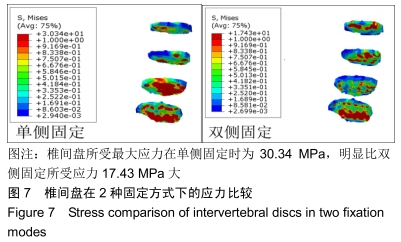
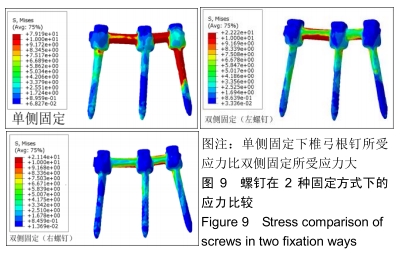
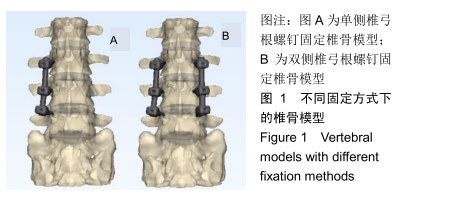
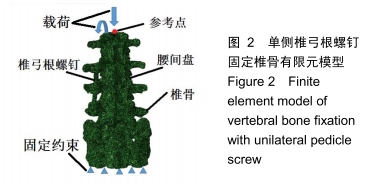
[1] 阎崇楠,王欢,范波,等.前凸弯棒预加压固定对胸腰段椎体骨折复位稳定的影响[J].中华创伤杂志,2017,33(1):19-25.
[2] LI Y, LEWIS G. Influence of surgical treatment for disc degeneration disease at C5-C6 on changes in some biomechanical parameters of the cervical spine. Med Eng Phys. 2010;32(6):595-603.
[3] SHIN DS, LEE K, KIM D. Biomechanical study of lumbar spine with dynamic stabilization device using finite element method. Computer Aided Design. 2007;39:559-567.
[4] COOMBS DJ, RULLKOETTER PJ, LAZ PJ. Efficient probabilistic finite element analysis of a lumbar motion segment. J Biomech. 2017;61: 65-74.
[5] 魏兵,许泽川,常山.有限元法分析腰椎椎弓根螺钉的生物力学特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(19):145-150.
[6] 漆伟,雷伟,严亚波.椎弓根螺钉长度变化对螺钉-骨复合体模型应力影响的三维有限元分析研究[J].医用生物力学,2010,25(3):206-211.
[7] 王博文,吴子祥,冯亚非,等.新型无尾帽自锁式椎弓根钉的设计与有限元力学分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019,34(1):11-14.
[8] ROHLMANN A , BOUSTANI HN , BERGMANN G , et al. A probabilistic finite element analysis of the stresses in the augmented vertebral body after vertebroplasty. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(9):1585-1595.
[9] 王宇,靳安民,方国芳,等.腰椎椎弓根螺钉系统断裂的三维有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2008,12(48):9439-9442.
[10] 黄菊英,李海云,菅凤增,等.腰椎间盘突出症有限元模型的建立与分析[J]. 中国现代神经疾病杂志,2012,12(4):394-398.
[11] 郭丹青,张顺聪,梁德,等.后路椎弓根螺钉钉道强化内固定治疗骨质疏松性椎体骨折的中长期临床疗效分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2019,29(1):41-48.
[12] 李青松,刘少喻,尹宗生.多节段腰椎后路椎体间及后外侧融合椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗老年骨质疏松骨折合并胸腰椎后凸畸形[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(4):26-31.
[13] 任亚明,罗杨,刘达,等. PMMA剂量和分布对重度骨质疏松人工骨中椎弓根螺钉稳定性的作用研究[J].安徽医学,2019,40(1):14-18.
[14] 曾忠友,汤永华,陈国军,等. 单侧椎板关节突螺钉固定与双侧椎弓根螺钉固定应用于下腰椎退变性疾病的比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(3): 216-221.
[15] 王辉,谭家昌,杨有猛,等.单侧椎弓根螺钉联合对侧椎板关节突螺钉固定微创治疗腰椎退行性疾病[J].颈腰痛杂志,2013,34(4):282-286.
[16] 于其华,刘旭,姚先杰,等.单、双侧钉棒内固定加椎间融合治疗退行性腰椎失稳症的疗效比较[J].颈腰痛杂志,2010,31(2):128-130.
[17] 葛鹏,申才良.腰椎融合器材料的发展、现状和进展[J].北方药学,2013, 10(5):47-48.
[18] WALKER MD, MCMAHON DJ, UDESKY J, et al. Application of high-resolution skeletal imaging to measurements of volumetric BMD and skeletal microarchitecture in ChineseAmerican and white women: explanation of a paradox.J Bone Miner Res. 2009;24(12): 1953-1959.
[19] 胡迎春,余兵浩,欧亚龙.人体腰椎节段CT图像的反求建模和有限元分析[J].广西科技大学学报,2014,25(2):13-16.
[20] 仰嘉轩,郭海玲,毛敦,等.骨质疏松症患者腰椎有限元模型的建立与骨强度分析[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2017,25(5):17-21.
[21] 张迪.颈腰椎脊柱内固定解剖和临床研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2018.
[22] 魏兵.脊柱骨折后路置钉方式的有限元研究[D].成都:成都医学院,2018.
[23] 杨伟铭,林定坤.单侧椎弓根螺钉固定椎间融合技术的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,5(5):462-464.
[24] 赵慧清,徐义春,侯刚,等.单侧与双侧椎弓根螺钉固定治疗腰椎退行性疾病的疗效比较[J]. 医药, 2015,7(19):167-168.
[25] 付喜良.胸腰椎骨折椎弓根螺钉植入方法[C]//中国中西医结合学会脊柱医学专业委员会学术年会暨湖南省中西结合医学会脊柱医学专业委员会成立大会, 2010.
[26] 何蔚.腰椎单侧及双侧椎弓根螺钉固定椎间融合术的生物力学和临床研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2009.
[27] NATARAJAN RN. Finite element model of a lumbar spinal motion segment to predict circadian variation in stature.Comput Struct.2003; 81:835-842.
[28] SU J, LI Z, CAO L. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of lumbar vertebra loaded by static stress and its biomechanical significance original research article. Chin J Traumatol.2009;12:153-156.
[29] 李斌,赵文志,陈秉智,等.人工椎间盘植入术后颈椎邻近节段生物力学变化的有限元分析[J].医用生物力学,2010,25(2):94-99.
|