| [1] Burnham JM, Kim DC, Kamineni S. Midshaft Clavicle Fractures: A Critical Review. Orthopedics. 2016;39(5):e814-e821. [2] Pang EQ, Zhang S, Harris A, et al. Treatment Trends in Older Adults With Midshaft Clavicle Fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2017;42(11):875-882. [3] van der Meijden OA, Gaskill TR, Millett PJ. Treatment of clavicle fractures: current concepts review. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(3): 423-429. [4] Bravman JT, Vidal AF. Midshaft clavicle fractures: are surgical indications changing?. Orthopedics. 2009;32(12):909-913. [5] Hoogervorst P, Appalsamy A, Meijer D, et al. Does altering projection of the fractured clavicle change treatment strategy?. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2019;28(3):e65-e70. [6] Wang XH, Guo WJ, Li AB, et al. Operative versus nonoperative treatment for displaced midshaft clavicle fractures: a meta-analysis based on current evidence. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2015;70(8):584-592. [7] Ahmed AF, Salameh M, AlKhatib N, et al. Open Reduction and Internal Fixation Versus Nonsurgical Treatment in Displaced Midshaft Clavicle Fractures: A Meta-Analysis. J Orthop Trauma. 2018;32(7):e276-e283. [8] Rehn CH, Kirkegaard M, Viberg B, et al. Operative versus nonoperative treatment of displaced midshaft clavicle fractures in adults: a systematic review. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24(7):1047-1053. [9] Woltz S, Krijnen P, Schipper IB. Plate Fixation Versus Nonoperative Treatment for Displaced Midshaft Clavicular Fractures: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(12): 1051-1057. [10] Liu J, Srivastava K, Washington T, et al. Cost-Effectiveness of Operative Versus Nonoperative Treatment of Displaced Midshaft Clavicle Fractures: A Decision Analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019;101(1):35-47. [11] Higgins JP, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions (Version 5. 1. 0). Available at: http://handbook.cochrane.org. [12] Ahrens PM, Garlick NI, Barber J, et al. The Clavicle Trial: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Operative with Nonoperative Treatment of Displaced Midshaft Clavicle Fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(16):1345-1354. [13] Andrade-Silva FB, Kojima KE, Joeris A, et al. Single, superiorly placed reconstruction plate compared with flexible intramedullary nailing for midshaft clavicular fractures: a prospective, randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(8):620-626. [14] Assobhi JE. Reconstruction plate versus minimal invasive retrograde titanium elastic nail fixation for displaced midclavicular fractures. J Orthop Traumatol. 2011;12(4):185-192. [15] Bhardwaj A, Sharma G, Patil A, et al. Comparison of plate osteosynthesis versus non-operative management for mid-shaft clavicle fractures-A prospective study. Injury. 2018;49(6):1104-1107. [16] Calbiyik M, Ipek D, Taskoparan M. Prospective randomized study comparing results of fixation for clavicular shaft fractures with intramedullary nail or locking compression plate. Int Orthop. 2017;41(1): 173-179. [17] Chen QY, Kou DQ, Cheng XJ, et al. Intramedullary nailing of clavicular midshaft fractures in adults using titanium elastic nail. Chin J Traumatol. 2011;14(5):269-276. [18] Ersen A, Atalar AC, Birisik F, et al. Comparison of simple arm sling and figure of eight clavicular bandage for midshaft clavicular fractures: a randomised controlled study. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B(11):1562-1565. [19] Ferran NA, Hodgson P, Vannet N, et al. Locked intramedullary fixation vs plating for displaced and shortened mid-shaft clavicle fractures: a randomized clinical trial. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19(6):783-789. [20] Hulsmans MH, van Heijl M, Houwert RM, et al. High Irritation and Removal Rates After Plate or Nail Fixation in Patients With Displaced Midshaft Clavicle Fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(2): 532-539. [21] Lee YS, Huang HL, Lo TY, et al. Surgical treatment of midclavicular fractures: a prospective comparison of Knowles pinning and plate fixation. Int Orthop.2008;32(4):541-545. [22] Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society. Nonoperative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. A multicenter, randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(1): 1-10. [23] van der Meijden OA, Houwert RM, Hulsmans M, et al. Operative treatment of dislocated midshaft clavicular fractures: plate or intramedullary nail fixation? A randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(8):613-619. [24] Melean PA, Zuniga A, Marsalli M, et al. Surgical treatment of displaced middle-third clavicular fractures: a prospective, randomized trial in a working compensation population. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015;24(4): 587-592. [25] Narsaria N, Singh AK, Arun GR, et al. Surgical fixation of displaced midshaft clavicle fractures: elastic intramedullary nailing versus precontoured plating. J Orthop Traumatol. 2014;15(3):165-171. [26] Qvist AH, Vaesel MT, Jensen CM, et al. Plate fixation compared with nonoperative treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures: a randomized clinical trial. Bone Joint J. 2018;100-B(10):1385-1391. [27] Robinson CM, Goudie EB, Murray IR, et al. Open reduction and plate fixation versus nonoperative treatment for displaced midshaft clavicular fractures: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(17):1576-1584. [28] Saha P, Datta P, Ayan S, et al. Plate versus titanium elastic nail in treatment of displaced midshaft clavicle fractures: A comparative study. Indian J Orthop.2014;48(6):587-593. [29] Smekal V, Irenberger A, Struve P, et al. Elastic stable intramedullary nailing versus nonoperative treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures-a randomized, controlled, clinical trial. J Orthop Trauma. 2009; 23(2):106-112. [30] Smekal V, Irenberger A, Attal RE, et al. Elastic stable intramedullary nailing is best for mid-shaft clavicular fractures without comminution: results in 60 patients. Injury.2011;42(4):324-329. [31] Tamaoki M, Matsunaga FT, Costa A, et al. Treatment of Displaced Midshaft Clavicle Fractures: Figure-of-Eight Harness Versus Anterior Plate Osteosynthesis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(14):1159-1165. [32] Virtanen KJ, Remes V, Pajarinen J, et al. Sling compared with plate osteosynthesis for treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures: a randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(17):1546-1553. [33] Woltz S, Stegeman SA, Krijnen P, et al. Plate Fixation Compared with Nonoperative Treatment for Displaced Midshaft Clavicular Fractures: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017; 99(2):106-112. [34] Zehir S, Zehir R, Sahin E, et al. Comparison of novel intramedullary nailing with mini-invasive plating in surgical fixation of displaced midshaft clavicle fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015;135(3):339-344. [35] George DM, McKay BP, Jaarsma RL. The long-term outcome of displaced mid-third clavicle fractures on scapular and shoulder function: variations between immediate surgery, delayed surgery, and nonsurgical management. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2015;24(5):669-676. [36] Rosa N, Marta M, Vaz M, et al. Recent developments on intramedullary nailing: a biomechanical perspective. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017;1408(1): 20-31. [37] Naveen BM, Joshi GR, Harikrishnan B. Management of mid-shaft clavicular fractures: comparison between non-operative treatment and plate fixation in 60 patients. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2017; 12(1):11-18. [38] Ozkul B, Saygili MS, Dincel YM, et al. Comparative Results of External Fixation, Plating, or Nonoperative Management for Diaphyseal Clavicle Fractures. Med Princ Pract. 2017;26(5):458-463. [39] McKee MD, Pedersen EM, Jones C, et al. Deficits following nonoperative treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(1):35-40. [40] van der Linde RA, Beetz I, van Helden SH. Plating for midshaft clavicular fractures: The impact on quality of life and functional outcome. Injury. 2017;48(12):2778-2783. [41] Mirzatolooei F. Comparison between operative and nonoperative treatment methods in the management of comminuted fractures of the clavicle. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2011;45(1):34-40. [42] Gausden EB, Villa J, Warner SJ, et al. Nonunion After Clavicle Osteosynthesis: High Incidence of Propionibacterium acnes. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(4):229-235. [43] Chen YF, Wei HF, Zhang C, et al. Retrospective comparison of titanium elastic nail (TEN) and reconstruction plate repair of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(4):495-501. [44] Hussain N, Sermer C, Prusick PJ, et al. Intramedullary Nailing Versus Plate Fixation for the Treatment Displaced Midshaft Clavicular Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:34912. [45] Calbiyik M, Zehir S, Ipek D. Minimally invasive implantation of a novel flexible intramedullary nail in patients with displaced midshaft clavicle fractures. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2016;42(6):711-717. [46] Wang J, Meng XH, Guo ZM, et al. Interventions for treating displaced midshaft clavicular fractures: a Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(11):e595. [47] Turner T, Green S, Tovey D, et al. Producing Cochrane systematic reviews-a qualitative study of current approaches and opportunities for innovation and improvement. Syst Rev. 2017;6(1):147. |
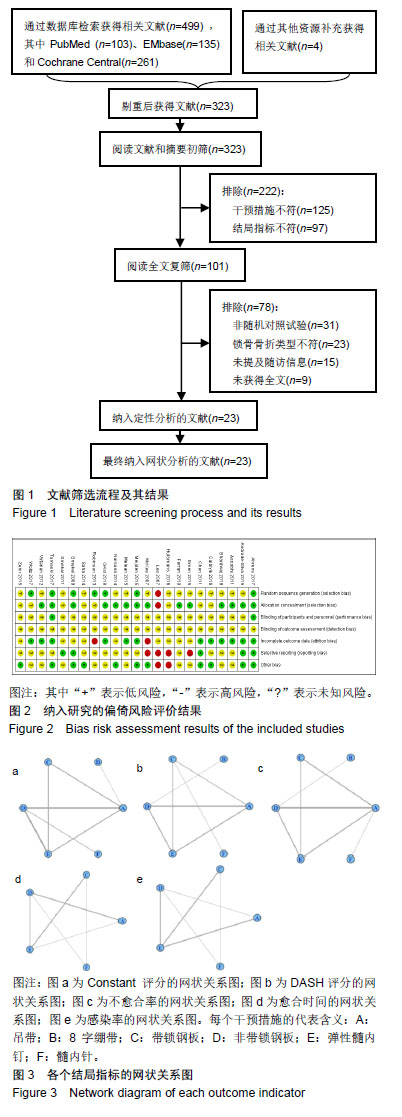
.jpg)
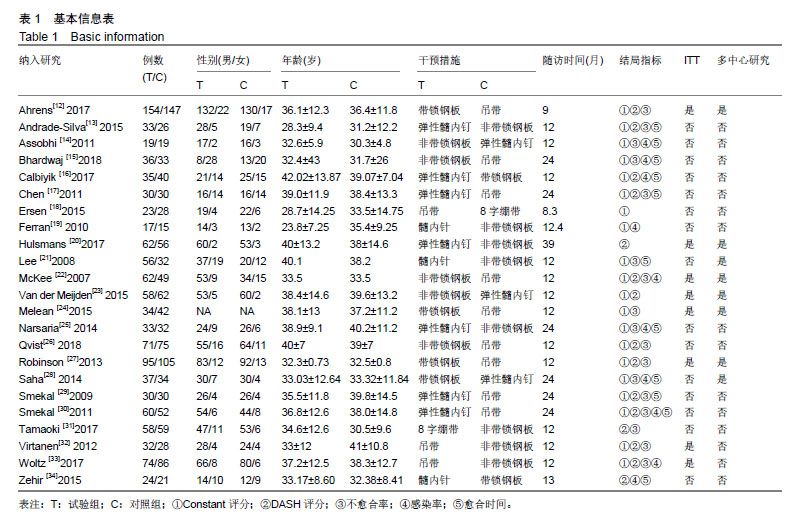
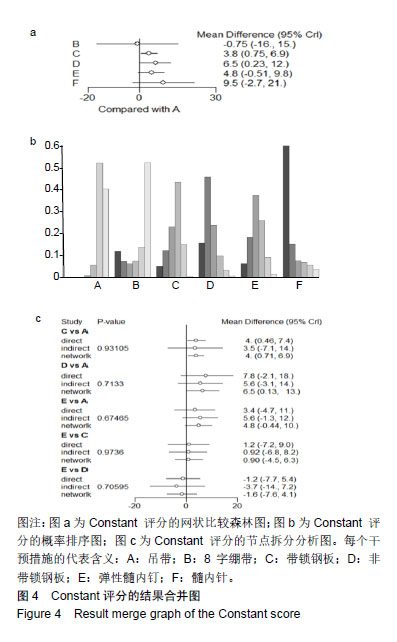
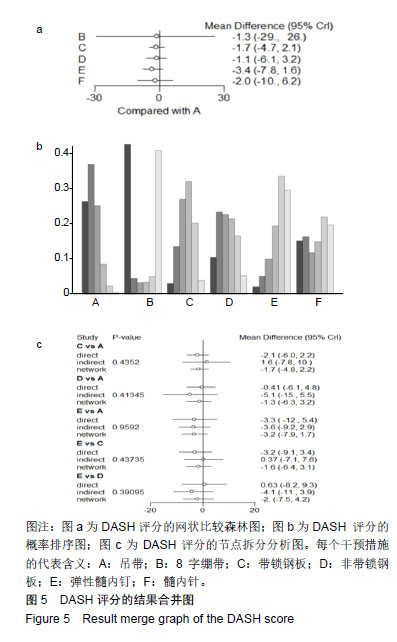
.jpg)