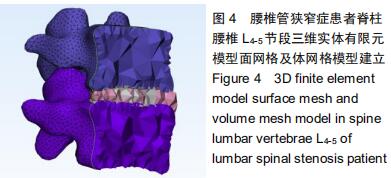
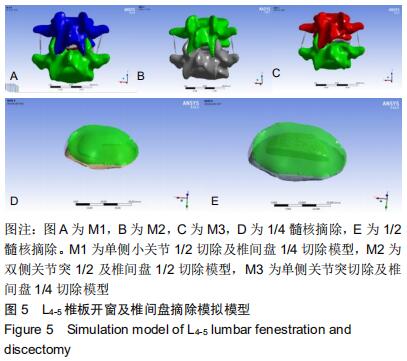
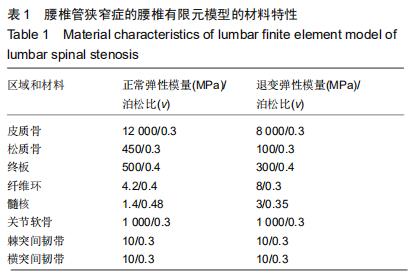
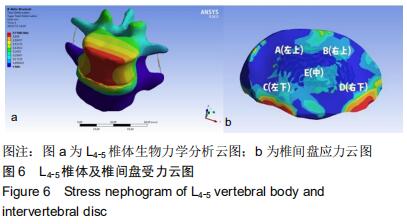
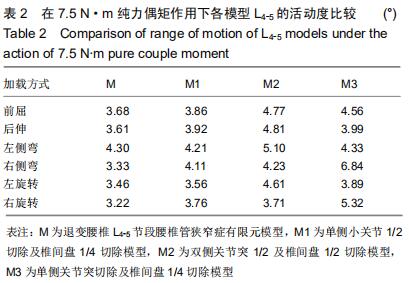
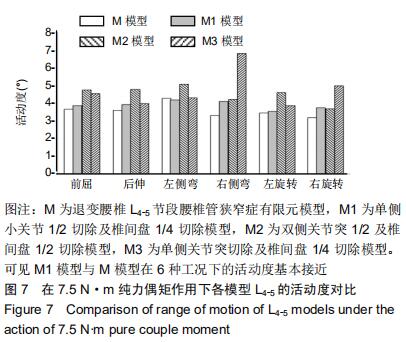
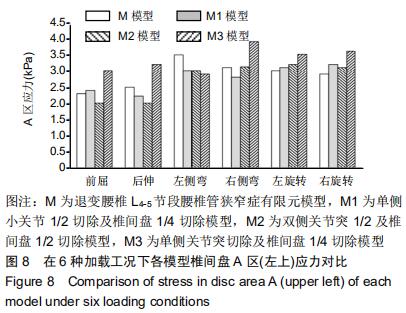
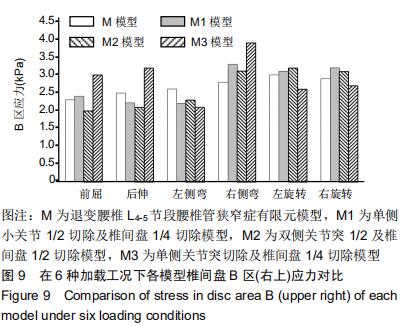
|
[1] MARQUES CJ, HILLEBRAND H, PAPAVERO L. The clinical significance of redundant nerve roots of the cauda equina in lumbar spinalstenosis patients: A systematic literature review and meta analysis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2018;174:40-47.
[2] MINAMIDE A, YOSHIDA M, SIMPSON AK, et al. Minimally invasive spinal decompression for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis and stenosis maintains stability and may avoid the need for fusion. Bone Joint J. 2018;100-B(4): 499-506.
[3] NELLENSTEIJN J, OSTELO R, BARTELS R, et al. Transforaminal endoscopic surgery for symptomatic lumbar disc herniations: a systematic review of the literature. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(2):181-204.
[4] 丁宇,张建军,崔洪鹏,等. 双管大通道椎板间内镜术式治疗腰椎管狭窄症[J]. 转化医学杂志,2018,7(5): 289-293.
[5] HOOGLAND T, SCHUBERT M, MIKLITZ B, et al. Transformational posterolateral endoscopic discectomy with or without the combination of a low-dose chymopapain: aprospective randomized study in 280 consecutive cases. Spine. 2006; 31(24): E890-E897.
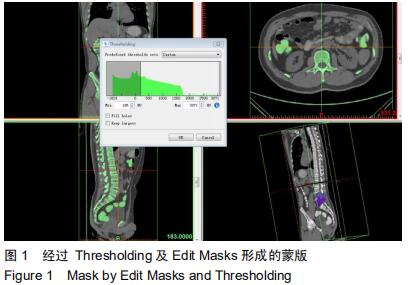
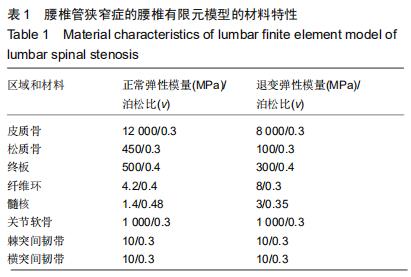
[6] 郝剑,朴哲,李继海,等.基于CT图像和逆向工程方法建立正常人体腰椎三维有限元模型[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(4): 593-596.
[7] MEAKIN J, SMITH F, GILBERT F, et al. The effect of axial load on thesagittal plane curvature of the upright human spine in vivo. J Biomech. 2008;41(13): 2850-2854.
[8] CHEN C, SHIH S. Biomechanical analysis of a new lumbarinterspinous device with optimized topology. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2018;56(8): 1333-1341.
[9] LI L, SHEN T, LI Y. A finite element analysis of stress distribution and disk displacement in response to lumbar rotation manipulation in the sitting and side-lying positions.J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2017;40(8):580-586.
[10] COOMBS DJ, RULLKOETTER PJ, LAZ PJ. Efficient probabilistic finiteelement analysis of a lumbar motion segment. J Biomech. 2017;61: 65-74.
[11] KIM H, LIM DH, OH HJ, et al. Effects of nonlinearity in the materials used for the semi-rigid pedicle screw systems on biomechanical behaviors of the lumbar spine after surgery. Biomed Mater. 2011;6(5): 055005.
[12] 王加谋,陈超,李前龙,等. 退变椎间盘在骨质疏松椎体应力分布中作用的有限元方法研究[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2007,15(7): 41-44, 48.
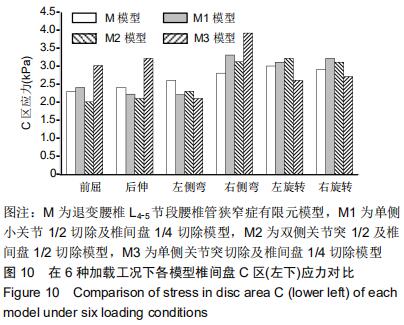
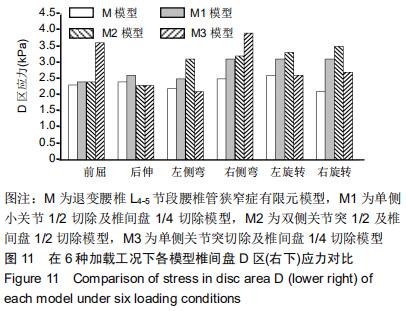
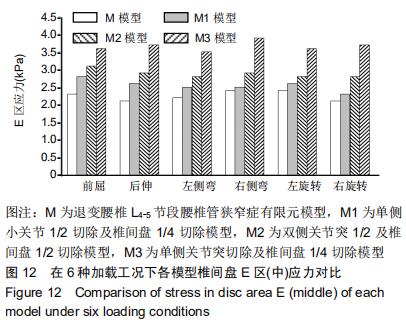
[13] 周仕炼,胡星新,杨曦,等. 退变性腰椎侧凸六种工况运动下的生物力学的有限元分析[J].华西医学,2018,33(9): 1099-1105
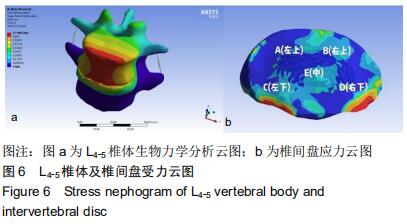
[14] 郑琦,应小樟,石仕元,等. 复杂性腰椎管狭窄症的有限元建模与分析[J].第三军医大学学报,2012,34(18):1897-1900.
[15] 买买提明.艾尼,陈华磊. Ansys Workbench18.0高级应用与实例解析[J].北京:机械工业出版社,2018:152-159.
[16] PYLES C, ZHANG J, DEMETROPOULOS C, et al. Material parameter determination of an l4-l5 motion segment finite element model under high loading rates. Biomed Sci Instrum. 2015;51: 206-213.
[17] YANG K, KING A. Mechanism of facet load transmission as ahypothesis for low-back pain. Spine. 1984;9(6): 557-565.
[18] DING Y, ZHU TY, ZHANG JJ, et al. Percutaneous endoscopicinter laminarapproach medial foraminal decompression in treating lumbar disc herniation orspinal stenosis. Spine. 2017;6: 375-381.
[19] 赵太茂,邱贵兴,仉建国,等. 291例腰椎管狭窄症患者的临床特点分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006,16(11): 812-815.
[20] ESPINHA LC, FERNANDES PR, FOLGADO J. Computational analysis of bone remodeling during an anterior cervical fusion. J Biomech. 2010; 43(15): 2875-2880.
[21] 樊瑜波,邓小燕:生物力学建模仿真与应用[M].上海:上海交通大学出版社,2017:1-5.
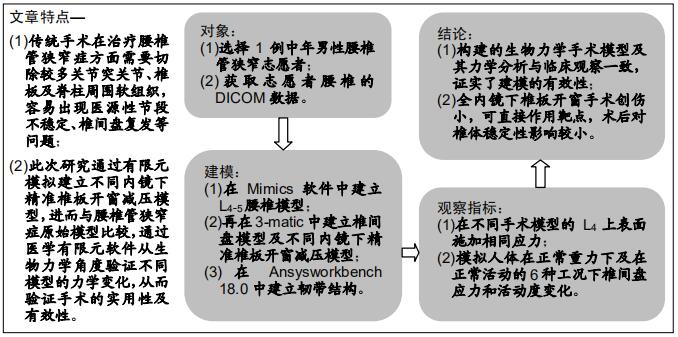
[22] 孙凤龙,李军,梁庆晨,等. 开放手术与脊柱内镜下行椎板减压治疗退变性 腰椎管狭窄症的临床对照研究[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2018,11(11):805-811.
|