[1] YANG NY, ZHOU Y, ZHAO HY, et al. Increased interleukin 1α and interleukin 1β expression is involved in the progression of periapical lesions in primary teeth. BMC Oral Health. 2018;18(1):124.
[2] SIDDIQUI YD, OMORI K, ITO T, et al. Resolvin D2 Induces Resolution of Periapical Inflammation and Promotes Healing of Periapical Lesions in Rat Periapical Periodontitis. Front Immunol. 2019;10:307.
[3] HOWAIT M, ALBASSAM A, YAMADA C, et al. Elevated Expression of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Promotes Inflammatory Bone Resorption Induced in a Mouse Model of Periradicular Periodontitis. J Immunol. 2019;202(7):2035-2043.
[4] KUDO H, TAKEICHI O, HATORI K, et al. A potential role for the silent information regulator 2 homologue 1 (SIRT1) in periapical periodontitis. Int Endod J. 2018;51(7):747-757.
[5] SHAH A, LEE D, SONG M, et al. Clastic cells are absent around the root surface in pulp-exposed periapical periodontitis lesions in mice. Oral Dis. 2018;24(1-2):57-62.
[6] JIANG C, WANG Q, SONG M, et al. Coronarin D affects TNF-α induced proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells. Arch Oral Biol. 2019;108:104519.
[7] DONG M, JIN H, ZUO M, et al. The potential effect of Bruton's tyrosine kinase in refractory periapical periodontitis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;112:108710.
[8] BAI MM, SHI W, TIAN JM, et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitory and anti-inflammatory components from the leaves of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver (duzhong). J Agric Food Chem. 2015; 63(8):2198-2205.
[9] KONG HJ, KANG JH. Efficacy of Juglandis semen complex extract for knee osteoarthritis: A pilot study protocol for a 12-week, single-center, randomized, controlled, double-blind clinical trial. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(34):e16956.
[10] WANG JY, YUAN Y, CHEN XJ, et al. Extract from Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. ameliorates arthritis via regulation of inflammation, synoviocyte proliferation and osteoclastogenesis in vitro and in vivo. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;194:609-616.
[11] WANG JY, CHEN XJ, ZHANG L, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. male flower extract on lipopolysaccharide- induced inflammation. Chin Med J (Engl). 2019;132(3):319-328.
[12] XING YF, HE D, WANG Y, et al. Chemical constituents, biological functions and pharmacological effects for comprehensive utilization of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver. Food Science and Human Wellness. 2019;8(2):177-188.
[13] JIA J, LIU M, WEN Q, et al. Screening of anti-complement active ingredients from Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. branches and their metabolism in vivo based on UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS/MS. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2019;1124:26-36.
[14] WANG CY, TANG L, HE JW, et al. Ethnobotany, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Properties of Eucommia ulmoides: A Review. Am J Chin Med. 2019;47(2):259-300.
[15] TANGPAKDEE J, TANAKA Y, SHIBA K, et al. Structure and biosynthesis of trans-polyisoprene from Eucommia ulmoides. Phytochemistry. 1997;45(1):75-80.
[16] HE X, WANG J, LI M, et al. Eucommia ulmoides Oliv.: ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology of an important traditional Chinese medicine. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;151(1):78-92.
[17] WANG JY, CHEN XJ, ZHANG L, et al. Comparative Studies of Different Extracts from Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. against Rheumatoid Arthritis in CIA Rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018;2018:7379893.
[18] FANG C, CHEN L, HE M, et al. Molecular mechanistic insight into the anti-hyperuricemic effect of Eucommia ulmoides in mice and rats. Pharm Biol. 2019;57(1):112-119.
[19] SUN WT, XU XY, LI XQ, et al. Effects of dietary geniposidic acid on growth performance, flesh quality and collagen gene expression of grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella. Aquaculture Nutrition. 2018; 24(3): 1112-1121.
[20] HUANG H, PAN L, PAN S, et al. Effects of dietary herbal formulae combined by Astragalus polysaccharides, chlorogenic acid and allicin in different combinations and proportions on growth performance, non-specific immunity, antioxidant status, vibriosis resistance and damage indexes of Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture Research. 2018; 49(2): 701-716.
[21] FUJIWARA A, NISHI M, YOSHIDA S, et al. Eucommicin A, a β-truxinate lignan from Eucommia ulmoides, is a selective inhibitor of cancer stem cells. Phytochemistry. 2016;122:139-145.
[22] LUO LF, WU WH, ZHOU YJ, et al. Antihypertensive effect of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. extracts in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010;129(2):238-243.
[23] ZHU MQ, XU WZ, WEN JL, et al. Dynamic changes of photosynthetic properties and chemical compositions of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver under two planting models. Industrial Crops and Products. 2017; 96: 46-56.
[24] YIN CM, DUAN YN, XIANG L, et al. Effects of phloridzin, phloretin and benzoic acid at the concentrations measured in soil on the root proteome of Malus hupehensis Rehd Seedlings. Scientia Horticulturae. 2018; 228: 10-17.
[25] DENG Y, MA F, RUIZ-ORTEGA LI, et al. Fabrication of strontium Eucommia ulmoides polysaccharides and in vitro evaluation of their osteoimmunomodulatory property. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019; 140:727-735.
[26] ZHU MQ, WEN JL, SU YQ, et al. Effect of structural changes of lignin during the autohydrolysis and organosolv pretreatment on Eucommia ulmoides Oliver for an effective enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresour Technol. 2015;185:378-385.
[27] ISHII K, HATORI K, TAKEICHI O, et al. Expression of the Forkhead box transcription factor Foxo3a in human periapical granulomas. J Oral Sci. 2018;60(4):479-483.
[28] SALLES AG, ANTUNES LAA, KÜCHLER EC, et al. Association between Apical Periodontitis and Interleukin Gene Polymorphisms: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Endod. 2018;44(3):355-362.
[29] RÔÇAS IN, SIQUEIRA JF JR. Frequency and levels of candidate endodontic pathogens in acute apical abscesses as compared to asymptomatic apical periodontitis. PLoS One. 2018;13(1): e0190469.
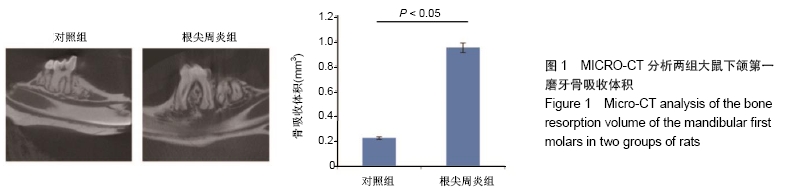
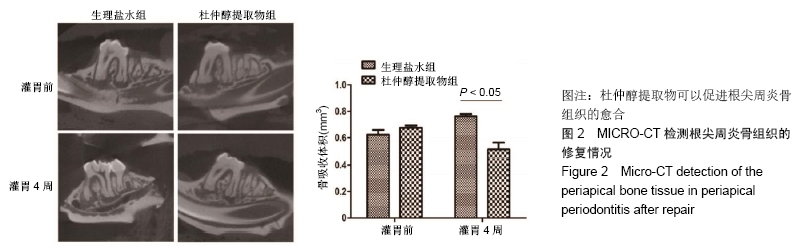
[30] CHEN S, LEI H, LUO Y, et al. Micro-CT analysis of chronic apical periodontitis induced by several specific pathogens. Int Endod J. 2019;52(7):1028-1039.
[31] WANG L, JIN H, AO X, et al. JAK2-STAT3 signaling pathway is involved in rat periapical lesions induced by Enterococcus faecalis. Oral Dis. 2019;25(7):1769-1779.
[32] HADAYA D, SOUNDIA A, GKOUVERIS I, et al. Development of Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw After Extraction of Teeth With Experimental Periapical Disease. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019;77(1):71-86.
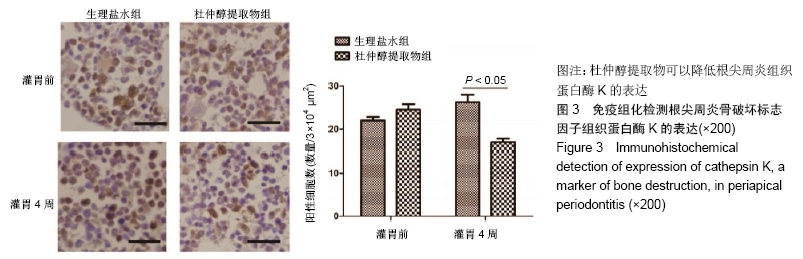
[33] LOTINUN S, ISHIHARA Y, NAGANO K, et al. Cathepsin K-deficient osteocytes prevent lactation-induced bone loss and parathyroid hormone suppression. J Clin Invest. 2019;129: 3058-3071.
[34] FANG W, HE A, XIANG MX, et al. Cathepsin K-deficiency impairs mouse cardiac function after myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019;127:44-56.
[35] PANG M, RODRÍGUEZ-GONZALEZ M, HERNANDEZ M, et al. AP-1 and Mitf interact with NFATc1 to stimulate cathepsin K promoter activity in osteoclast precursors. J Cell Biochem. 2019; 120(8):12382-12392.
[36] WALIA B, LINGENHELD E, DUONG L, et al. A novel role for cathepsin K in periosteal osteoclast precursors during fracture repair. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018;1415(1):57-68.
[37] MONS E, JANSEN IDC, LOBODA J, et al. The Alkyne Moiety as a Latent Electrophile in Irreversible Covalent Small Molecule Inhibitors of Cathepsin K. J Am Chem Soc. 2019;141(8): 3507-3514.
[38] LEUSINK FK, KOUDOUNARAKIS E, FRANK MH, et al. Cathepsin K associates with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2018;18(1):385.
|