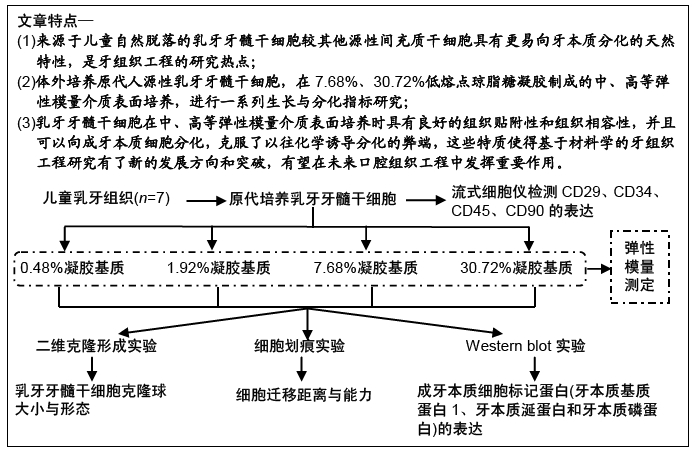
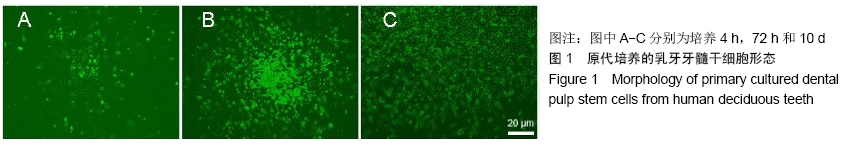
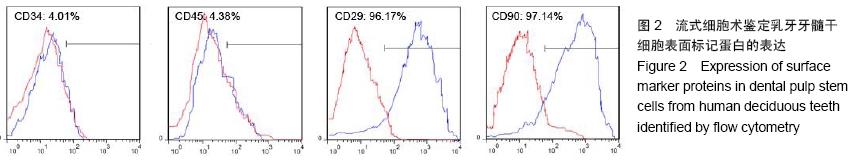
[1] WILLIAMS AR, HARE JM. Mesenchymal stem cells: biology, pathophysiology, translational findings, and therapeutic implications for cardiac disease. Circ Res. 2011;109(8): 923-940.
[2] UCCELLI A, MORETTA L, PISTOIA V. Mesenchymal stem cells in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(9): 726-736.
[3] KUO CK, TUAN RS. Tissue engineering with mesenchymal stem cells. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag. 2003;22(5):51-56.
[4] ZHANG YD, CHEN Z, SONG YQ, et al. Making a tooth: growth factors, transcription factors, and stem cells. Cell Res. 2005;15(5):301-316.
[5] VICTOR AK, REITER LT. Dental pulp stem cells for the study of neurogenetic disorders. Hum Mol Genet. 2017;26(R2): R166-R171.
[6] WANG X, WU TT, JIANG L, et al. Deferoxamine-Induced Migration and Odontoblast Differentiation via ROS-Dependent Autophagy in Dental Pulp Stem Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(6):2535-2547.
[7] HASTURK O, ERMIS M, DEMIRCI U, et al. Square prism micropillars on poly(methyl methacrylate) surfaces modulate the morphology and differentiation of human dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019; 178:44-55.
[8] OSATHANON T, SAWANGMAKE C, NOWWAROTE N, et al. Neurogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells using different induction protocols. Oral Dis. 2014;20(4): 352-358.
[9] KRIFKA S, SPAGNUOLO G, SCHMALZ G, et al. A review of adaptive mechanisms in cell responses towards oxidative stress caused by dental resin monomers. Biomaterials. 2013; 34(19):4555-4563.
[10] NUTI N, CORALLO C, CHAN BM, et al. Multipotent Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells: a Literature Review. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2016;12(5):511-523.
[11] MAO AS, SHIN JW, MOONEY DJ. Effects of substrate stiffness and cell-cell contact on mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Biomaterials. 2016;98:184-191.
[12] LIN X, SHI Y, CAO Y, et al. Recent progress in stem cell differentiation directed by material and mechanical cues. Biomed Mater. 2016;11(1):014109.
[13] JIANG L, SUN Z, CHEN X, et al. Cells Sensing Mechanical Cues: Stiffness Influences the Lifetime of Cell-Extracellular Matrix Interactions by Affecting the Loading Rate. ACS Nano. 2016;10(1):207-217.
[14] TSE JR, ENGLER AJ. Stiffness gradients mimicking in vivo tissue variation regulate mesenchymal stem cell fate. PLoS One. 2011;6(1):e15978.
[15] 刘晓智,刘振林,姜忠敏,等.不同物理密度介质诱导干细胞表达多种组织细胞标记蛋白[J].中华实验外科杂志,2012,29(2):341.
[16] 刘晓智.蛋白质SUMO化修饰在低温与高热应激条件下的细胞保护功能研究[D].天津:天津医科大学,2017.
[17] GRAZIANO A, D'AQUINO R, LAINO G, et al. Dental pulp stem cells: a promising tool for bone regeneration. Stem Cell Rev. 2008;4(1):21-26.
[18] GU L, SHAN T, MA YX, et al. Novel Biomedical Applications of Crosslinked Collagen. Trends Biotechnol. 2019;37(5): 464-491.
[19] SULIMAN S, MUSTAFA K, KRUEGER A, et al. Nanodiamond modified copolymer scaffolds affects tumour progression of early neoplastic oral keratinocytes. Biomaterials. 2016;95: 11-21.
[20] LI G, ZHOU T, LIN S, et al. Nanomaterials for Craniofacial and Dental Tissue Engineering. J Dent Res. 2017;96(7):725-732.
[21] TAN J, XU X, LIN J, et al. Dental Stem Cell in Tooth Development and Advances of Adult Dental Stem Cell in Regenerative Therapies. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015; 10(5): 375-383.
[22] BIANCO P."Mesenchymal" stem cells. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014;30:677-704.
[23] ANKRUM JA, ONG JF, KARP JM. Mesenchymal stem cells: immune evasive, not immune privileged. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32(3):252-260.
[24] UCCELLI A, MORETTA L, PISTOIA V. Mesenchymal stem cells in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(9): 726-736.
[25] FIORE EJ, DOMÍNGUEZ LM, BAYO J, et al. Taking advantage of the potential of mesenchymal stromal cells in liver regeneration: Cells and extracellular vesicles as therapeutic strategies. World J Gastroenterol. 2018;24(23): 2427-2440.
[26] MURAKAMI M, HAYASHI Y, IOHARA K, et al. Trophic Effects and Regenerative Potential of Mobilized Mesenchymal Stem Cells From Bone Marrow and Adipose Tissue as Alternative Cell Sources for Pulp/Dentin Regeneration. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(9):1753-1765.
[27] ZHANG W, YANG G, WANG X, et al. Magnetically Controlled Growth-Factor-Immobilized Multilayer Cell Sheets for Complex Tissue Regeneration. Adv Mater. 2017;29(43): 1703795.
[28] VINING KH, SCHERBA JC, BEVER AM, et al. Synthetic Light-Curable Polymeric Materials Provide a Supportive Niche for Dental Pulp Stem Cells. Adv Mater. 2018;30(4).
[29] BOTELHO J, CAVACAS MA, MACHADO V, et al. Dental stem cells: recent progresses in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Ann Med. 2017;49(8):644-651.
[30] XUAN K, LI B, GUO H, et al. Deciduous autologous tooth stem cells regenerate dental pulp after implantation into injured teeth. Sci Transl Med. 2018;10(455):eaaf3227.
|