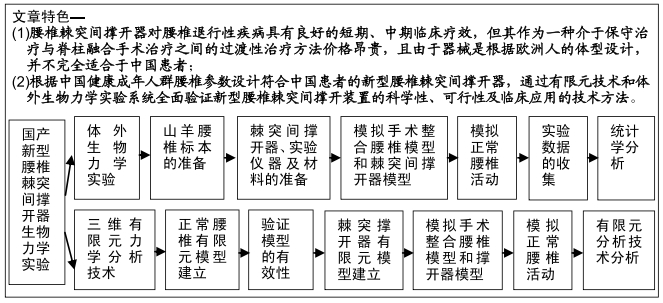
1.1 设计 模型研究与基础研究。
1.2 时间及地点 于2016年3月至2018年4月在哈尔滨医科大学附属第一医院骨一科病房和门诊进行“国产新型腰椎棘突间撑开器有限元分析”课题相关资料的采集和三维有限元生物力学分析。于2018年6月至11月在天津市骨科研究所(室内温度为22 ℃,湿度50%)进行“国产新型腰椎棘突间撑开器体外生物力学实验”的具体实施和数据采集、统计学分析。
1.3 材料 获取60名志愿者的脊柱CT数据,男女各30名,年龄18-50岁,平均年龄在36岁左右;体质量40-80 kg,平均65 kg;身高155-175 cm,平均162 cm。首先,排除脊柱病理、骨质疏松、退化、创伤、肿瘤等病理的变化人群。与患者预先签署检查知情同意书并详细告知在连续螺旋CT扫描机上进行T12-S1扫描有CT辐射危险性,向其详细说明辐射的危害性。实验获得哈尔滨医科大学附属第一医院伦理委员会批准。选取24只成年、同龄、同体质量雄性山羊,由哈尔滨天阳禽类屠宰场提供,体质量约50 kg,所有山羊同时间宰杀并取其腰椎,样本拍摄X射线排除肿瘤、畸形等先天性疾病。
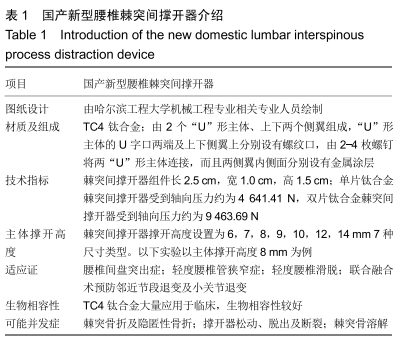
国产新型腰椎棘突间撑开器介绍见表1。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 国产新型腰椎棘突间撑开器的有限元分析 正常腰椎三维有限元模型建立:记录每位志愿者的性别、年龄。志愿者躺于CT机上,采取平躺放松的姿势,保持自然生理弯曲以进行扫描。采用连续螺旋CT(Light
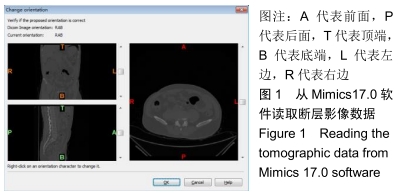
Speed 64,GE,美国)进行T12-S1断层扫描,扫描条件:电压120 kV、层厚0.625 mm、矩阵512×512,将扫描结果用DICOM格式保存。DICOM文件可以通过导入Mimics17.0进而实现对目标位置的三位重构。将CT文件导入Mimics17.0之后,软件会自动读取CT文件中的层距、像素等信息,从图中可以看出明显的颜色差异,其中白色代表骨骼,黑色为空气,其余影像单位为软组织,见图1。
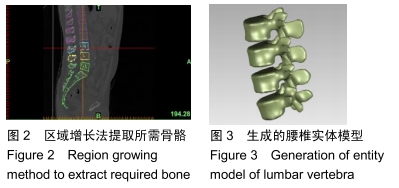
读取断层影像数据区域增长分割出腰椎骨组织,利用不同的颜色形成不同的蒙面,由于CT拍摄质量或不同位置灰度接近,在区域增长、广泛时偶尔会选择到预期之外的骨骼。对CT分析结果进行分析,通过边缘分割、除噪等特殊手法排除冗余信息,对最终数据开展三维表面重建,得出L2-L5椎体三维模型。生成三维模型如图2所示。
以stl格式保存建成的三维模型。stl文件无法被主流CAD软件直接进行编辑,需要导入Geomagic12进行逆向工程,生成实体。采取网格医生命令修复生成实体中的不良面;通过去除特征命令删除不必要的特征,对模型进行简化;调整模型表面的光滑度,简化三角面;采用自动及手工添加的方式确定模型的关键点,根据关键点连接形态曲线,据此构建曲面,进而生成实体模型,见图3。
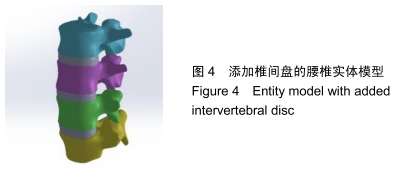
将生成的实体模型另存为step格式导入solidworks中,手工添加椎间盘,并划分出髓核和纤维环,见图4。
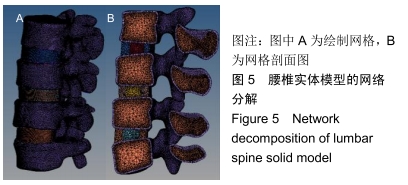
将图4导入Hypermesh中并进行网络分解,最终结合解剖情况,划分为四面体单元,划分结果,见图5。
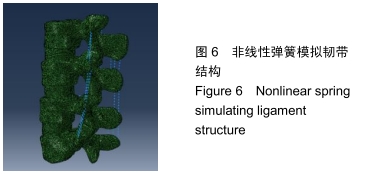
将Hypermesh生成的网格另存为inp文件,导入ABAQUS6.14中,用非线性弹簧单元模拟韧带结构,见图6。
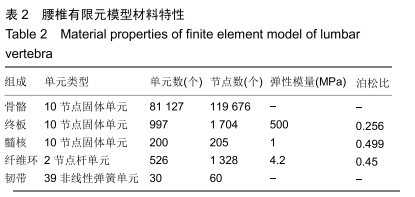
模型材料属性的定义:人体脊柱的结构复杂,而且各部分的功能、材质都有较大区别,因此椎体的模型材料各个部分的材质并不均一,根据目前的经验数据,得出腰椎有限元模型材料特性赋值,见表2。
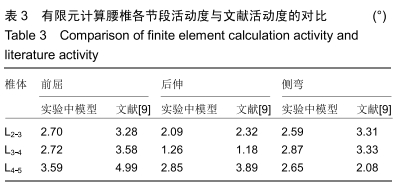
有限元模型的有效性验证:目前有限元模型主要应用于新型医学发现的验证领域,为现代医学的临床实践提供相应的特性分析依据,要取得良好的模拟效果,必须保证有限元模型与临床上的结果高度相符,因此应该对有限元技术进行模型验证。基于此进行如下实验,根据上文定义的相应约束条件与荷载情况,将相应模型在Ahaqus中进行求解,求出垂直载荷+前屈扭矩、垂直载荷+后伸扭矩、垂直载荷+侧弯扭矩、垂直载荷+旋转扭矩4种荷载情况下对应的腰椎活动范围,并于之前的研究对比,通过比对结果来分析模型的可靠性。
国产新型腰椎棘突间撑开器模型的建立:首先使用SolidWorks完成对撑开器的建模过程,另存为step文件。将step文件导入ABAQUS中进行材质赋予,施加载荷和边界条件,划分网格并添加接触关系,完成有限元模型的建立。
国产新型棘突间撑开器腰椎非融合系统模型的建立:对撑开器模型进行适当的简化,在SolidWorks中完成对撑开器和脊椎模型的装配并导入Hypermesh完成网格的划分,最后将网格文件导入abaqus6.14完成材料属性定义、边界条件和接触设置。L3、L4棘突与撑开器上下表面为接触,L4、L5棘突与撑开器左右两翼内侧面为接触。完成了撑开器植入下腰椎的有限元模型见图7。
定义接触、边界条件和载荷:对相关的接触、边界条件和荷载定义如下,定义椎间盘与椎体之前的软骨终版存在的上下关系为tie,定义L4关节突和L5关节突之间的相邻面为接触,将有接触关系的上面关节与下面关节定义为限制性滑动。据此开展实验,认定L5椎体下终板不发生移动,即使外加应力,在其受力的各个角度也不存在活动度。同时出于贴近实践考虑,使得L2上终板与椎体之间相应位置耦合,再施加相应的荷载。研究共施加4种载荷:①垂直载荷+前屈扭矩:其中垂直荷载为将400 N的力施加于L4椎体相应位置,前屈扭矩为将7.5 N的前屈力施加于L4椎体相应位置;②垂直载荷+后伸扭矩:其中垂直荷载为将400 N的力施加于L4椎体相应位置,后伸扭矩为将7.5 N的后伸力施加于L4椎体相应位置;③垂直载荷+侧弯扭矩:其中垂直荷载为将400 N的力施加于L4椎体上方相应位置,侧弯扭矩为将7.5 N的侧屈力施加于L4椎体相应位置;④垂直载荷+旋转扭矩:其中垂直荷载为将400 N的力施加于L4椎体上方相应位置,旋转扭矩为将7.5 N的旋转力施加于L4椎体相应位置,见图8。

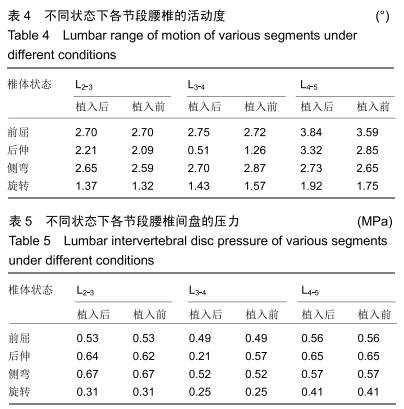
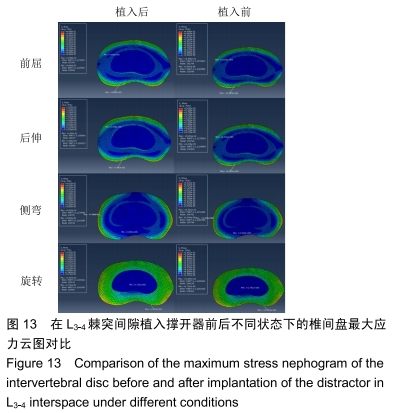
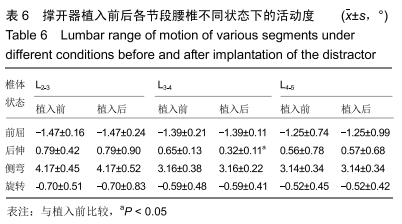
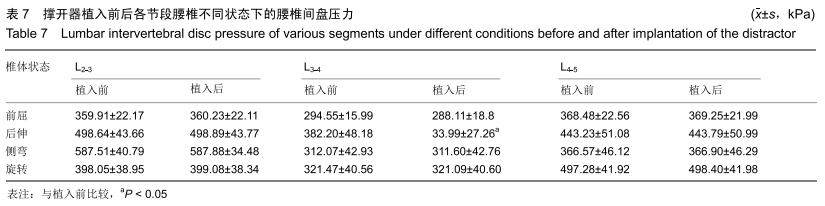
主要观察指标:在腰椎前屈、后伸、侧弯和旋转等活动下,腰椎L2-3、L3-4、L4-5不同节段在撑开器植入前与植入后的活动度与椎间盘压力变化情况。
1.4.2 国产新型腰椎棘突间撑开器体外生物力学分析
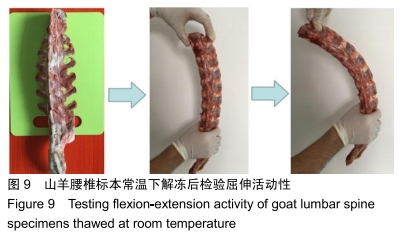
山羊腰椎标本的制备:通过手术刀及组织剪等彻底清理24只山羊腰椎周围的肌肉组织,对于椎间盘、关节突关节、棘间韧带和棘上韧带进行合理的保护,对标本进行包埋完成后用病理袋密封标本,存放在-20 ℃的冰箱内待测试。生物力学实验前自然解冻12-18 h,屈伸活动良好方可实验,见图9。
新型腰椎棘突间撑开器的制备与植入:国产新型腰椎棘突间撑开器由2个“U”形主体、上下2个侧翼组成,这样能更好的贴合腰椎棘突的生理曲度。在“U”形主体的U字口两端及上下侧翼上分别设有螺纹口,由2-4枚螺钉将两“U”形主体连接,而且两侧翼内侧面分别设有金属涂层,便于棘突与撑开器骨性融合,以此来弥补国外棘突间撑开器高松动率的缺点,减少二次翻修的可能,见图10。其材质为钛合金[创生医疗器械(中国)有限公司]制成,钛合金在骨关节耗材中早已应用于临床,其生物惰性已经得到验证,可以显著缩短研究周期。根据不同山羊腰椎棘突的要求通过3D打印技术打印出不同型号撑开器。此外还需要相关的手术器械,包括游标卡尺、咬骨钳、手术刀等,通过手术器械去除适量的肌肉暴露山羊腰椎关节囊,L3-4棘突间去除棘间韧带,保留棘上韧带,使撑开器支撑高度等于或略大于中立位棘突间高度,可均匀分担椎间盘后环及关节突关节应力[5],植入距离是U型顶端距离硬脊膜≤5 mm,过深或过浅会出现不同的并发症[6]。植入过程见图11所示。实验分组:每一具标本先经过完整状态测试,即完整状态组;测试完成后,于L3-4棘突间隙植入国产新型棘突间撑开器按照同样的方法测试,即撑开器植入组。

力学加载方法:在MTS 858 Bionix II脊柱运动测试系统(美国MTS公司)上进行力学加载,所有标本均被控制在扭矩大小为4 N·m、恒定轴向压力40 N的858 Bionix II脊柱运动测试系统机器(美国MTS公司)上[7],每组动作重复3次,测定脊柱前屈、后伸、侧弯、轴向旋转的活动度,为了保证数据的准确性,取各方向运动时第3次数据进行分析,消除样本蠕变带来的影响。校正NDI
Optrotrak Certus三维动态捕捉系统(加拿大NDI公司),定义空间X轴、Y轴和Z轴。后伸(+),前屈(-);左侧弯(+),右侧弯(-);左侧旋(+),右侧旋(-)以上为脊柱运动角度的正负值。L1-L5双侧的横突均贴有一个红外线发光二极管(marker点),每一个marker点的运动轨迹都可以反映在NDI Optrotrak Certus三维动态捕捉系统中。根据数学公式计算出撑开器植入前后腰椎活动度。手术刀于待测定的椎间盘中央作一平行于终板长约1 cm长水平切口,将间盘压力测试针头(直径约1 mm)平行椎体终板刺入椎间盘后环,连接好Gaeltec专用&通用目标传感器(英国Gaeltec Devices公司)测定相应椎间盘内压。整个测试过程中始终保持测试针头置于椎间盘的后环位置。测量L2-3、L3-4、L4-5椎间盘压力值。每5 min向已解冻的标本喷水一次, 以防止标本脱水或退化[8],见图12所示。

主要观察指标:在前屈、后伸、侧弯和旋转等活动下,腰椎L2-3、L3-4、L4-5不同节段植入撑开器前后的活动度与椎间盘压力对比情况。
1.5 统计学分析 应用SPSS 20.0软件对数据进行统计学分析,撑开器植入前后腰椎的活动度、椎间盘负荷的数据采用以x(_)±s表示。已行方差齐性检验,符合正态分布,采用配对样本t 检验对植入前后的数据进行分析;以P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。