中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (16): 2542-2548.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0222
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
黄芩苷可影响帕金森病模型大鼠纹状体星形胶质细胞缝隙连接蛋白43的表达
韩雪洁1,2,哈力达•巴合提汗2,高 华3,杨新玲2
- 1新疆医科大学第一附属医院神经内科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830000; 2新疆医科大学第二附属医院神经内科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830063;3新疆医科大学第五附属医院神经内科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054
Baicalin increases connexin 43 expression in striatal astrocytes of rats with Parkinson’s disease
Han Xue-jie1, 2, Halleda•Balikarthan2, Gao Hua3, Yang Xin-ling2
- 1Department of Neurology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Neurology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830063, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 3Department of Neurology, the Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
缝隙连接蛋白43(Cx43):目前发现Cx43存在于多达34种组织和46种细胞中,在中枢系统中星形胶质细胞之间存在最多的Cx43。6个Cx43组成半通道,2个半通道相互连接组成缝隙连接(GJ),缝隙连接一般均成簇分布,当它们开放时,可以允许小于分子质量1.2 ku的小分子物质,如离子、代谢分子、第二信使等自由通过,是物质运输和信号传导的通道。
6-羟基多巴胺(6-OHDA):6-OHDA与正常的神经递质结构类似,容易被纹状体错误摄入到多巴胺神经末梢,经过一系列的破坏,逆向运输至黑质神经元细胞,使之变性坏死,进而破坏中脑黑质的多巴胺神经元,使其破坏。帕金森病大鼠模型与人类的帕金森病在病理和生化功能表现相似,包括多巴胺能神经元变性坏死、星形胶质细胞的激活、TH活性及多巴胺含量降低等特征。不同剂量的6-OHDA注射可以模拟不同时期的帕金森病的病程,优点在于可以根据6-OHDA的剂量的不同,可模拟帕金森病的早、中期的病理变化。
文题释义:
缝隙连接蛋白43(Cx43):目前发现Cx43存在于多达34种组织和46种细胞中,在中枢系统中星形胶质细胞之间存在最多的Cx43。6个Cx43组成半通道,2个半通道相互连接组成缝隙连接(GJ),缝隙连接一般均成簇分布,当它们开放时,可以允许小于分子质量1.2 ku的小分子物质,如离子、代谢分子、第二信使等自由通过,是物质运输和信号传导的通道。
6-羟基多巴胺(6-OHDA):6-OHDA与正常的神经递质结构类似,容易被纹状体错误摄入到多巴胺神经末梢,经过一系列的破坏,逆向运输至黑质神经元细胞,使之变性坏死,进而破坏中脑黑质的多巴胺神经元,使其破坏。帕金森病大鼠模型与人类的帕金森病在病理和生化功能表现相似,包括多巴胺能神经元变性坏死、星形胶质细胞的激活、TH活性及多巴胺含量降低等特征。不同剂量的6-OHDA注射可以模拟不同时期的帕金森病的病程,优点在于可以根据6-OHDA的剂量的不同,可模拟帕金森病的早、中期的病理变化。
.jpg) 文题释义:
缝隙连接蛋白43(Cx43):目前发现Cx43存在于多达34种组织和46种细胞中,在中枢系统中星形胶质细胞之间存在最多的Cx43。6个Cx43组成半通道,2个半通道相互连接组成缝隙连接(GJ),缝隙连接一般均成簇分布,当它们开放时,可以允许小于分子质量1.2 ku的小分子物质,如离子、代谢分子、第二信使等自由通过,是物质运输和信号传导的通道。
6-羟基多巴胺(6-OHDA):6-OHDA与正常的神经递质结构类似,容易被纹状体错误摄入到多巴胺神经末梢,经过一系列的破坏,逆向运输至黑质神经元细胞,使之变性坏死,进而破坏中脑黑质的多巴胺神经元,使其破坏。帕金森病大鼠模型与人类的帕金森病在病理和生化功能表现相似,包括多巴胺能神经元变性坏死、星形胶质细胞的激活、TH活性及多巴胺含量降低等特征。不同剂量的6-OHDA注射可以模拟不同时期的帕金森病的病程,优点在于可以根据6-OHDA的剂量的不同,可模拟帕金森病的早、中期的病理变化。
文题释义:
缝隙连接蛋白43(Cx43):目前发现Cx43存在于多达34种组织和46种细胞中,在中枢系统中星形胶质细胞之间存在最多的Cx43。6个Cx43组成半通道,2个半通道相互连接组成缝隙连接(GJ),缝隙连接一般均成簇分布,当它们开放时,可以允许小于分子质量1.2 ku的小分子物质,如离子、代谢分子、第二信使等自由通过,是物质运输和信号传导的通道。
6-羟基多巴胺(6-OHDA):6-OHDA与正常的神经递质结构类似,容易被纹状体错误摄入到多巴胺神经末梢,经过一系列的破坏,逆向运输至黑质神经元细胞,使之变性坏死,进而破坏中脑黑质的多巴胺神经元,使其破坏。帕金森病大鼠模型与人类的帕金森病在病理和生化功能表现相似,包括多巴胺能神经元变性坏死、星形胶质细胞的激活、TH活性及多巴胺含量降低等特征。不同剂量的6-OHDA注射可以模拟不同时期的帕金森病的病程,优点在于可以根据6-OHDA的剂量的不同,可模拟帕金森病的早、中期的病理变化。摘要
背景:在帕金森病发病中,缝隙连接蛋白43(connexin43,Cx43)作为一种重要的调节蛋白,如何更大的发挥其减少多巴胺能神经元损伤的作用目前还不十分明确。研究显示黄芩苷具有抑制帕金森病的炎症反应及氧化应激等作用,可以预防帕金森病模型大鼠的多巴胺神经元的变形损伤。
目的:探讨黄芩苷对帕金森病模型大鼠行为学及星形胶质细胞Cx43表达的影响。
方法:80只SD雄性大鼠中随机取10只设为正常组(不造模),另外70只采用6-羟基多巴胺在右侧纹状体单侧双点毁损法制作偏侧帕金森病大鼠旋转模型。将造模成功的40只大鼠随机分成模型组(生理盐水)、美多芭治疗组(美多芭125 mg/kg)、黄芩苷低剂量组(50 mg/kg)和黄芩苷高剂量组(100 mg/kg),药物连续治疗28 d。行为学测试观察各组大鼠旋转行为的改变,免疫组化检测TH细胞数量变化、免疫组化及Western Blot法确定Cx43的表达量。
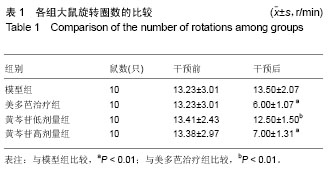
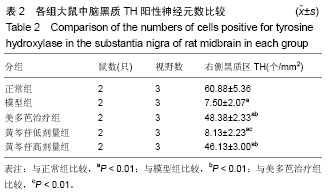
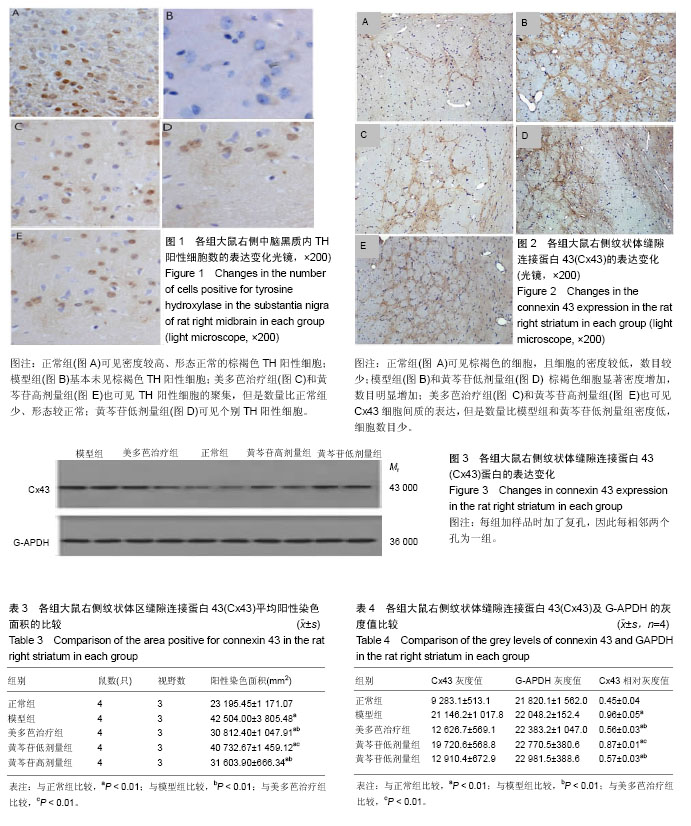
结果与结论:①行为学测试结果:正常组干预前后均未有旋转行为,其他4组模型大鼠在注射阿扑吗啡5 min后开始出现旋转行为,药物干预前均为13 r/min左右(P > 0.05),干预后美多芭治疗组和黄芩苷高剂量组旋转圈数较模型组显著减少(P < 0.01);②黑质区TH阳性细胞数量:与模型组比较,黄芩苷低剂量组增加不明显(P > 0.05),美多芭治疗组和黄芩苷高剂量组TH细胞数量均较模型组明显增加(P < 0.01);③Cx43表达:免疫组化及Western Blot结果示,模型组Cx43表达较正常组显著升高(P < 0.01);黄芩苷低剂量组与模型组比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),美多芭治疗组和黄芩苷高剂量组Cx43表达水平相似,但均较模型组显著降低(P < 0.01);④提示:100 mg/kg黄芩苷可显著改善帕金森病大鼠的转圈行为,可明显提高TH细胞的活性,减少6-羟基多巴胺对帕金森病黑质神经元的损害。Cx43在帕金森病模型大鼠纹状体星形胶质细胞中的表达上调,黄芩苷对Cx43的表达有下调作用,100 mg/kg黄芩苷的作用与美多芭相似。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-4392-7810(韩雪洁)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
缝隙连接蛋白43(Cx43):目前发现Cx43存在于多达34种组织和46种细胞中,在中枢系统中星形胶质细胞之间存在最多的Cx43。6个Cx43组成半通道,2个半通道相互连接组成缝隙连接(GJ),缝隙连接一般均成簇分布,当它们开放时,可以允许小于分子质量1.2 ku的小分子物质,如离子、代谢分子、第二信使等自由通过,是物质运输和信号传导的通道。
6-羟基多巴胺(6-OHDA):6-OHDA与正常的神经递质结构类似,容易被纹状体错误摄入到多巴胺神经末梢,经过一系列的破坏,逆向运输至黑质神经元细胞,使之变性坏死,进而破坏中脑黑质的多巴胺神经元,使其破坏。帕金森病大鼠模型与人类的帕金森病在病理和生化功能表现相似,包括多巴胺能神经元变性坏死、星形胶质细胞的激活、TH活性及多巴胺含量降低等特征。不同剂量的6-OHDA注射可以模拟不同时期的帕金森病的病程,优点在于可以根据6-OHDA的剂量的不同,可模拟帕金森病的早、中期的病理变化。
文题释义:
缝隙连接蛋白43(Cx43):目前发现Cx43存在于多达34种组织和46种细胞中,在中枢系统中星形胶质细胞之间存在最多的Cx43。6个Cx43组成半通道,2个半通道相互连接组成缝隙连接(GJ),缝隙连接一般均成簇分布,当它们开放时,可以允许小于分子质量1.2 ku的小分子物质,如离子、代谢分子、第二信使等自由通过,是物质运输和信号传导的通道。
6-羟基多巴胺(6-OHDA):6-OHDA与正常的神经递质结构类似,容易被纹状体错误摄入到多巴胺神经末梢,经过一系列的破坏,逆向运输至黑质神经元细胞,使之变性坏死,进而破坏中脑黑质的多巴胺神经元,使其破坏。帕金森病大鼠模型与人类的帕金森病在病理和生化功能表现相似,包括多巴胺能神经元变性坏死、星形胶质细胞的激活、TH活性及多巴胺含量降低等特征。不同剂量的6-OHDA注射可以模拟不同时期的帕金森病的病程,优点在于可以根据6-OHDA的剂量的不同,可模拟帕金森病的早、中期的病理变化。