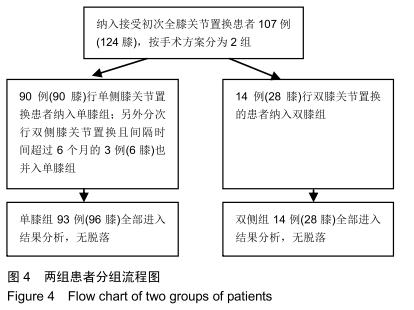
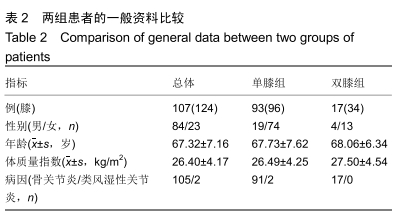
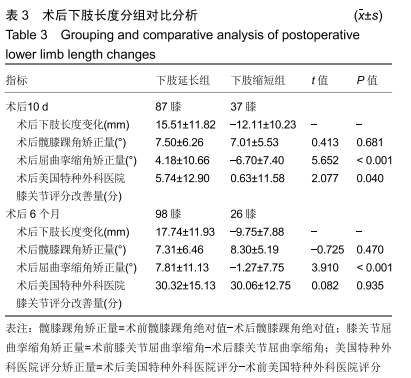
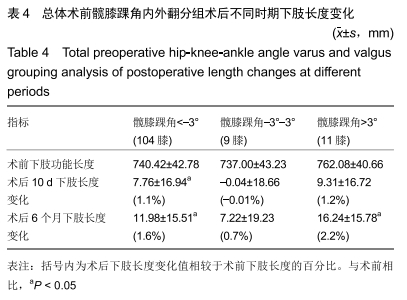
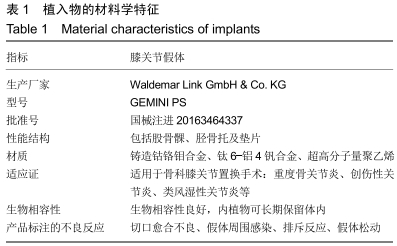
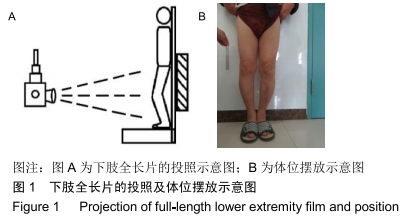
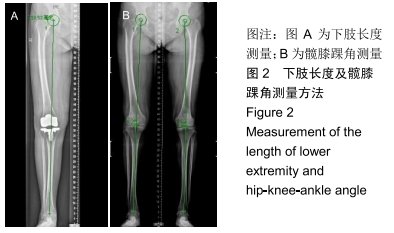
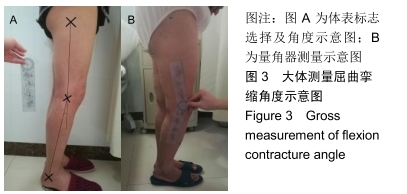
[1] TANG X, WANG S, ZHAN S, et al. The prevalence of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis in china: results from the china health and retirement longitudinal study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(3): 648-653.
[2] 张晓盈,彭嘉婧,刘传慧,等.骨关节炎患者用药治疗现状的全国多中心大样本现场调查[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(6): 1044-1048.
[3] 雷光华,王坤正.骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018年版)解读[J].中华骨科杂志, 2018,38(12): 716-717.
[4] HOOPER G, ROTHWELL A, FRAMPTON C. The low contact stress mobile-bearing total knee replacement: a prospective study with a minimum follow-up of ten years. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009;91(1): 58-63.
[5] CHANG MJ, SO S, PARK CD, et al. Long-term follow-up and survivorship of single-radius, posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci. 2018;23(1): 92-96.
[6] HEESTERBEEK PJC, VAN HOUTEN AH, KLENK JS, et al. Superior long-term survival for fixed bearing compared with mobile bearing in ligament-balanced total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(5):1524-1531.
[7] RITTER MA, KEATING EM, SUEYOSHI T, et al. Twenty-five-years and greater, results after nonmodular cemented total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2016; 31(10):2199-2202.
[8] 裴福兴.中国髋、膝关节置换的现状及展望[J].中国骨与关节杂志, 2012, 1(1) 4-8.
[9] BHAVE A, MONT M, TENNIS S, et al. Functional problems and treatment solutions after total hip and knee joint arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87(1): 9-21.
[10] ULRICH SD, BHAVE A, MARKER DR, et al. Focused rehabilitation treatment of poorly functioning total knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;464(464): 138-145.
[11] AUSTIN MS, HOZACK WJ, SHARKEY PF, et al. Stability and leg length equality in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18(3): 88-90.
[12] GURNEY B, MERMIER CR, GIBSON A, et al. Effects of limb-length discrepancy on gait economy and lower-extremity muscle activity in older adults. J Bone Joint Surg. 2001;83-A(6):907-915.
[13] LANG JE, SCOTT RD, LONNER JH, et al. Magnitude of limb lengthening after primary total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(3): 341-346.
[14] KIM SH, RHEE SM, LIM JW, et al. The effect of leg length discrepancy on clinical outcome after TKA and identification of possible risk factors. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(8): 2678-2685.
[15] VAIDYA S, PATEL M, PANGHATE A, et al. Total knee arthroplasty: Limb length discrepancy and functional outcome. Indian J Orthop. 2010;44(3):300-307.
[16] TIPTON S, SUTHERLAND J, SCHWARZKOPF R. Change in limb length after total knee arthroplasty. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2015;6(3): 197-201.
[17] 陈进良,袁华,冯剑楠,等. 影响DR双下肢全长拼接技术成功率的因素分析及控制策略[J].中国医疗设备, 2018,33(12):87-90.
[18] GAO F, MA J, SUN W, et al. Radiographic assessment of knee–ankle alignment after total knee arthroplasty for varus and valgus knee osteoarthritis. Knee. 2017; 24(1): 107-115.
[19] BORGBJERG J, MADSEN F, ODGAARD A. Patient self-assessed passive range of motion of the knee cannot replace health professional measurements. J Knee Surg. 2017;30:829-834.
[20] INSALL JN, RANAWAT CS, AGLIETTI P, et al. A comparison of four models of total knee-replacement prostheses. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976;58(6): 754-765.
[21] KIM YH, YOON SH, KIM JS. The long-term results of simultaneous fixed-bearing and mobile-bearing total knee replacements performed in the same patient. J Bone Joint Surg. 2007;89-B(10): 1317-1323.
[22] KANE RL, SALEH KJ, WILT TJ, et al. The Functional outcomes of total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87(8): 1719-1724.
[23] LANG JE, SCOTT RD, LONNER JH, et al. Magnitude of limb lengthening after primary total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(3): 341-346.
[24] AARON A, WEINSTEIN D, THICKMAN D, et al. Comparison of orthoroentgenography and computed tomography in the measurement of limb-length discrepancy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992;74(6): 897-902.
[25] TANZER M, MILLER J. The natural history of flexion contracture in total knee arthroplasty. A prospective study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;248(248): 129-134.
[26] CHINNAPPA J, CHEN DB, HARRIS IA, et al. Predictors and functional implications of change in leg length following total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(9): 2725-2729.
[27] MUFTY S, VANDENNEUCKER H, BELLEMANS J. The influence of leg length difference on clinical outcome after revision TKA. Knee. 2014;21(2): 424-427.
[28] OHMORI T, KABATA T, KAJINO Y, et al. Three-dimensional limb lengthening after total knee arthroplasty in a simulation study. Mod Rheumatol. 2018;28(6):1029-1034.
[29] SHETTY GM, MULLAJI A, KHALIFA AA, et al. The effect of sagittal knee deformity on preoperative measurement of coronal mechanical alignment during total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2017; 29(2):110-114.
|