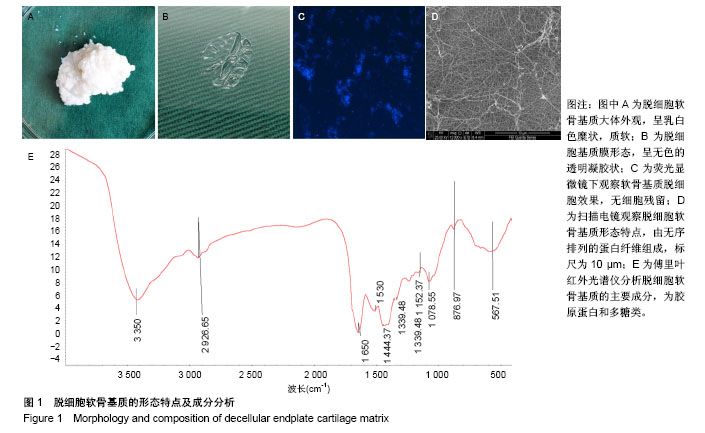
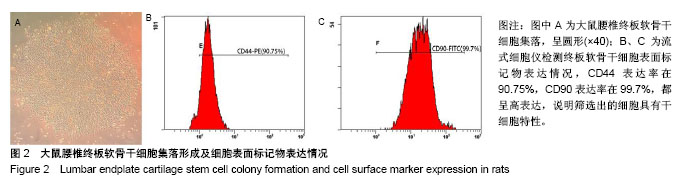
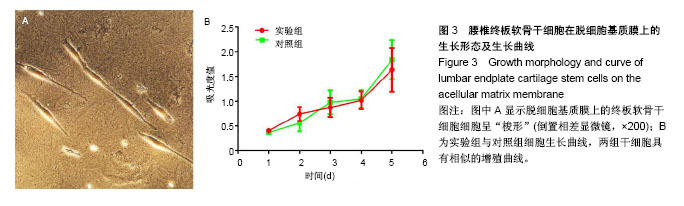
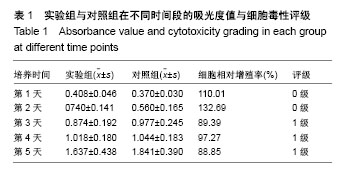
| [1] Chiu TJ,Wang JW,Chen YJ,et al.Intraarterial Cisplatin and intravenous adriamycin in nonmetastatic osteosarcoma of the extremities: a single institution experience in Taiwan.Chang Gung Med J.2009;32(1):72-80.[2] Hughes SP,Freemont AJ,Hukins DW,et al.The pathogenesis of degeneration of the intervertebral disc and emerging therapies in the management of back pain.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2012;94(10): 1298-304.[3] Andersson GB.Epidemiological features of chronic low-back pain. Lancet.1999;354(9178): 581-585.[4] 周志杰.腰椎融合术后邻近节段退变的手术相关危险因素分析和早期临床观察[D].浙江大学,2012.[5] Hansraj KK.Stem Cells in Spine Surgery.Surg Technol Int.2016;XXIX: 348-358.[6] 秦春英,梁继文,张锋,等.丝素蛋白在医学领域的应用研究[J].轻纺工业与技术,2010,39(5):63-65.[7] Jin HJ, Kaplan DL.Mechanism of silk processing in insects and spiders. Nature.2003;424(6952): 1057-1061.[8] 孟永春,陈晓峰,南开辉,等.胶原/生物活性玻璃/壳聚糖增强型复合支架[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(21):3367-3373.[9] 帕尔哈提•阿布肚热合曼,木合塔尔•霍加,多力昆•吾甫尔,等.体外诱导聚氧乙烯-聚氧丙烯醚共聚物水凝胶内兔牙髓干细胞成骨向分化的研究[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2016,51(7):420-425.[10] Zhang J,Nie J,Zhang Q,et al.Preparation and characterization of bionic bone structure chitosan/hydroxyapatite scaffold for bone tissue engineering.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2014;25(1): 61-74.[11] 张旭婧,许燕,周建平,等.骨组织工程支架的不同孔隙率对成形性能的影响分析[J].机械设计与研究, 2016,32(5):151-154.[12] 刘晨,王晟昊,王奕彬,等.兔纤维环干细胞与猪脱细胞纤维环 基质的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(41):6655-6660.[13] Sekiya I,Larson BL,Smith JR,et al.Expansion of human adult stem cells from bone marrow stroma: conditions that maximize the yields of early progenitors and evaluate their quality.Stem Cells.2002;20(6): 530-541.[14] Risbud MV,Guttapalli A,Tsai TT,et al.Evidence for skeletal progenitor cells in the degenerate human intervertebral disc.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(23):2537-2544.[15] Lee DH,Joo SD,Han SB,et al.Isolation and expansion of synovial CD34(-)CD44(+)CD90(+) mesenchymal stem cells: comparison of an enzymatic method and a direct explant technique. Connect Tissue Res. 2011;52(3):226-234.[16] Hou Y,Wang X,Yang J,et al.Development and biocompatibility evaluation of biodegradable bacterial cellulose as a novel peripheral nerve scaffold.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(5):1288-1298.[17] 郝和平.ISO10993-1.医疗器械生物学评鉴标准实施指南[M].北京:中国标准出版社,2000: 285-295,334-347.[18] 孙皎.生物材料和医疗器械的生物学评价[J].中国医疗器械杂志,2003, 27(1):1-3,8.[19] 孙立魁,骆红宇.医疗器械生物学评价国际标准进展与2010年ISO/TC194年会[J].中国医疗器械杂志, 2010,34(4):245.[20] 熊党生.生物材料与组织工程[M].北京:科学出版社,2010:25-28.[21] 杜晓丹,陈鸿波,杨昭鹏.我国医疗器械检验机构产品技术要求预评价工作现状、问题和建议[J].中国药事, 2017,31(9):1085-1089.[22] 丁建勇,郑如恒,乔玉磊,等.深低温冷冻保存降低大鼠气管移植物免疫原性的机制[J].复旦学报(医学版),2008,35(1):94-98.[23] 邓玖征,张友乐,李翔.低温冻存同种异体骨膜和骨髓移植免疫原性研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2014,28(5):649-653.[24] 朱祥,陈旭义,刘英富,等.胶原及丝素蛋白支架材料在脊髓组织工程中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(39):6359-6363.[25] 徐云强,刘迎节,李瑞欣,等.胶原/丝素蛋白神经导管修复周围神经缺损的研究与应用进展[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(38):5745-5751.[26] 田莉,闵思佳.丝素蛋白在组织工程细胞支架方面的研究进展[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2006,23(6): 1375-1378.[27] 丁晓明,徐宝山,杨强.丝素蛋白应用于椎间盘纤维环组织工程的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(7):613-616. |
.jpg)

.jpg)