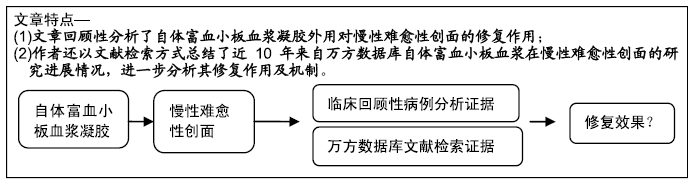
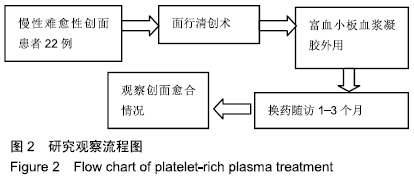
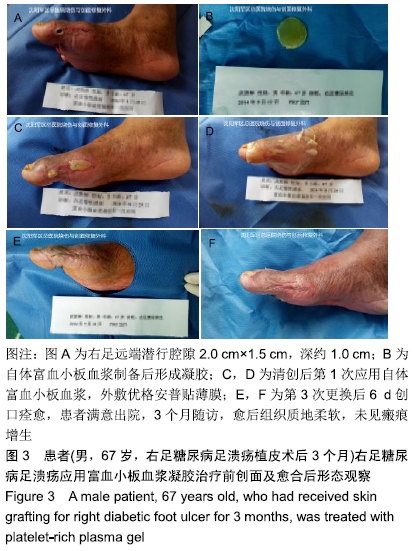
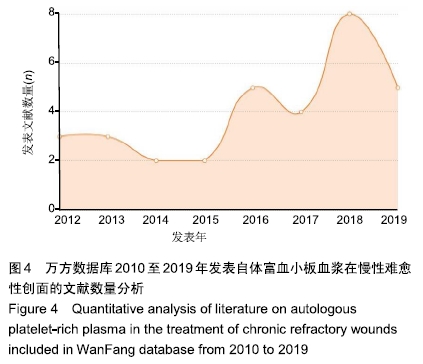
[1] 徐铮宇,宋文奇.富含血小板的血浆在骨修复方面的研究和应用[J].国外医学(骨科学分册),2002,23(4):236-237.
[2] 赵子春,李钊伟,闫红秀,等.富血小板血浆治疗股骨干缺血萎缩型骨不连:前瞻性随机对照临床试验[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(28): 4442-4447.
[3] 唐保明,杨爱荣,李钊伟,等.富含血小板血浆治疗慢性骨髓炎不愈合创面临床研究[J].青海医药杂志,2016,46(1):2-6.
[4] 刘强,邵家松.慢性难愈性创面的形成机制及治疗进展[J].中国临床新医学, 2013,12(9):917-920.
[5] 孙家潭,任广理,贾凤亭,等.神经刺激器定位下肢神经阻滞在高龄糖尿病足截肢术中的应用[J].临床军医杂志, 2014,42(11):1198-1199.
[6] 杨华瑞,陈园,鲍同柱.自体富血小板血浆在组织缺损与修复中的应用[J].海南医学,2016,27(11):1830-1832.
[7] DAI WL, ZHOU AG, ZHANG H, et al. Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arthroscopy. 2017;33(3):659-670.e1.
[8] ESCAMILLA CM, DOMÍNGUEZ-MALDONADO G, CÓRDOBA-FERNÁNDEZ A. Efficacy and safety of the use of platelet-rich plasma to manage venous ulcers. J Tissue Viability. 2017;26(2):138-143.
[9] SANTE LD, VILLANI C, SANTILLI V, et al. Intra-articular hyaluronic acid vs platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of hip osteoarthritis. Med Ultrason. 2016;18(4):463-468.
[10] 李全,王凌峰.难愈性创面治疗新进展[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2012,7(4):414-417.
[11] 邬佳敏,王达利,贺钧,等.难愈创面局部注射自体富血小板血浆临床观察[J].贵州医药,2019,43(5):749-750.
[12] 张晓冬,曲铁兵.自体富血小板凝胶换药辅助治疗难愈合创面初步探讨[J].中华创伤杂志,2012,28(7):658-660.
[13] 张苏燕,金雪琴.自体富血小板血浆治疗慢性难愈合伤口的手术配合[J].中西医结合心血管病电子杂志,2018,6(15):50-51.
[14] 龙照忠,首家保,王彤华,等.自体富血小板血浆在慢性创面修复中的研究进展[J].中国保健营养,2019,29(20):35.
[15] 赵月强,朱占永,李爱林,等.富血小板血浆治疗慢性难愈性创面的临床研究[J].临床外科杂志,2016,24(3):175-178.
[16] 陈健,谢包根,黄永新,等.富血小板血浆联合清创术治疗难愈性创面的疗效观察[J].中国美容医学,2018,27(4):11-14.
[17] 陈大康,冯晓林,李义贵,等.富血小板血浆治疗四肢难治性创面的临床研究[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2018,35(11):2150-2151.
[18] 何丽苇,王顺,陈会欣.自体富血小板血浆治疗难愈性创面短期疗效观察[J].中国输血杂志,2018,31(10):1163-1165.
[19] 伍鹏欢,袁艾东,史本超.不同浓度富血小板血浆在慢性难愈合创面的临床疗效分析[J].中国伤残医学,2019,27(15):19-23.
[20] 张杨杨,邱啸臣,贾赤宇.富血小板血浆技术在整形外科领域的应用[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2012,7(6):671-673.
[21] 陈健民,陈立安,陈梓锋,等.富血小板血浆修复慢性难愈合伤口的应用[J].岭南现代临床外科,2013,13(3):210-213.
[22] 刘晓韬,洪小芳,张志文,等.富血小板血浆治疗慢性难愈合伤口效果分析[J].当代医学,2013,19(9):61.
[23] 陈震宇,张会增.创面封闭式引流结合富血小板血浆治疗难愈性创面短期疗效观察[J].中国骨伤,2014,27(3):247-249.
[24] 李明,章军辉,李淑敏,等.应用自体富血小板血浆治疗慢性难愈性创面的实验研究[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2016,10(6):624-629.
[25] 高文华,张宏亮,胡玉庆,等.自体富血小板血浆凝胶联合皮瓣移植修复对难愈性创面的治疗效果[J].局解手术学杂志, 2018,27(2):88-92.
[26] 郭荣,王芳,陈欢,等.蝎肽凝胶联合富血小板血浆在修复溃疡创面中的应用[J].临床外科杂志,2018,26(5):386-389.
[27] 杨永熙,冯佳雄,黄晓涛,等.富血小板血浆治疗慢性难愈性伤口的临床研究[J].中国基层医药,2016,23(11):1637-1640.
[28] 杨颖.自体富血小板血浆联合多种治疗方法治疗难愈性伤口的效果观察[J].健康必读,2018,(13):90.
[29] 黄晓燕.富血小板血浆治疗难愈伤口的应用研究及相关护理[J].中国医药指南,2012,10(14):338-339.
[30] 黄山东,费志军,陈俊泽,等.富血小板血浆治疗深部组织外露的外伤性难愈性创面的疗效观察[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2017, 11(6):666-670.
[31] 周谋,林放,施琳颖,等.输血科开展富血小板血浆治疗的可行性探讨—附176例PRP应用的疗效分析[J].中国输血杂志, 2018,31(6): 579-582.
[32] 肖义青,宋灿,姚静,等.富血小板血浆的制备及其在整形外科中的应用进展[J].山东医药,2015,55(17):95-97.
[33] 易中梅,周渝萌,李晨晨,等.1例自体PRP对股骨内侧难愈合性创面的修复效果报道[J].检验医学与临床,2019,16(5):717-718.
[34] 彭艳.富血小板血浆激活PI3K/AKT/NFB信号通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞再生及修复功能的相关研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2013.
[35] 张志文,刘晓韬,洪小芳.富血小板血浆治疗下肢骨折术后难愈性伤口初步探讨[J].中国现代医生,2014,52(22):36-38,41.
[36] 李明.自体富血小板血浆对膝关节退行性变和难愈性创面治疗作用的实验研究[D].济南:山东大学,2016.
[37] 江辉耀.自体富血小板血浆治疗难愈合伤口的研究进展[J].首都食品与医药,2016,23(8):23-23,24.
[38] 杨蔡伟,熊敏,冒海军.PRP治疗难愈性骨或腱性组织外露创面的疗效分析[J].现代医学,2017,45(12):1704-1708.
[39] 刘风.自体富血小板凝胶治疗糖尿病皮肤慢性难愈合创面的机制及临床应用进展[J].重庆医学,2017,46(6):848-850,864.
[40] 徐林刚,杨冠龙,王丽英,等.序贯综合疗法治疗慢性难愈性压疮[J].河南外科学杂志,2019,25(2):40-42.
[41] 李文丹.冻干血小板在深Ⅱ度烫伤大鼠模型中对创面愈合作用研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2015.
[42] 余龙威.冻存的浓缩生长因子血浆膜促进慢性创面愈合的临床研究[D].湛江:广东医科大学,2017.
[43] 王凌峰,李俊亮.难愈性创面与细菌的探讨[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2012,7(4):341-345.
[44] 胡国林,巴特.封闭负压引流技术治疗56例骨外露创面的临床疗效[J].临床军医杂志,2013,41(4):379-380.
[45] 许东浩.富含血小板血浆在足踝外科领域的临床应用[J].实用骨科杂志,2016,22(5):432-435.
[46] YÜMÜN G, KAHAMAN C, KAHAMAN N, et al. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy combined with platelet-rich plasma on diabetic wounds: an experimental rat model. Arch Med Sci. 2016; 12(6):1370-1376.
[47] 刘哲伟,苏开新,陈军,等.富含血小板血浆外敷在深Ⅱ度烧伤创面修复中的临床应用[J].天津医药,2014,47(12):1213-1215.
[48] 刘玉昌,刘建宁,李亚洲.重组人酸性成纤维细胞生长因子促进儿童创面愈合的多中心、开放性随机对照试验[J].中国药师, 2015,18(1): 77-79.
[49] 张祥运,丁晓斌,林秀峰,等.重组人表皮生长因子联合硫辛酸治疗糖尿病足的临床观察[J].中国药房,2016,27(29):4147-4149.
[50] 孙桂芳,张晓芬,陈亚峰,等.转化生长因子-β1/Smads信号在增生性瘢痕形成中的作用研究进展[J].创伤外科杂志, 2015,17(5):473-477.
[51] 赵培东,刘艳玲.重组人表皮生长因子对大面积烧伤创面愈合的影响[J].河南医学研究,2016,25(12):1-2.
[52] 陈连旭,敖英芳.富含血小板血浆在运动创伤修复中的应用[J].中国运动医学杂志,2011,30(1):86-93.
[53] RADICE F, YÁNEZ R, GUTIÉRREZ V, et al. Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging findings in anterior cruciate ligament grafts with and without autologous platelet-derived growth factors. Arthroscopy. 2010;26(1):50-57.
[54] 李思敏,周晋,颜承伟,等.富血小板血浆缓释载体在骨组织工程中的研究进展[J].口腔医学研究,2015,38(6):632-637.
[55] 吴开泽,陈献聪,康禹,等.富血小板血浆在膝关节骨关节炎治疗中的应用[J].国际骨科学杂志,2015,31(6):414-418.
[56] 吴浩浪,杨广智,谢振生,等.自体富含血小板血浆(PRP)在慢性局限性湿疹治疗中临床疗效观察[J].现代诊断与治疗, 2015,30(6): 1353-1354.
[57] LI L, CHEN D, WANG C, et al. Autologous platelet-rich gel for treatment of diabetic chronic refractory cutaneous ulcers: a prospective, randomized clinical trial. Wound Repair Regen. 2015;23(4):495-505.
[58] LI L, WANG C, WANG Y, et al. Impact of topical application of autologous platelet-rich gel on medical expenditure and length of stay in hospitals in diabetic patients with refractory cutaneous ulcers. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2012;43(5): 762-765.
|