中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (19): 3037-3043.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1187
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
黄芩苷治疗小鼠动脉粥样硬化模型的作用与机制
孙治中1,江艳君1,纪树亮1,石础硕1,张 填1,周小琦1,杨智华1,陈悦轩1,罗川晋2
- (1广州中医药大学第一临床医学院,广东省广州市 510000;2广州中医药大学第一附属医院,广东省广州市 510000)
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1187 ORCID: 0000-0002-4976-9596(孙治中)
Role of baicalin in the treatment of mouse models of atherosclerosis and the underlying mechanism
Sun Zhizhong1, Jiang Yanjun1, Ji Shuliang1, Shi Chushuo1, Zhang Tian1, Zhou Xiaoqi1, Yang Zhihua1, Chen Yuexuan1, Luo Chuanjin2
- (1First Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China; 2the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
.jpg)
文题释义:
核因子κB:是一种调控炎症信号的重要转录因子,通过调节多种免疫分子和炎症递质的基因表达而参与动脉粥样硬化的病理过程,在动脉粥样硬化形成中起着激活作用;核因子κB激活是炎症反应的前提条件,动脉粥样硬化形成的前提。
动脉粥样硬化:是由于血管内皮细胞和平滑肌细胞受到各种危险因素,如病毒、机械损伤、免疫复合物,特别是氧化型低密度脂蛋白的损伤,使血管局部产生的一种过度慢性炎症增生反应。
摘要
背景:现代实验室及临床研究表明,黄芩苷可通过抗氧化应激、抑制血管平滑肌细胞增殖和迁移等多途径发挥抗动脉粥样硬化效应,但其作用机制尚不明确。
目的:观察黄芩苷对动脉粥样硬化小鼠血脂、一氧化氮及核因子κB与其下游炎症因子水平的影响。
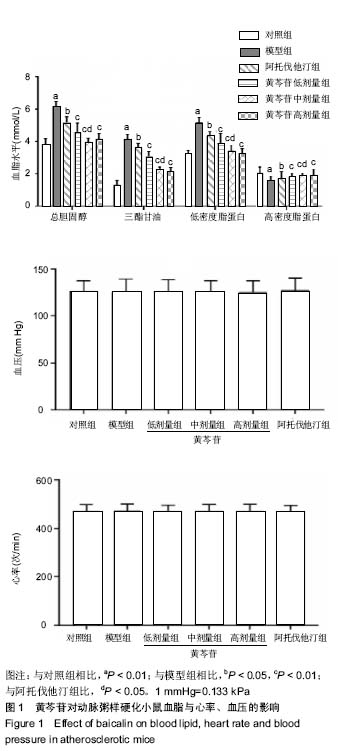
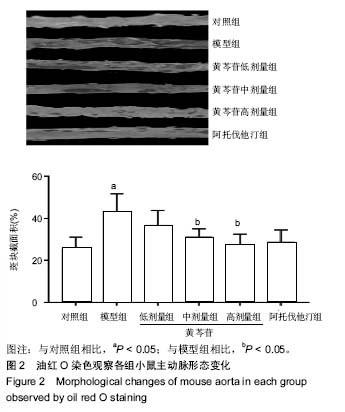
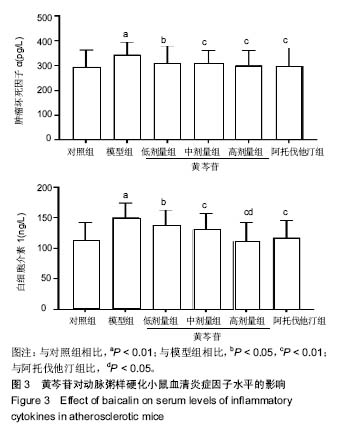
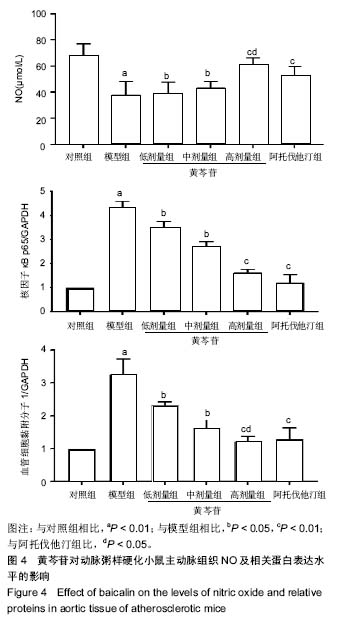
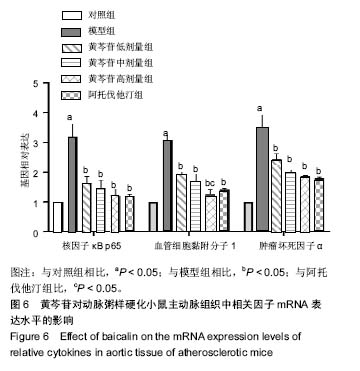
方法:将60只雄性ApoE-/-小鼠随机分为5组,每组10只:对照组给予普通饲料喂养,其余5组给予高脂饲料喂养12周,建立动脉粥样硬化模型;随后对照组、模型组灌胃给予生理盐水,阿托伐他汀组灌胃给予阿托伐他汀5 mg/(kg•d),黄芩苷低、中、高剂量组分别灌胃给予50,75,100 mg/(kg•d)黄芩苷。连续给药4周后,采用全自动生化仪测定血脂水平,油红O染色观察主动脉斑块变化,ELISA法检测血清炎症因子水平,Western blot检测主动脉中核因子κB p65、血管细胞黏附分子1蛋白表达,硝酸酶还原法测量主动脉一氧化氮水平,实时荧光定量RT-PCR检测主动脉组织核因子κB p65、血管细胞黏附分子1、肿瘤坏死因子αmRNA的表达。
结果与结论:①与对照组比较,模型组总胆固醇、三酰甘油、低密度脂蛋白水平升高(P < 0.05),高密度脂蛋白水平降低(P < 0.05),主动脉内膜厚度与斑块截面积增加(P < 0.05),炎症因子肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1水平升高(P < 0.05),NO水平降低(P <0.05),核因子κB p65、血管细胞黏附分子1蛋白表达升高 (P < 0.05),核因子κB p65、血管细胞黏附分子1、肿瘤坏死因子α mRNA表达升高(P < 0.05);②与模型组比较,阿托伐他汀组及黄芩苷低、中、高剂量组血脂水平明显改善(P < 0.05),炎症因子水平降低(P < 0.05),NO水平升高(P < 0.05),主动脉内膜厚度与斑块截面积减少,核因子κB p65、血管细胞黏附分子1蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05),核因子κB p65、血管细胞黏附分子1、肿瘤坏死因子α mRNA表达降低(P < 0.05),其中黄芩苷的改善作用存在剂量依赖性;③与阿托伐他汀组比较,黄芩苷高剂量组总胆固醇、白细胞介素1、血管细胞黏附分子1蛋白及基因表达降低(P < 0.05),NO水平升高(P < 0.05);④结果表明,黄芩苷可能通过改善血脂与抑制核因子κB炎症通路等途径对抗动脉粥样硬化形成。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-4976-9596(孙治中)
中图分类号:
.jpg)