| [1]Volarevic V,Erceg S,Bhattacharya SS,et al.Stem cell-based therapy for spinal cord injury.Cell Transplant.2013;22(8):1309-1323.[2]Abdolreza B,Hassan EVS,Majid AS,et al.Melatonin treatment reduces astrogliosis and apoptosis in rats with traumatic brain injury.Iran J Basic Med Sci.2015;18(9):867-872.[3]Alvismiranda HR,Alcalacerra G,Moscotesalazar LR.Microglia: roles and rules in brain traumatic injury.Romanian Neurosurgery. 2013; 20(1):34-45.[4]Saijo K,Glass CK.Microglial cell origin and phenotypes in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol.2011;11(11):775-787. [5]Femminella GD,Ninan S,Atkinson R,et al.Does Microglial Activation Influence Hippocampal Volume and Neuronal Function in Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease Dementia? J Alzheimers Dis. 2016; 51(4):1275-1289.[6]吕威,李志刚,姚海江,等.针灸治疗脊髓损伤的临床研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践, 2015,21(12):1411-1414. [7]范筱,汪今朝,刘宇.针灸治疗脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱疗效和安全性的Meta分析[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2017,25(9):35-43.[8]李晓宁,迟蕾.夹脊配合督脉电针治疗脊髓损伤后功能障碍临床观察[J].上海针灸杂志,2015;34(10):972-975.[9]陈兰芳,张学君,林栋,等.电针长强穴对FMR1基因敲除小鼠海马CA1区PSD-95、CREB蛋白表达的影响[J].康复学报, 2015,25(4):18-21.[10]张学君,吴强.电针督脉不同穴对自闭症模型大鼠学习记忆能力及海马CA1区PSD-95蛋白表达的影响[J].中国针灸, 2013,33(7):627-631.[11]Chen WF,Chen CH,Chen NF,et al.Neuroprotective Effects of Direct Intrathecal Administration of Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor in Rats with Spinal Cord Injury.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2015;21(9):698-707.[12]高连军,孙迎春,李建军,等.不同时间电针刺激对大鼠脊髓损伤后磁共振弥散张量纤维束成像部分各向异性值均值的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践, 2014,20(8):728-733. [13]郭义,方剑乔.实验针灸学[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2012.[14]Yang T,Wu L,Wang H,et al.Inflammation Level after Decompression Surgery for a Rat Model of Chronic Severe Spinal Cord Compression and Effects on Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Neurologia Medico Chirurgica. 2015;55(7):578-586.[15]Samy DM,Hassan PS,Ismail CA,et al.Agmatine inhibits nuclear factor-κB nuclear translocation in acute spinal cord compression injury rat model.Alex J Med.2016;52(3):251-260.[16]Haas C,Fischer I.Human Astrocytes Derived from Glial Restricted Progenitors Support Regeneration of the Injured Spinal Cord.J Neurotrauma.2013;30(12):1035-1052. [17]Jin Y,Shumsky JS,Fischer I. Axonal regeneration of different tracts following transplants of human glial restricted progenitors into the injured spinal cord in rats.Brain Res.2018;1686:101-112.[18]Hong P,Jiang M,Li H.Functional requirement of dicer1 and miR-17-5p in reactive astrocyte proliferation after spinal cord injury in the mouse. Glia.2014;62(12):2044-2060.[19]Takazawa A, Kamei N, Adachi N, et al.Endoplasmic reticulum stress transducer old astrocyte specifically induced substance contributes to astrogliosis after spinal cord injury.Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(3): 536-540.[20]Lebkuechner I,Wilhelmsson U,Möllerström E,et al. Heterogeneity of Notch signaling in astrocytes and the effects of GFAP and vimentin deficiency.J Neurochem. 2015;135(2):234-248. [21]Magnusson JP,Goritz C,Tatarishvili J,et al.A latent neurogenic program in astrocytes regulated by Notch signaling in the mouse.Science. 2014; 346(6206):237-241.[22]Marinelli C, Di Liddo R, Facci L,et al.Ligand engagement of Toll-like receptors regulates their expression in cortical microglia and astrocytes. J Neuroinflammation. 2015;12(1):244.[23]Haan N,Zhu B, Wang J, et al. Crosstalk between macrophages and astrocytes affects proliferation, reactive phenotype and inflammatory response, suggesting a role during reactive gliosis following spinal cord injury.J Neuroinflammation.2015;12(1):1-10.[24]Atmaca HT,Kul O,Karaku? E,et al.Astrocytes, microglia/macrophages, and neurons expressing Toll-like receptor 11 contribute to innate immunity against encephalitic Toxoplasma gondii infection. Neuroscience. 2014;269(1):184-191. [25]Lukovic D,Stojkovic M,Moreno-Manzano V,et al.Concise Review: Reactive Astrocytes and Stem Cells in Spinal Cord Injury: Good Guys or Bad Guys?Stem Cells. 2015;33(4):1036-1041.[26]Zhou X, He X, Ren Y.Function of microglia and macrophages in secondary damage after spinal cord injury.Neural Regen Res.2014; 9(20):1787-1795.[27]Gensel JC,Zhang B.Macrophage activation and its role in repair and pathology after spinal cord injury.Brain Res. 2015;1619:1-11.[28]党圆圆.SOCS3敲除对小鼠脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞/巨噬细胞极化作用及功能恢复的影响[D].北京:中国人民解放军医学院, 2016.[29]Kim JY,Choi GS, Cho YW,et al.Attenuation of spinal cord injury-induced astroglial and microglial activation by repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in rats.J Korean Med Sci. 2013;28(2):295-299.[30]Fu PC, Tang RH, Yu ZY, et al.The Rho-associated kinase inhibitors Y27632 and fasudil promote microglial migration in the spinal cord via the ERK signaling pathway.Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(4):677-683.[31]Greenhalgh AD,David S.Differences in the Phagocytic Response of Microglia and Peripheral Macrophages after Spinal Cord Injury and Its Effects on Cell Death.J Neurosci. 2014; 34(18):6316-6322.[32]Boekhoff TM, nsinger EM,Carlson R,et al.Microglial contribution to secondary injury evaluated in a large animal model of human spinal cord trauma.J Neurotrauma.2012;29(5):1000-1011.[33]Fujiki M,Zhang Z,Guth L,et al.Genetic influences on cellular reactions to spinal cord injury: Activation of macrophages/microglia and astrocytes is delayed in mice carrying a mutation (WldS) that causes delayed Wallerian degeneration.J Comp Neurol.1996;371(3):469-484.[34]Fan H,Zhang K,Shan L,et al.Reactive astrocytes undergo M1 microglia/macrohpages-induced necroptosis in spinal cord injury.Mol Neurodegener.2016;11:14.[35]范筱,张俐.益气活血法调控脊髓损伤后相关基因的表达[J].中华中医药杂志,2017,32(3):289-292. |
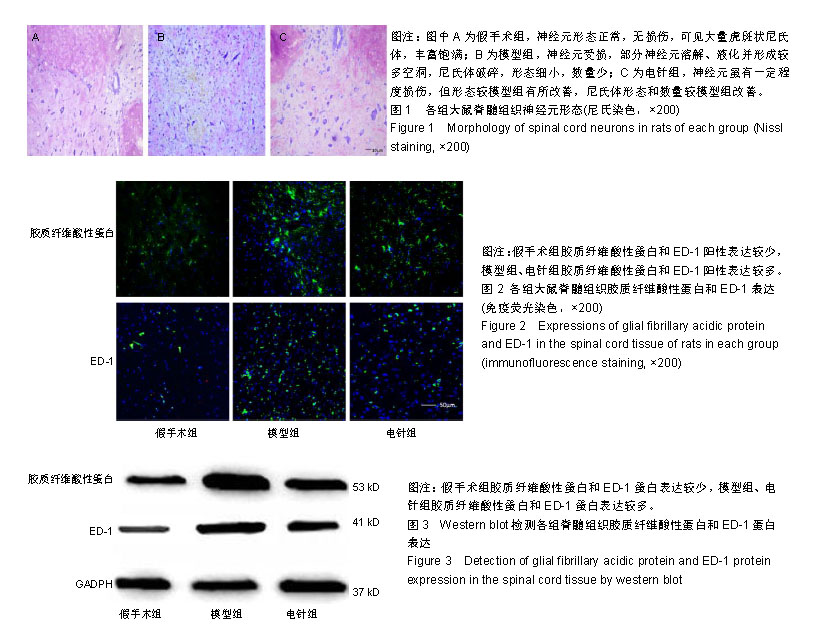
.jpg)
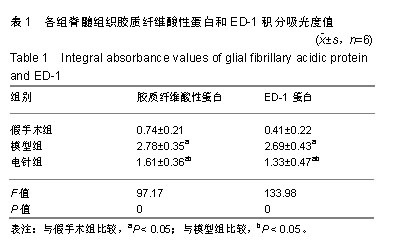
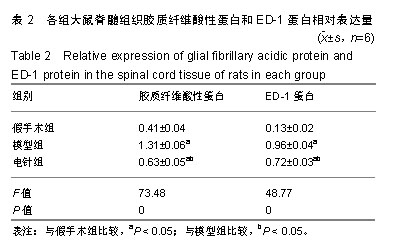
.jpg)
.jpg)