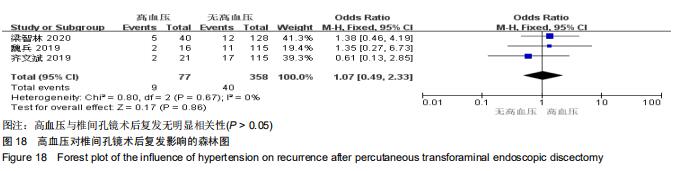
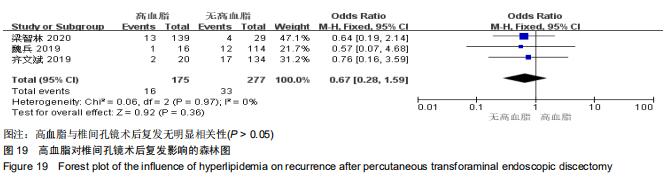
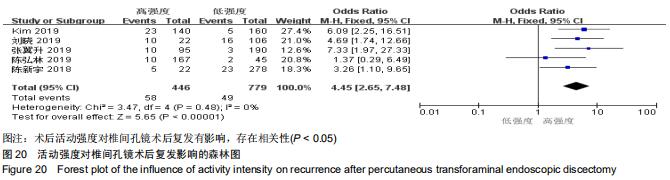
[9] 梁智林,海涌,杨晋才,等.经皮椎间孔镜治疗腰椎间盘突出症术后复发影响因素研究[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2020,9(1):5-10.
[10] KIM HS, YOU JD, JU C. Predictive Scoring and Risk Factors of Early Recurrence after Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy. BioMed Research Int. 2019. doi: 10.1155/2019/6492675.
[11] 齐文斌,朱彦海.经皮椎间孔镜手术治疗腰椎间盘突出症的疗效观察及术后复发的相关因素分析[J].颈腰痛杂志,2019,40(6): 776-780.
[12] 刘晓.经皮椎间孔镜治疗腰椎间盘突出症术后复发的危险因素分析[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2019.
[13] 张翼升.经皮椎间孔镜治疗腰椎间盘突出症术后复发相关因素的研究[D].南宁:广西中医药大学,2019.
[14] 魏兵.腰椎间盘突出症患者椎间孔镜手术后复发的危险因素分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2019,25(2):101-104, 116.
[15] 陈弘林.腰椎间盘突出症内镜术后复发的影响因素分析[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2019.
[16] XU JT, LI YW, WANG B, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy for lumbar disc herniation with modic changes via a transforaminal approach: a retrospective study. Pain physician. 2019;22(6):E601.
[17] 陈新宇,于崇龙,王嘉鹏,等.椎间孔镜治疗腰椎间盘突出症术后复发因素的探讨[J].临床医药文献电子杂志,2018,5(96):73-74.
[18] 李莹,唐谨,吴从俊,等.椎间孔镜下治疗腰椎间盘突出症术后复发相关因素及再次处理效果探讨[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2018, 26(11):37-41.
[19] KIM JM, LEE SH, AHN Y, et al. Recurrence after successful percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2007;50(2):82-85.
[20] VIALLE LR, VIALLE EN, SUÁREZ HENAO JE, et al. Lumbar disc herniation. Rev Bras Ortop. 2015;45(1):17-22.
[21] LIANG J, CHEN C, ZHAO H. Revision surgery after percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal discectomy compared with primary open surgery for symptomatic lumbar degenerative disease. Orthopaedic Surg. 2019;11(4): 620-627.
[22] PAN Z, HA Y, YI S, et al. Efficacy of transforaminal endoscopic spine system (tessys) technique in treating lumbar disc herniation. Med Science Monit. 2016;22:530-539.
[23] RUETTEN S, KOMP M, MERK H, et al. Full-endoscopic interlaminar and transforaminal lumbar discectomy versus conventional microsurgical technique: a prospective, randomized, controlled study. Spine. 2008;33:931-939.
[24] 唐谨,李莹,吴从俊,等.经皮椎间孔镜与椎间盘镜下手术治疗腰椎间盘突出症效果比较的Meta分析[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2019, 27(3):23-28.
[25] SHIN EH, CHO KJ, KIM YT, et al. Risk factors for recurrent lumbar disc herniation after discectomy. Int Orthop. 2019; 43(4):963-967.
[26] LI Z, YANG H, LIU M, et al. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of recurrent lumbar disk herniation:a retrospective analysis of three hundred twenty-one cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018;43(21):1463-1469.
[27] SUK KS, LEE HM, MOON SH, et al. Recurrent lumbar disc herniation: results of operative management. Spine. 2001; 26(6):672-676.
[28] CARRAGEE EJ, HAN MY, SUEN PW, et al. Clinical outcomes after lumbar discectomy for sciatica: the effects of fragment type and anular competence. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85(1):102-108.
[29] MOBBS RJ, NEWCOMBE RL, CHANDRAN KN. Lumbar discectomy and the diabetic patient: incidence and outcome. J Clin Neurosci. 2001;8(1):10-13.
[30] PARK CH, PARK ES, LEE SH, et al. Risk factors for early recurrence after transforaminal endoscopic lumbar disc decompression. Pain Physician. 2019;22(2):E133-E138.
[31] BILGE K, ZELIHA T, UMIT A. Functional results and the risk factors of reoperations after lumbar disc surgery. Eur Spine J. 2005;14:43-48.
[32] CINOTTI G, ROYSAM GS, EISENSTEIN SM, et al. Ipsilateral recurrent lumbar disc herniation. A prospective, controlled study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998;80(5):825-832.
[33] KIM KT, PARK SW, KIM YB. Disc height and segmental motion as risk factors for recurrent lumbar disc herniation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(24):2674-2678.
[34] MEREDITH DS, HUANG RC, NGUYEN J, et al. Obesity increases the risk of recurrent herniated nucleus pulposus after lumbar microdiscectomy. Spine J. 2010;10(7):575-580.
[35] 郑旭浩,张小磊,江立波,等.细胞自噬在糖尿病大鼠椎间盘退变中的作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2013,29(11):2011-2016.
[36] HEINDEL P, TUCHMAN A, HSIEH PC, et al. Reoperation Rates After Single-level Lumbar Discectomy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42(8):E496-E501.
[37] CHENG J, WANG H, ZHENG W, et al. Reoperation after lumbar disc surgery in two hundred and seven patients. Int Orthop. 2013;37(8):1511-1517.
[38] SENCER A, YORUKOGLU AG, AKCAKAYA MO, et al. Fully endoscopic interlaminar and transforaminal lumbar discectomy: short-term clinical results of 163 surgically treated patients. World Neurosurg. 2014;82(5):884-890.
[39] SHIMIA M, BABAEI-GHAZANI A, SADAT BE, et al. Risk factors of recurrent lumbar disk herniation. Asian J Neurosurg. 2013;8(2):93-96.
[40] 天航,刘效仿,曹正霖,等.椎间孔镜治疗腰椎间盘突出症术后复发因素的探讨[J].江西医药,2016,51(1):9-11.
[41] LEE DY, LEE SH. Learning curve for percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy. Neurol Med Chir. 2008;48(9): 383-388.
[42] YAO Y, LIU H, ZHANG H, et al. Risk factors for recurrent herniation after percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy. World Neurosurg. 2017;100:1-6.
|