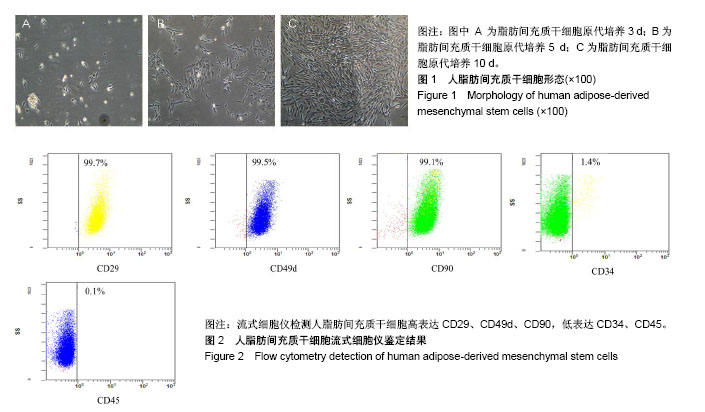
| [1] 李兰娟,段钟平. 肝衰竭诊治指南(2012年版)[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2013, 21(3):210-216. [2] 刘景丰,张翔.肝衰竭的肝移植治疗进展[J].中华肝脏病杂志, 2017, 25(9):655-658. [3] Squillaro T, Peluso G, Galderisi U. Clinical Trials With Mesenchymal Stem Cells: An Update. Cell Transplant. 2016; 25(5):829-848.[4] Fierabracci A, Del Fattore A, Luciano R, et al. Recent advances in mesenchymal stem cell immunomodulation: the role of microvesicles. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(2):133-149.[5] Wong SP, Rowley JE, Redpath AN, et al. Pericytes, mesenchymal stem cells and their contributions to tissue repair. Pharmacol Ther. 2015;151:107-120.[6] Volarevic V, Nurkovic J, Arsenijevic N, et al. Concise review: Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of acute liver failure and cirrhosis. Stem Cells. 2014; 32(11):2818-2823. [7] Liu WH, Song FQ, Ren LN, et al. The multiple functional roles of mesenchymal stem cells in participating in treating liver diseases. J Cell Mol Med. 2015;19(3):511-520. [8] Lee CW, Chen YF, Wu HH, et al. Historical Perspectives and Advances in Mesenchymal Stem Cell Research for the Treatment of Liver Diseases. Gastroenterology. 2018;154(1): 46-56.[9] Wu Z, Han M, Chen T, et al. Acute liver failure: mechanisms of immune-mediated liver injury. Liver Int. 2010;30(6):782-794.[10] Wang X, Ning Q. Immune mediated liver failure. EXCLI J. 2014;13:1131-1144.[11] 李晓东. HBV相关慢加急性肝衰竭免疫病理发病机制研究进展[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2015, 18(3):317-320.[12] Bassi G, Pacelli L, Carusone R, et al. Adipose-derived stromal cells (ASCs). Transfus Apher Sci. 2012;47(2):193-198.[13] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.[14] Bourin P, Bunnell BA, Casteilla L, et al. Stromal cells from the adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction and culture expanded adipose tissue-derived stromal/stem cells: a joint statement of the International Federation for Adipose Therapeutics and Science (IFATS) and the International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT). Cytotherapy. 2013; 15(6):641-648.[15] Liu WH, Song FQ, Ren LN, et al. The multiple functional roles of mesenchymal stem cells in participating in treating liver diseases. J Cell Mol Med. 2015;19(3):511-520. [16] Bajek A, Gurtowska N, Olkowska J, et al. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells as a Tool in Cell-Based Therapies. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2016;64(6):443-454.[17] Tabatabaei Qomi R, Sheykhhasan M. Adipose-derived stromal cell in regenerative medicine: A review. World J Stem Cells. 2017;9(8):107-117.[18] Chen G, Jin Y, Shi X, et al. Adipose-derived stem cell-based treatment for acute liver failure. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015; 6:40.[19] Deng L, Kong X, Liu G, et al. Transplantation of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Efficiently Rescues Thioacetamide-Induced Acute Liver Failure in Mice. Transplant Proc. 2016;48(6):2208-2215. [20] 史光军,张亚东,胡音音,等. 脂肪间充质干细胞移植上调肝脏增殖细胞核抗原表达促进肝细胞的再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2017, 21(17):2690-2695.[21] Grimes CA, Jope RS. The multifaceted roles of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in cellular signaling. Prog Neurobiol. 2001;65(4):391-426.[22] Beurel E, Grieco SF, Jope RS. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3): regulation, actions, and diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 2015;148:114-131.[23] Mishra R, Nagini S, Rana A. Expression and inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 alpha/ beta and their association with the expression of cyclin D1 and p53 in oral squamous cell carcinoma progression. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:20.[24] Beurel E, Michalek SM, Jope RS. Innate and adaptive immune responses regulated by glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3). Trends Immunol. 2010;31(1):24-31.[25] 谈志丽,钟欢,朱彤,等. 糖原合成激酶3β在急性肝衰竭免疫炎症反应中的作用及机制研究进展[J]. 免疫学杂志, 2017,33(6): 547-552. [26] Chen L, Ren F, Zhang H, et al. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3β ameliorates D-GalN/LPS-induced liver injury by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress-triggered apoptosis. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45202.[27] Zhang H, Wang W, Fang H, et al. GSK-3β inhibition attenuates CLP-induced liver injury by reducing inflammation and hepatic cell apoptosis. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014: 629507.[28] 张向颖,任锋,魏琳琳,等. 糖原合成酶激酶3β在乙型重型肝炎肝衰竭中的作用研究[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2016, 24(4):265-269. [29] Ren F, Zhang L, Zhang X, et al. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3β promotes autophagy to protect mice from acute liver failure mediated by peroxisome proliferator- activated receptor α. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7: e2151.[30] 杨丙章,任锋,温韬,等. 糖原合成酶激酶-3β在D-GalN/LPS诱导的小鼠急性肝衰竭中的作用[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2012, 20(36):3656-3662. |
.jpg)
.jpg)