中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (23): 3673-3677.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2659
• 肌肉肌腱韧带组织构建 tissue construction of the muscle, tendon and ligament • 上一篇 下一篇
脑瘫尖足患儿站立和行走中下肢肌肉的表面肌电图
许 萍1,梁雷超1,梁贞文1,蔡 明1,陈 博2,黄 萍2,张琳琳1
- 1上海健康医学院,上海市 201318;2上海市伤骨科研究所,上海市中西医结合防治骨与关节病损重点实验室, 上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院,上海市 200025
Surface electromyogram features of the lower limb muscles in cerebral palsy children standing and walking on tiptoes
Xu Ping1, Liang Leichao1, Liang Zhenwen1, Cai Ming1, Chen Bo2, Huang Ping2, Zhang Linlin1
- 1Shanghai University of Medicine and Health Sciences, Shanghai 201318, China; 2Shanghai Institute of Traumatology and Orthopaedics, Shanghai Key Laboratory for Prevention and Treatment of Bone and Joint Diseases with Integrated Chinese-Western Medicine, Shanghai Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China
摘要:
文题释义:
表面肌电图(surface lectromyography,SEMG):是分析相关肌肉功能状况的一种无创性检查手段,可以客观评定静止或运动时肌肉的活动情况。在控制良好的情况下,肌电信号活动的变化在很大程度上能够定量反映肌肉功能状态、肌张力、肌力水平、多肌群协调性等肌肉的变化,对肌肉功能状况提供客观指标,对于肌肉相关疾病的康复设计、康复治疗,特别是疗效评定有着不可替代的重要作用。
平均振幅:是用来描述一段时间内肌电幅值的平均变化特征。一般认为与运动单位募集程度和兴奋节律的同步化有关,它间接反映肌肉收缩力大小。一定范围内,平均振幅与肌肉收缩过程中参与工作运动单位数量呈正比,反映了肌肉收缩强度的变化。
背景:在控制良好的情况下,肌电信号活动的变化在很大程度上能够定量反映肌肉功能状态、肌张力、肌力水平、多肌群协调性等肌肉的变化,对肌肉功能状况提供客观指标。
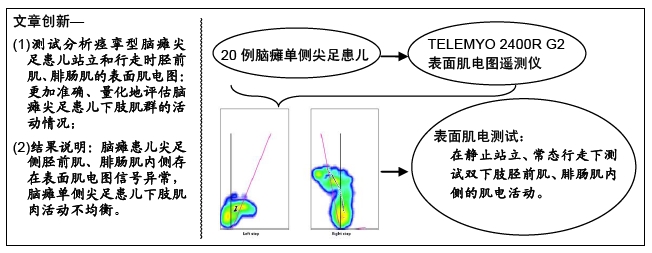
目的:探讨脑瘫尖足患儿站立和行走中下肢肌肉的表面肌电图变化。
方法:应用美国NORAXON公司生产的 TELEMYO 2400R G2表面肌电图遥测仪对20例脑瘫单侧尖足患儿在静止站立、常态行走下进行双下肢胫前肌、腓肠肌内侧的表面肌电测试。比较受试者尖足侧与对侧肌肉的肌电活动。研究方案经过了上海瑞金医院伦理委员会批准,所有受试者及监护人均签署了“知情同意书”。
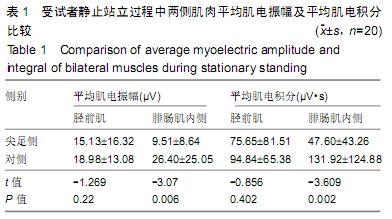
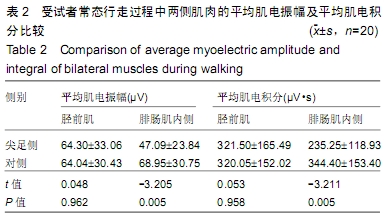
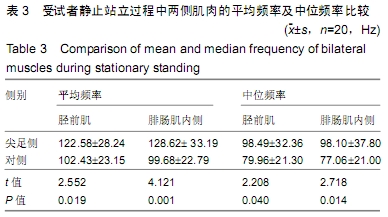
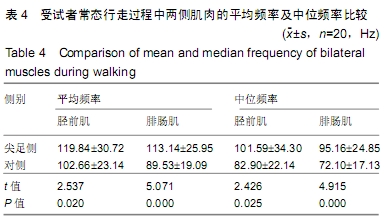
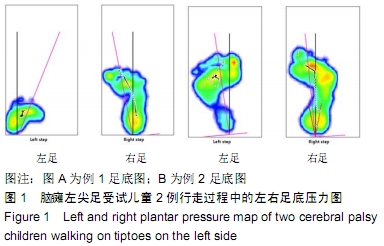
结果与结论:①受试者静止站立和常态行走时,其尖足侧腓肠肌内侧的平均肌电振幅、平均肌电积分均低于对侧(P < 0.05);②受试者静止站立和常态行走时,其尖足侧胫前肌和腓肠肌内侧的平均频率、中位频率均高于对侧(P < 0.05);③结果说明,脑瘫患儿尖足侧胫前肌、腓肠肌内侧存在表面肌电图信号异常,脑瘫单侧尖足患儿下肢肌肉活动不均衡,提示表面肌电图对脑瘫患儿神经肌肉系统功能状态的评价具有实用价值。
ORCID: 0000-0001-8732-8452(许萍);0000-0001-9909-3355(梁雷超)中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: