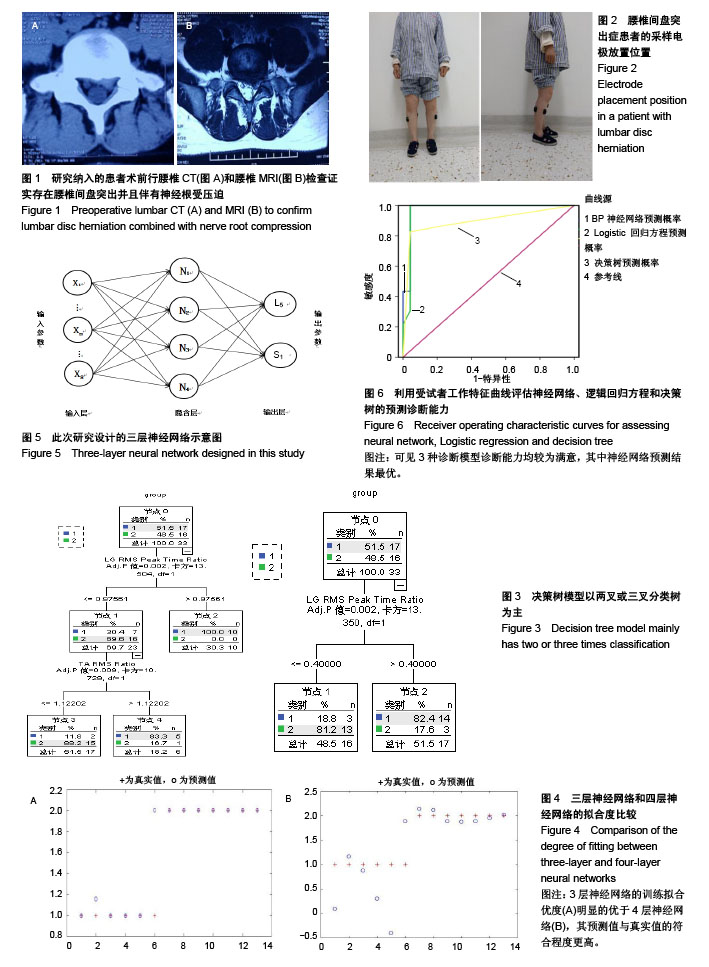
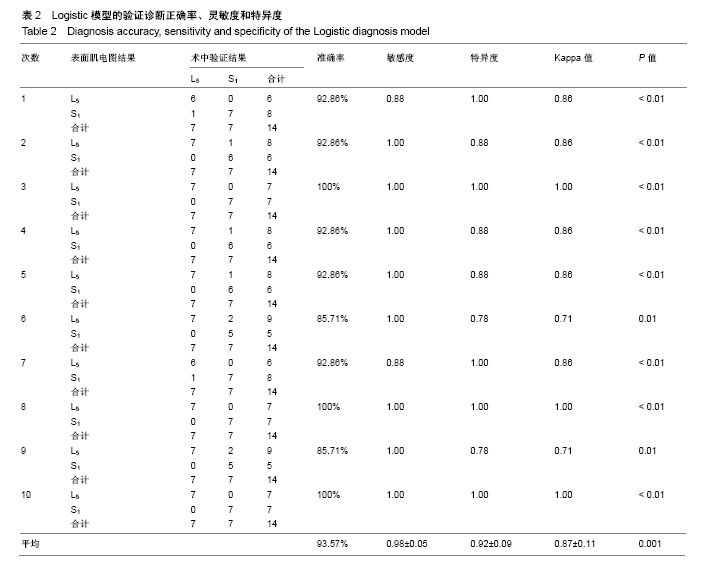
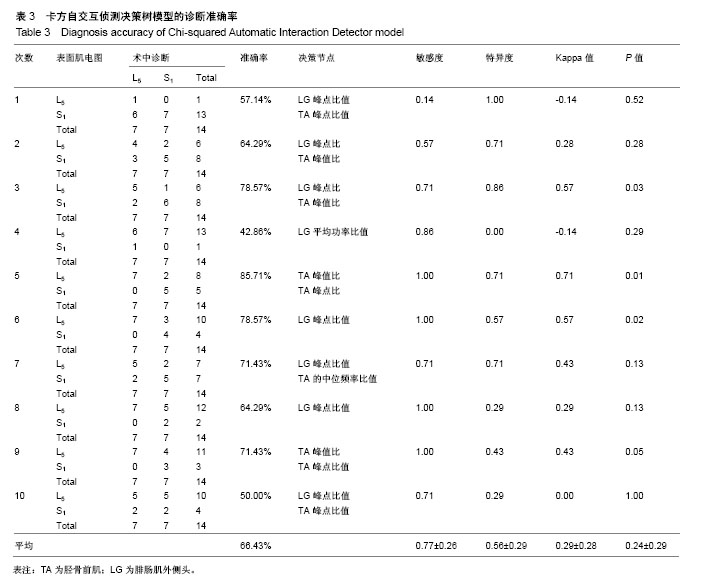
| [1] Lee JK, Amorosa L, Cho SK, et al. Recurrent lumbar disk herniation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18(6):327-337.[2] Schoenfeld AJ, Laughlin M, Bader JO, et al. Characterization of the incidence and risk factors for the development of lumbar radiculopathy. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012;25(3):163-167.[3] 杜金龙. 肌电图在腰椎间盘突出症(L4-5节段)受损神经根定位诊断中的应用[D].宁夏医科大学,2014.[4] Konstantinou K, Dunn KM. Sciatica:review of epidemiological studies and prevalence estimates. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(22):2464-2472.[5] Huang YP, Bruijn SM, Lin JH, et al. Gait adaptations in low back pain patients with lumbar disc herniation:trunk coordination and arm swing. Eur Spine J. 2010;20(3):491.[6] Lee JH, An JH, Lee SH, et al. Three-dimensional gait analysis of patients with weakness of ankle dorsiflexor as a result of unilateral L5 radiculopathy. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2010;23(2):49-54.[7] 胡有谷. 腰椎间盘突出症[M]. 4版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2011.[8] Kreiner DS, Hwang SW, Easa JE, et al. An evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation with radiculopathy. Spine J. 2014;14(1):180-191.[9] Al NN, Schneiders AG, Hendrick PA. Neurological examination of the peripheral nervous system to diagnose lumbar spinal disc herniation with suspected radiculopathy:a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine J. 2013;13(6):657-674.[10] Micankova AB, Vohanka S, Dusek L, et al. Prediction of long-term clinical outcome in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(12):2611-2619.[11] Chawalparit O, Churojana A, Chiewvit P, et al. The limited protocol MRI in diagnosis of lumbar disc herniation. J Med Assoc Thai. 2006;89(2): 182-189.[12] Tawa N, Rhoda A, Diener I. Accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging in detecting lumbo-sacral nerve root compromise:a systematic literature review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17(1):386.[13] Oikawa Y, Eguchi Y, Inoue G, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging of lumbar spinal nerve in subjects with degenerative lumbar disorders. Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;33(8):956-961.[14] Kuijper B, Tans JT, van der Kallen BF, et al. Root compression on MRI compared with clinical findings in patients with recent onset cervical radiculopathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2011;82(5):561-563.[15] Reinhold M, Ederer C, Henninger B, et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for the diagnosis of patients with lumbar nerve root entrapment syndromes:results from a pilot study. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(2):319-326.[16] 向为. 生物视觉启发下的特征提取和目标分类方法研究[D].北京交通大学,2009.[17] 黄晓霞,严玉洁,尉敏琦,等. logistic回归、决策树和神经网络在脑卒中高危筛查中的性能比较[J]. 中国慢性病预防与控制,2016,24(6):412-415.[18] Delen D, Walker G, Kadam A. Predicting breast cancer survivability:a comparison of three data mining methods. Artif Intell Med. 2005; 34(2): 113-127.[19] Barr K. Electrodiagnosis of lumbar radiculopathy. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2013;24(1):79-91.[20] Wang Y, Nataraj A. Foot drop resulting from degenerative lumbar spinal diseases:clinical characteristics and prognosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2014;117:33-39.[21] Boccia G, Dardanello D, Rosso V, et al. The Application of sEMG in Aging:A Mini Review. Gerontology. 2015;61(5):477-484.[22] 李云超,邱虹,陈广,等. 颅内动脉瘤破裂的临床危险因素分析[J]. 中国全科医学,2012,15(21):2388-2390.[23] 来丹飞,陈雪东. 基于决策树的门脉高压脾切术并发门脉血栓的早期诊断与预测[J]. 湖州师范学院学报,2013,35(6):69-74.[24] 王剑,刘殿武,曹国玉,等. 树模型在慢性乙肝与肝硬化和肝癌临床诊断中的应用[J]. 医学争鸣,2008,29(12):1135-1137.[25] Wickenberg-Bolin U, Göransson H, Fryknäs M, et al. Improved variance estimation of classification performance via reduction of bias caused by small sample size. Bmc Bioinformatics. 2006;7(1):1-8.[26] Mordohai P. Dimensionality Estimation, Manifold Learning and Function Approximation using Tensor Voting. J Mach Learn Res. 2010;11(1):411-450.[27] 陈卉,王晓华. 数据挖掘技术在计算机辅助肺癌诊断中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2007,11(5):879-881.[28] 黄晓霞,严玉洁,尉敏琦,等. Logistic回归、决策树和神经网络在脑卒中高危筛查中的性能比较[J]. 中国慢性病预防与控制,2016,24(6):412-415.[29] 刘绿. Logistic回归模型、神经网络模型和决策树模型在乳腺癌的彩超影像诊断中的比较研究[D].南华大学,2013.[30] Chou HL, Yao CT, Su SL, et al. Gene expression profiling of breast cancer survivability by pooled cDNA microarray analysis using logistic regression, artificial neural networks and decision trees. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013; 14(1):100.[31] Jenhani I, Amor NB, Elouedi Z. Decision trees as possibilistic classifiers. Int J Approx Reason. 2008;48(3):784-807.[32] Amini P, Ahmadinia H, Poorolajal J, et al. Evaluating the high risk groups for suicide:A comparison of Logistic regression, support vector machine, decision tree and artificial neural network. Iran J Public Health. 2016;45(9):1179-1187.[33] Monta ÃO, Moreno JJ, Palmer PA, et al. Artificial neural networks applied to forecasting time series. Psicothema. 2011;23(2):322-329.[34] Delen D, Oztekin A, Tomak L. An analytic approach to better understanding and management of coronary surgeries. Dec Support Syst. 2012;52(3):698-705.[35] Wang J, Li M, Hu YT, et al. Comparison of hospital charge prediction models for gastric cancer patients:neural network vs. decision tree models. Bmc Health Serv Res. 2009;9(1):161.[36] Aguilar C, Westman E, Muehlboeck JS, et al. Different multivariate techniques for automated classification of MRI data in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment. Psychiatry Res. 2013;212(2): 89-98.[37] Chen H, Zhang J, Xu Y, et al. Performance comparison of artificial neural network and logistic regression model for differentiating lung nodules on CT scans. Exp Syst Appl. 2012;39(13):11503-11509.[38] Ayer T, Chhatwal J, Alagoz O,et al. Informatics in radiology:comparison of logistic regression and artificial neural network models in breast cancer risk estimation. Radiographics. 2010;30(1):13-22.[39] Pai DR, Lawrence KD, Klimberg RK, et al. Experimental comparison of parametric, non-parametric, and hybrid multigroup classification. Exp Syst Appl. 2012;39(10):8593-8603. |
.jpg)
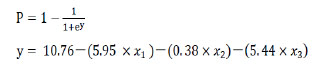
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)