中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (15): 2373-2379.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1170
• 组织构建与生物活性因子 tissue construction and bioactive factors • 上一篇 下一篇
神经生长因子β对椎管内神经鞘瘤细胞增殖的影响
陈德平1,刘盛泽1,陈 实1,从长春2,刘树义3,肖 颖4
- (厦门大学附属福州第二医院,1神经外科,4病理科,福建省福州市 350007;2厦门大学附属翔安医院神经外科,福建省厦门市 361000;3西安医学院,陕西省西安市 710000)
Effect of nerve growth factor-beta on proliferation of intraspinal schwannomas
Chen Deping1, Liu Shengze1, Chen Shi1, Cong Changchun2, Liu Shuyi3, Xiao Ying4
- (1Department of Neurosurgery, 4Department of Pathology, Fuzhou Second Hospital Affiliated to Xiamen University, Fuzhou 350007, Fujian Province, China; 2Department of Neurosurgery, Xiang’an Hospital Affiliated to Xiamen University, Xiamen 361000, Fujian Province, China; 3Xi’an Medical University, Xi’an 710000, Shaanxi Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
椎管内神经鞘瘤:又名椎管内许旺细胞瘤,在脊髓肿瘤中发病率占首位,整个椎管的各个节段均可发生,大多为单发,好发于脊髓外硬膜下,多位于脊髓的侧面,起源于脊神经根,多数为良性肿瘤,极少数可发展为恶性肿瘤,多见于成年人,性别差异不大。临床表现为肢体麻木、疼痛、无力以及尿便功能障碍等。
NGF/TrkA信号通路:神经生长因子(Nerve Growth Factor,NGF)结合TrkA 受体可导致受体二聚化,激活内在激酶活性,从而引起多种信号通路的激活,包括RAS/MAPK,PI3K/AKT 和PLCγ通路等,该信号通路与肿瘤发生、增殖、血管生成以及转移等相关,且目前对该信号通路的研究主要集中于人的恶性肿瘤,如胃癌、结直肠癌、胰腺癌、乳腺癌等。
.jpg)
文题释义:
椎管内神经鞘瘤:又名椎管内许旺细胞瘤,在脊髓肿瘤中发病率占首位,整个椎管的各个节段均可发生,大多为单发,好发于脊髓外硬膜下,多位于脊髓的侧面,起源于脊神经根,多数为良性肿瘤,极少数可发展为恶性肿瘤,多见于成年人,性别差异不大。临床表现为肢体麻木、疼痛、无力以及尿便功能障碍等。
NGF/TrkA信号通路:神经生长因子(Nerve Growth Factor,NGF)结合TrkA 受体可导致受体二聚化,激活内在激酶活性,从而引起多种信号通路的激活,包括RAS/MAPK,PI3K/AKT 和PLCγ通路等,该信号通路与肿瘤发生、增殖、血管生成以及转移等相关,且目前对该信号通路的研究主要集中于人的恶性肿瘤,如胃癌、结直肠癌、胰腺癌、乳腺癌等。
摘要
背景:研究已经证实,在人的良恶性肿瘤中NGF/TrkA信号通路促进肿瘤细胞增殖、分化的效应与PI3K/AKT信号通路密切相关,然而,关于NGF/TrkA信号通路在椎管内神经鞘瘤发病机制的研究甚少。
目的:观察神经生长因子β对椎管内神经鞘瘤细胞增殖的影响及初步研究NGF/TrkA信号通路在椎管内神经鞘瘤中的发病机制。
方法:收集肿瘤标本并消化培养获得高纯度肿瘤细胞作为实验细胞;分别给予细胞不同浓度的神经生长因子β(15,30,60,120,240 μg/L)、K252a(100,200,300,400,500,600 nmol/L)、LY294002(10,20,30,40,50,60 μmol/L)、神经生长因子β(120 μg/L)+K252a(TrkA受体抑制剂,400 nmol/L)、神经生长因子β(120 μg/L)+LY294002(PI3K抑制剂,50 μmol/L)作用一定时间;通过MTT法评估细胞增殖情况,Western blot检测TrkA、AKT、p-AKT(Ther308)、p-GSK-3β蛋白质的表达情况,RT-PCR检测TrkA、AKT蛋白质对应的mRNA表达情况。
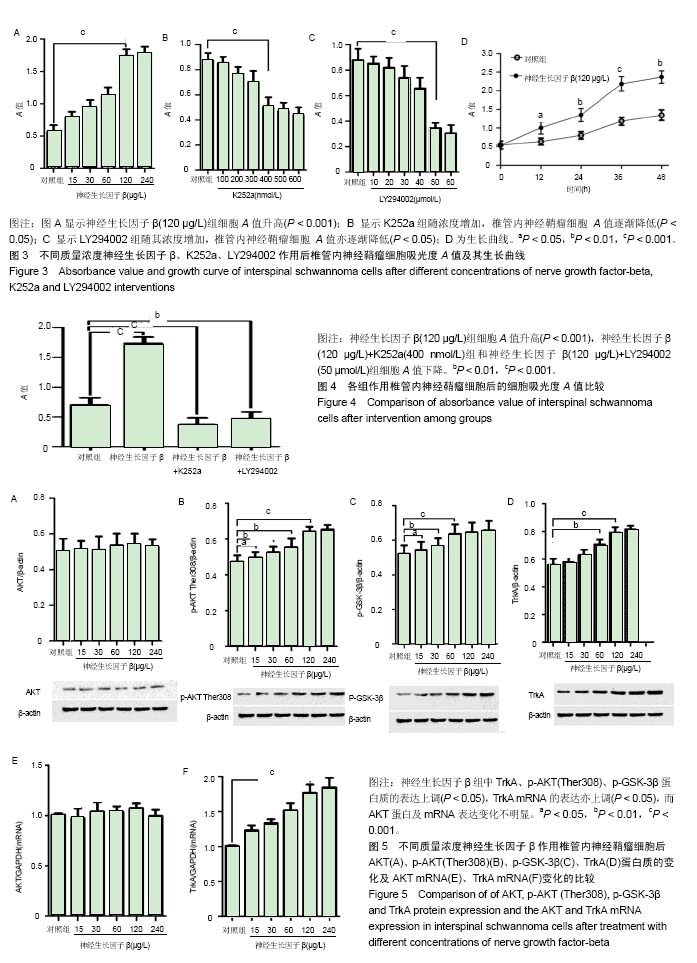
结果与结论:①与对照组比较,神经生长因子β组细胞吸光值(A值)随神经生长因子β的质量浓度增加而升高(P < 0.05),于120 μg/L时升高幅度最大(P < 0.001),K252a、LY294002组细胞A值不断下降(P < 0.05),分别于浓度400 nmol/L、50 μmol/L时下降幅度最大(P < 0.001);②神经生长因子β组中TrkA、p-AKT (Ther308)、p-GSK-3β蛋白质的表达上调(P < 0.05),TrkA mRNA的表达也上调(P < 0.05);③神经生长因子β(120 μg/L)+K252a(400 nmol/L)组细胞A值下降(P < 0.001),TrkA、p-AKT(Ther308)、p-GSK-3β蛋白质的表达下调(P < 0.05),TrkA mRNA的表达亦下调(P < 0.05);④神经生长因子β(120 μg/L)+LY294002 (50 μmol/L)组细胞A值下降(P < 0.01),p-AKT(Ther308)、p-GSK-3β蛋白质的表达下调(P < 0.05);⑤各组中AKT蛋白质及其对应的mRNA的表达无明显变化(P > 0.05);⑥结果表明,神经生长因子β能够促进椎管内神经鞘瘤细胞增殖,其增殖可能与NGF/TrkA信号通路中TrkA、p-AKT(Ther308)及p-GSK-3β等蛋白质的表达水平有关。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-7866-477X(陈德平)
背景:研究已经证实,在人的良恶性肿瘤中NGF/TrkA信号通路促进肿瘤细胞增殖、分化的效应与PI3K/AKT信号通路密切相关,然而,关于NGF/TrkA信号通路在椎管内神经鞘瘤发病机制的研究甚少。
目的:观察神经生长因子β对椎管内神经鞘瘤细胞增殖的影响及初步研究NGF/TrkA信号通路在椎管内神经鞘瘤中的发病机制。
方法:收集肿瘤标本并消化培养获得高纯度肿瘤细胞作为实验细胞;分别给予细胞不同浓度的神经生长因子β(15,30,60,120,240 μg/L)、K252a(100,200,300,400,500,600 nmol/L)、LY294002(10,20,30,40,50,60 μmol/L)、神经生长因子β(120 μg/L)+K252a(TrkA受体抑制剂,400 nmol/L)、神经生长因子β(120 μg/L)+LY294002(PI3K抑制剂,50 μmol/L)作用一定时间;通过MTT法评估细胞增殖情况,Western blot检测TrkA、AKT、p-AKT(Ther308)、p-GSK-3β蛋白质的表达情况,RT-PCR检测TrkA、AKT蛋白质对应的mRNA表达情况。
结果与结论:①与对照组比较,神经生长因子β组细胞吸光值(A值)随神经生长因子β的质量浓度增加而升高(P < 0.05),于120 μg/L时升高幅度最大(P < 0.001),K252a、LY294002组细胞A值不断下降(P < 0.05),分别于浓度400 nmol/L、50 μmol/L时下降幅度最大(P < 0.001);②神经生长因子β组中TrkA、p-AKT (Ther308)、p-GSK-3β蛋白质的表达上调(P < 0.05),TrkA mRNA的表达也上调(P < 0.05);③神经生长因子β(120 μg/L)+K252a(400 nmol/L)组细胞A值下降(P < 0.001),TrkA、p-AKT(Ther308)、p-GSK-3β蛋白质的表达下调(P < 0.05),TrkA mRNA的表达亦下调(P < 0.05);④神经生长因子β(120 μg/L)+LY294002 (50 μmol/L)组细胞A值下降(P < 0.01),p-AKT(Ther308)、p-GSK-3β蛋白质的表达下调(P < 0.05);⑤各组中AKT蛋白质及其对应的mRNA的表达无明显变化(P > 0.05);⑥结果表明,神经生长因子β能够促进椎管内神经鞘瘤细胞增殖,其增殖可能与NGF/TrkA信号通路中TrkA、p-AKT(Ther308)及p-GSK-3β等蛋白质的表达水平有关。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-7866-477X(陈德平)
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
椎管内神经鞘瘤:又名椎管内许旺细胞瘤,在脊髓肿瘤中发病率占首位,整个椎管的各个节段均可发生,大多为单发,好发于脊髓外硬膜下,多位于脊髓的侧面,起源于脊神经根,多数为良性肿瘤,极少数可发展为恶性肿瘤,多见于成年人,性别差异不大。临床表现为肢体麻木、疼痛、无力以及尿便功能障碍等。#br#
NGF/TrkA信号通路:神经生长因子(Nerve Growth Factor,NGF)结合TrkA 受体可导致受体二聚化,激活内在激酶活性,从而引起多种信号通路的激活,包括RAS/MAPK,PI3K/AKT 和PLCγ通路等,该信号通路与肿瘤发生、增殖、血管生成以及转移等相关,且目前对该信号通路的研究主要集中于人的恶性肿瘤,如胃癌、结直肠癌、胰腺癌、乳腺癌等。#br#
#br#
#br#
文题释义:#br#
椎管内神经鞘瘤:又名椎管内许旺细胞瘤,在脊髓肿瘤中发病率占首位,整个椎管的各个节段均可发生,大多为单发,好发于脊髓外硬膜下,多位于脊髓的侧面,起源于脊神经根,多数为良性肿瘤,极少数可发展为恶性肿瘤,多见于成年人,性别差异不大。临床表现为肢体麻木、疼痛、无力以及尿便功能障碍等。#br#
NGF/TrkA信号通路:神经生长因子(Nerve Growth Factor,NGF)结合TrkA 受体可导致受体二聚化,激活内在激酶活性,从而引起多种信号通路的激活,包括RAS/MAPK,PI3K/AKT 和PLCγ通路等,该信号通路与肿瘤发生、增殖、血管生成以及转移等相关,且目前对该信号通路的研究主要集中于人的恶性肿瘤,如胃癌、结直肠癌、胰腺癌、乳腺癌等。#br#
#br#