中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (26): 4144-4149.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0935
• 纳米生物材料 nanobiomaterials • 上一篇 下一篇
介孔二氧化硅作为无机纳米药物载体的构建及生物活性
刘 莹1,史 巍2,龚 锐3,朱宏明1
- 1天津医科大学中新生态城医院药剂科,天津市 300467;天津医科大学第二医院,2肝胆胰外科,3药学部,天津市 300211
Construction of mesoporous silica as an inorganic nano-drug carrier and its bioactivity
Liu Ying1, Shi Wei2, Gong Rui3, Zhu Hong-ming1
- 1Department of Pharmaceutical Preparation Section, SINO-SIGAPORE ECO-CITY Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300467, China; 2Department of Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery, 3Department of Pharmacy, the Second Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300211, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
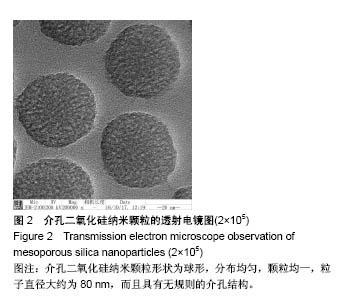
介孔二氧化硅:介孔材料是一类孔径处于2-50 nm 之间的多孔的固体材料。介孔二氧化硅是一种无机高分子材料,可作为无机纳米药物载体,具有生物相容性好、比表面积大、孔径和孔容可调节、孔道均匀、安全性高等特点,同时其表面丰富的硅羟基也为表面修饰提供了基础,可与配体进行偶联,增强其靶向性。
荧光探针:是一类荧光性分子,其在在紫外-可见-近红外区有特征荧光,并且其荧光性质(强度、激发和发射波长、偏振等)可随环境的性质,如极性、折射率、黏度等改变而灵敏地改变。荧光探针法是一种灵敏的、可提供细胞内靶分子时空信息的活性氧检测方法。目前常用的荧光探针有HE(检测O2-)、DCFH和DHR(检测H2O2)等。
背景:目前已有大量基于介孔二氧化硅平台构建刺激响应药物运输体系的报道,但在控制循环过程中仍存在药物泄露情况。
目的:研究介孔二氧化硅纳米药物载体(MS@FcAA/P@CD@RGD)的制备方法及生物活性。
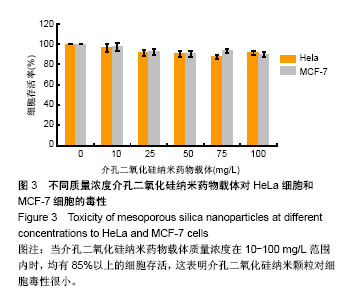
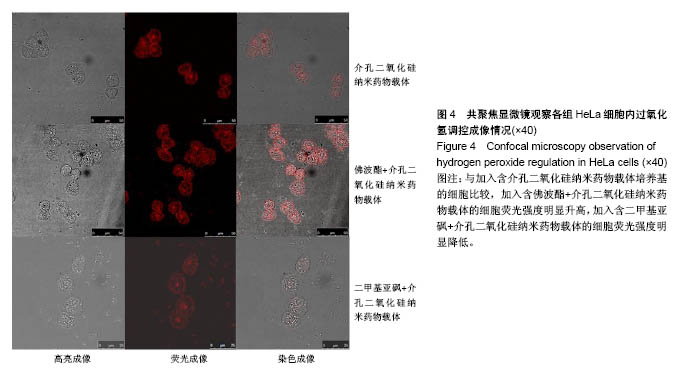
方法:利用MCM-41型介孔二氧化硅纳米颗粒作为细胞内控制药物释放的载体,在其孔道中包载二茂铁和荧光探针,再用β-环糊精堵孔,用整合素抑制剂RGD作为靶向基团,合成介孔二氧化硅纳米药物载体MS@FcAA/P@CD@RGD。以人宫颈癌细胞HeLa和人乳腺癌细胞MCF-7 分别作为目标细胞和对照细胞进行MTT 实验,评价不同质量浓度介孔二氧化硅纳米药物载体的细胞毒性。将传代后的HeLa细胞分3组培养,分别加入含佛波酯(诱导细胞生成大量H2O2)+MS@FcAA/P@CD@RGD的培养基、含二甲基亚砜(清除细胞内H2O2)+MS@FcAA/P@CD@RGD的培养基、含MS@FcAA/P@CD@RGD培养基,培养3 h后,利用激光共聚焦显微镜观察纳米颗粒荧光的变化,评价该纳米载药体系对细胞内H2O2的响应情况。
结果与结论:①当介孔二氧化硅纳米药物载体质量浓度在10-100 mg/L范围内时,均有85%以上的HeLa细胞和MCF-7细胞存活;②与加入含MS@FcAA/P@CD@RGD培养基的HeLa细胞比较,加入佛波酯+ MS@FcAA/P@CD@RGD的HeLa细胞荧光强度明显升高,加入二甲基亚砜+MS@FcAA/P@CD@RGD的HeLa细胞荧光强度明显降低;③结果表明,介孔二氧化硅纳米药物载体对细胞毒性很小,对内源性过氧化氢有一定的响应。
ORCID: 0000-0003-1116-9453(刘莹)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)