[1] AHN Y. Percutaneous endoscopic decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2014;11(6):605-616.
[2] NELLENSTEIJN J, OSTELO R, BARTELS R, et al. Transforaminal endoscopic surgery for symptomatic lumbar disc herniations: a systematic review of the literature. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(2):181-204.
[3] 丁宇,张建军,崔洪鹏,等.双管大通道椎板间内镜术式治疗腰椎管狭窄症[J].转化医学杂志,2018,7(5):289-293.
[4] 陈康,曾建成,修鹏,等.经皮椎板间入路内镜下椎管减压治疗老年腰椎侧隐窝狭窄症[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(8):458-467.
[5] 吴俊龙,张超,周跃.微创脊柱内镜技术的发展现状与展望[J].骨科,2016, 7(1):65-68.
[6] ZHANG JJ, CUI HP, DING Y, et al. Endoscopic Foraminoplasty and Neuro-Ventral Decompression for the Treatment of Lumbar Disc Herniation Combining with Lateral Recess Stenosis. J Spine. 2018; 7(2): 412-417.
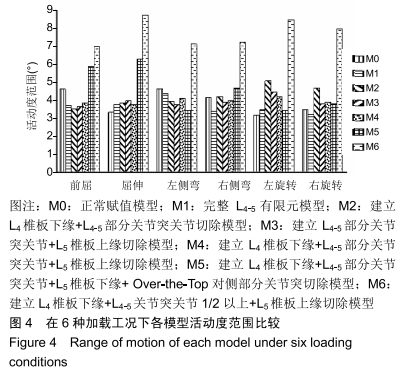
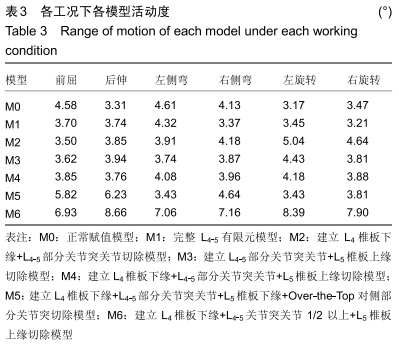
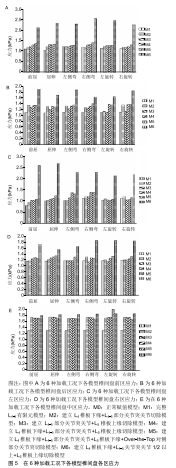
[7] 文毅,苏峰,刘肃,等.L4-5椎体有限元模型建立及退变椎间盘力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(8):1222-1227.
[8] 王加谋,陈超,李前龙,等.退变椎间盘在骨质疏松椎体应力分布中作用的有限元方法研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2007,15(7):41-44.
[9] KOPPERDAHL DL, MORGAN EF, KEAVENY TM. Quantitative computed tomography estimates of the mechanical properties of human vertebral trabecular bone. J Orthop Res. 2002;20(4):801-805.
[10] 郑琦,廖胜辉,石仕元,等.有限元模拟复杂性腰椎管狭窄症减压手术[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2013,30(1):45-51.
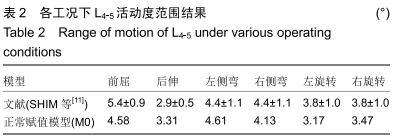
[11] SHIM CS, PARK SW, LEE SH, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of an interspinous stabilizing device, Locker. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33(22):E820-827.
[12] DING Y, ZHU TY, ZHANG JJ, et al. Percutaneous endoscopicinter laminar approach: medial foraminal decompression in treating lumbar disc herniation or spinal stenosis. J Spine. 2017; 6: 375-381.
[13] SHAMJI MF, MROZ T, HSU W, et al. Management of Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis in the Elderly. Neurosurgery. 2015;77 Suppl 4:S68-74.
[14] 赵太茂,邱贵兴,仉建国,等. 291例腰椎管狭窄症患者的临床特点分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006,16(11):812-815.
[15] MINAMIDE A, SIMPSON AK, OKADA M, et al. Microendoscopic Decompression for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis With Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: The Influence of Spondylolisthesis Stage (Disc Height and Static and Dynamic Translation) on Clinical Outcomes. Clin Spine Surg. 2019;32(1):E20-E26.
[16] SUN W, XUE C, TANG XY, et al. Selective versus multi-segmental decompression and fusion for multi-segment lumbar spinal stenosis with single-segment degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):46.
[17] 梁海峰,陆顺一,刘书豪,等.高龄腰椎管狭窄症患者的手术方式选择及疗效[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2018,28(8):705-712.
[18] 孙凤龙,李军,梁庆晨,等.开放手术与脊柱内镜下行椎板减压治疗退变性腰椎管狭窄症的临床对照研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2018,11(11): 805-811.
[19] CAO S, CUI H, LU Z, et al. "Tube in tube" interlaminar endoscopic decompression for the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis: Technique notes and preliminary clinical outcomes of case series. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(35):e17021.
[20] PAHOLPAK P, DEDEOGULLARI E, LEE C, et al. Do modic changes, disc degeneration, translation and angular motion affect facet osteoarthritis of the lumbar spine. Eur J Radiol. 2018;98:193-199.
[21] 徐云峰,乐晓峰,刘波,等.腰椎关节突关节的解剖学特征、生物力学特性、退变影响因素及表现研究进展[J].山东医药, 2018,58(23):116-119.
[22] SHIRAZI-ADL A. Finite-element evaluation of contact loads on facets of an L2-L3 lumbar segment in complex loads. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1991;16(5):533-541.
[23] 周跃,罗刚,初同伟,等. 腰椎单侧小关节突分级切除的生物力学影响及微创外科的修复与重建[J].中华医学杂志,2007,87(19):1334-1338.
[24] STERBA M, AUBIN CÉ, WAGNAC E, et al. Effect of impact velocity and ligament mechanical properties on lumbar spine injuries in posterior-anterior impact loading conditions: a finite element study. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2019;57(6):1381-1392.
[25] IVANOV A, FAIZAN A, SAIRYO K, et al. Minimally invasive decompression for lumbar spinal canal stenosis in younger age patients could lead to higher stresses in the remaining neural arch-a finite element investigation. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2007;50(1):18-22.
[26] 秦大平,张晓刚,宋敏,等.有限元分析在骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折脊柱力学动态变化中的应用[J].中华中医药杂志,2019,34(1):206-211.
[27] 王子平,陆耀刚,崔崟,等.腰椎间盘突出症与腰椎管腔狭窄症伴马尾综合征[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2006,21(11):924-925.
[28] LEE JH, SIM KC, KWON HJ, et al. Effectiveness of lumbar epidural injection in patients with chronic spinal stenosis accompanying redundant nerve roots. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(9):e14490.
[29] MATSUWAKA ST, LIEM BC. The Role of Exercise in Treatment of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Symptoms. Current Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Reports. 2018;6(1):36-44.
|