中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (15): 2369-2372.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1163
• 组织构建细胞学实验 cytology experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
豚鼠鼻黏膜成纤维细胞的分离、培养及鉴定
庄翔莉1,吴 博2,陈莹莹3,甘思雨4,林 青5,郑 健1,5
- (1福建中医药大学,福建省福州市 350122;2福建中医药大学附属第二人民医院,福建省福州市 350003;3泉州市中医院,福建省泉州市 362000;4福建中医药大学附属第三人民医院,福建省福州市 350108;5福建中医药大学附属人民医院,福建省福州市 350004)
Isolation, culture and identification of guinea pig nasal mucosa fibroblasts
Zhuang Xiangli1, Wu Bo2, Chen Yingying3, Gan Siyu4, Lin Qing5, Zheng Jian1,5
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
变态反应性鼻炎:又称变应性鼻炎,是特应性个体接触致敏原后由IgE介导的介质(主要是组胺)释放、并有多种免疫活性细胞和细胞因子等参与的鼻黏膜慢性炎症反应性疾病,以鼻痒、喷嚏、鼻分泌亢进、鼻黏膜肿胀等为主要特点。
豚鼠:荷兰猪又名天竺鼠、葵鼠、豚鼠、几内亚猪,在动物学的分类是哺乳纲啮齿目豚鼠科豚鼠属。尽管名字叫“几内亚猪”,但是这种动物既不是猪,也并非来自几内亚。它们的祖先来自南美洲的安第斯山脉,根据生物化学和杂交分析,豚鼠是一种天竺鼠诸如白臀豚鼠(C. aperea)、艳豚鼠(C. fulgida)或草原豚鼠(C. tschudii)等近缘物种经过驯化的后代。豚鼠是珍贵的皮肉兼用的多用途草食动物。荷兰猪成年体质量1.0-1.5 kg,体长20-30 cm,皮毛紧披,富有光泽,种属分布共5属15种,为南美洲特产。
背景:鼻黏膜成纤维细胞可通过分泌多种细胞因子和趋化因子,参与多种鼻部疾病的炎症反应和损伤修复;豚鼠是最适合用于变态反应性疾病研究的实验动物之一。
目的:探讨豚鼠鼻黏膜成纤维细胞分离、培养、纯化和鉴定的有效方法。
方法:胶原酶消化法分离豚鼠鼻黏膜成纤维细胞,经差速贴壁法纯化后,采用倒置相差显微镜进行形态学观察,波形蛋白免疫细胞化学法鉴定成纤维细胞,并通过MTT检测法绘制细胞生长曲线。
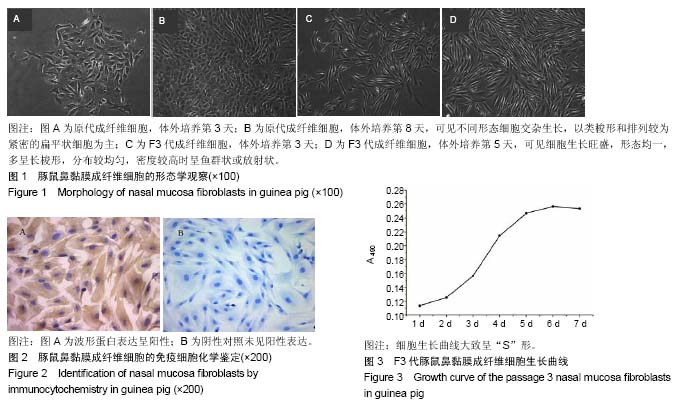
结果与结论:①倒置相差显微镜下可见原代鼻黏膜成纤维细胞中有不同形态细胞交杂生长,以类梭形和扁平状细胞为主,细胞成团散落分布;纯化后的成纤维细胞形态均一,多呈长梭形,分布较均匀,呈鱼群状或放射状排列;②免疫细胞化学染色显示,成纤维细胞波形蛋白表达呈阳性;③细胞生长曲线大致呈“S”形。④结果表明,所分离培养的细胞具有典型的成纤维细胞生物学特征。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-3919-3762(庄翔莉)
中图分类号:
.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
变态反应性鼻炎:又称变应性鼻炎,是特应性个体接触致敏原后由IgE介导的介质(主要是组胺)释放、并有多种免疫活性细胞和细胞因子等参与的鼻黏膜慢性炎症反应性疾病,以鼻痒、喷嚏、鼻分泌亢进、鼻黏膜肿胀等为主要特点。#br#
豚鼠:荷兰猪又名天竺鼠、葵鼠、豚鼠、几内亚猪,在动物学的分类是哺乳纲啮齿目豚鼠科豚鼠属。尽管名字叫“几内亚猪”,但是这种动物既不是猪,也并非来自几内亚。它们的祖先来自南美洲的安第斯山脉,根据生物化学和杂交分析,豚鼠是一种天竺鼠诸如白臀豚鼠(C. aperea)、艳豚鼠(C. fulgida)或草原豚鼠(C. tschudii)等近缘物种经过驯化的后代。豚鼠是珍贵的皮肉兼用的多用途草食动物。荷兰猪成年体质量1.0-1.5 kg,体长20-30 cm,皮毛紧披,富有光泽,种属分布共5属15种,为南美洲特产。#br#
#br#
#br#
文题释义:#br#
变态反应性鼻炎:又称变应性鼻炎,是特应性个体接触致敏原后由IgE介导的介质(主要是组胺)释放、并有多种免疫活性细胞和细胞因子等参与的鼻黏膜慢性炎症反应性疾病,以鼻痒、喷嚏、鼻分泌亢进、鼻黏膜肿胀等为主要特点。#br#
豚鼠:荷兰猪又名天竺鼠、葵鼠、豚鼠、几内亚猪,在动物学的分类是哺乳纲啮齿目豚鼠科豚鼠属。尽管名字叫“几内亚猪”,但是这种动物既不是猪,也并非来自几内亚。它们的祖先来自南美洲的安第斯山脉,根据生物化学和杂交分析,豚鼠是一种天竺鼠诸如白臀豚鼠(C. aperea)、艳豚鼠(C. fulgida)或草原豚鼠(C. tschudii)等近缘物种经过驯化的后代。豚鼠是珍贵的皮肉兼用的多用途草食动物。荷兰猪成年体质量1.0-1.5 kg,体长20-30 cm,皮毛紧披,富有光泽,种属分布共5属15种,为南美洲特产。#br#
#br#