| [1] Muldoon LL, Alvarez JI, Begley DJ, et al. Immunologic privilege in the central nervous system and the blood. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013;33(1):13-21. [2] Jha MK, Suk K, G1ia. based biomarkers and their functional role in the CNS. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2013;10:43-63.[3] Gonz61ez H, Elgueta D, Montoya A, et al. Neuroimmune regulation of mieroglial activity involved in neuro-inflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. J Neuroimmunol. 2014;274:1-13. [4] Sveinbjornsdottir S. The clinical symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem. 2016;139:318. [5] He H, Wang S, Tian J, et al. Protective effects of 2, 3, 5, 4-tetra-hydroxystilbene-2-O-B-dglucoside in the MPTP-induced mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: Involvement of reactive of oxygen species mediated JNK, P38 and mitochondrial pathways. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;767:175-182.[6] Benskey MJ, Perez RG, Manfredsson FP. The contribution of alpha synuclein to neuronal survival and function-implications for parkinson′s disease. J Neurochem. 2016;137(3):331-359. [7] Gallagher DA, Schapira AH. Etiopathogenesis and treatment of Parkinson′s disease. Curr Top Med Chem. 2009;9(10):860-868. [8] Giordano S, Darley-Usmar V, Zhang J. Autophagy as an essential cellular antioxidant pathway in neurodegenerative disease. Redox Biol. 2014;2(1):82-90. [9] Labandeira-Garcia JL, Rodriguez-Pallares J, Dominguez-Meijide A, et al. opamine-angiotensin interactions in the basal ganglia and their relevance for Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2013;28(10): 1337-1342. [10] Borrajo A, Rodriguez-Perez AI, Diaz-Ruiz C, et al. Microglial TNF-alpha mediates enhancement of dopaminergic degeneration by brain angiotensin. Glia. 2014;62(1):145-157. [11] Hirsch EC, Vyas S, Hunot S. Neuroinflanunation in Parkinson's Disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2011;18:85-64. [12] 杨丽娟,董军,陆大祥,等.姜黄素对脂多糖激活小胶质细胞条件培养基诱导损伤的海马神经元保护作用及机制[J].中国病理生理杂志,2010, 26(4):742-747.[13] 和青.LPS经鼻小鼠帕金森病模型的建立及Rho激酶靶点干预探讨[D].上海:复旦大学,2013.[14] Smith AR, Shenvi SV, Widlansky M, et al. Lipoicacid as a potential therapy for chronicdisease associated with oxidative stress. Curr Med Chem. 2004;11(9):1135-1146. [15] 李艳花,和青,尉杰忠,等.硫辛酸对 脂多糖 诱导的帕金森病小鼠黑质多巴胺能神经元损伤的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2015,31(2): 201-206.[16] Zaitone SA, Abo-Eimatty DM, Shaalan AA. Acety1-L-carnitine and a-lipoicacid affect rotenone-induced damage in nigral dopaminergic neurons of rat brain implication for Parkinson’ s disease therapy. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012;100(3): 347-360. [17] Müller U, Krieglstein J. Prolonged pretreatment with alpha-lipoic acid protects cultured neurons against hypoxic, glutamate-, or iron-induced injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1995;15(4): 624-630. [18] Perez-Matos MC, Morales-Alvarez MC, Mendivil CO. Lipids: A Suitable Therapeutic Target in Diabetic Neuropathy? . J Diabetes Res. 2017;2017:6943851. [19] Dong Y, Wang H, Chen Z. Alpha-Lipoic Acid Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury via Insulin Receptor and PI3K/Akt-Dependent Inhibition of NADPH Oxidase. Int J Endocrinol. 2015;2015, 903186. [20] Kamarudin MN, Mohd Raflee NA, Hussein SS, et al. (R)-(+)-α-lipoic acid protected NG108-15 cells against H?O?-induced cell death through PI3K-Akt/GSK-3β pathway and suppression of NF-κβ-cytokines. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014;8: 1765-1780. [21] Kones R. Mitochondfial therapy for Parkinson’s disease: neuroprotective pharmaconutrition may be disease-modifying. Clin Pharmacol. 2010;2:185-198. [22] 马玲,周勇,王莉,等.硫辛酸减轻高尿酸血症大鼠氧化应激损伤[J].基础医学与临床,2015,35(8):1037-1041. [23] Rochette L, Ghibu S, Richard C, et al. Direct and indirect antioxidant properties of alpha-lipoic acid and therapeutic potential. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013;57(1):114-125. [24] Kleinkauf-Rocha J, Bobermin LD, Machado PM, et al. Lipoicacid increases glutamate uptake, glutamine symhetase activity and glutathione content in C6 astrocyte cell line. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2013;31(3):165-170. [25] [Papanas N, Ziegler D. Efficacy of α-lipoic acid in diabetic neuropathy. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2014;15(18):2721-2731. [26] Zhao L, Hu FX. Alpha-Lipoic acid treatment of aged type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with acute cerebral infarction. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18(23):3715-3719. [27] Saygin M, Asci H, Cankara FN, et al. The impact of high fructose on cardiovascular system: Role of alpha-lipoicacid. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2015;35(2):194-204. [28] Hegazy SK, Tolba OA, Mostafa TM, et al. Alpha•lipoicacid improves subclinical left ventricular dysfunction in asymptomatie patients with type 1 diabetes. Rev Diabet Stud. 2013;10(1):58-67. [29] Koriyama Y, Nakayama Y, Matsugo S, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of lipoic acid through inhibition of GSK-3β in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV-2 microglial cells. Neurosci Res. 2013;77(1-2):87-96. [30] Jiang S, Zhu W, Li C, et al. α-Lipoic acid attenuates 脂多糖-induced cardiac dysfunction through a PI3K/Akt-dependent mechanism. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013;16(1):100-107. [31] Ying Z, Xie X, Chen M, et al. Alpha-lipoic acid activates eNOS through activation of PI3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Vascul Pharmacol. 2015;64:28-35. [32] Liu SF, Malik AB. NF-kappa B activation as a pathological mechanism of septic shock and inflammation. Am J Physiol, Cell Mol Physiol. 2006;290(1):L622-L645. [33] Wu DC, Teismann P, Tieu K, et al. NADPH oxidase mediates oxidative stress in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine model of Parkinson′s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100(10):6145-6150. [34] Zhang F, Qian L, Flood PM, et al. Inhibition of IkappaB kinase-beta protectsdopamine neurons against lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010;333(3):822-833. [35] Li Y, Ma QG, Zhao LH, et al. Effects of lipoic acid on immune function, the antioxidant defense system, and inflammation-related genes expression of broiler chickens fed aflatoxin contaminated diets. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(4):5649-5662. [36] Kim HS, Kim HJ, Park KG, et al. Alpha-lipoic acid inhibits matrix metallop-roteinase-9 expression by inhibiting NF-kappaB transcriptional activity. Exp Mol Med. 2001;39(1):106-113. [37] Li G, Fu J, Zhao Y, Ji K, et al. Alpha-lipoic acid exerts anti-inflammatory effects on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated rat mesangial cells via inhibition of nuclear factor kappa b(NF-kappab) signaling pathway. Inflammation. 2015;38(2):510-519. [38] Koriyama Y, Nakayama Y, Matsugo S. et al Anti-inflammatory effects of lipoic acid through inhibition of GSK-3β in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV-2 microglial cells. Neurosci Res. 2013;77(1/2):87-96. [39] Li YH, He Q, Yu JZ, et al. Lipoic acid protects dopaminergic neurons in lps-induced parkinson′s disease model. Metab Brain Dis. 2015;30(5):1-10. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
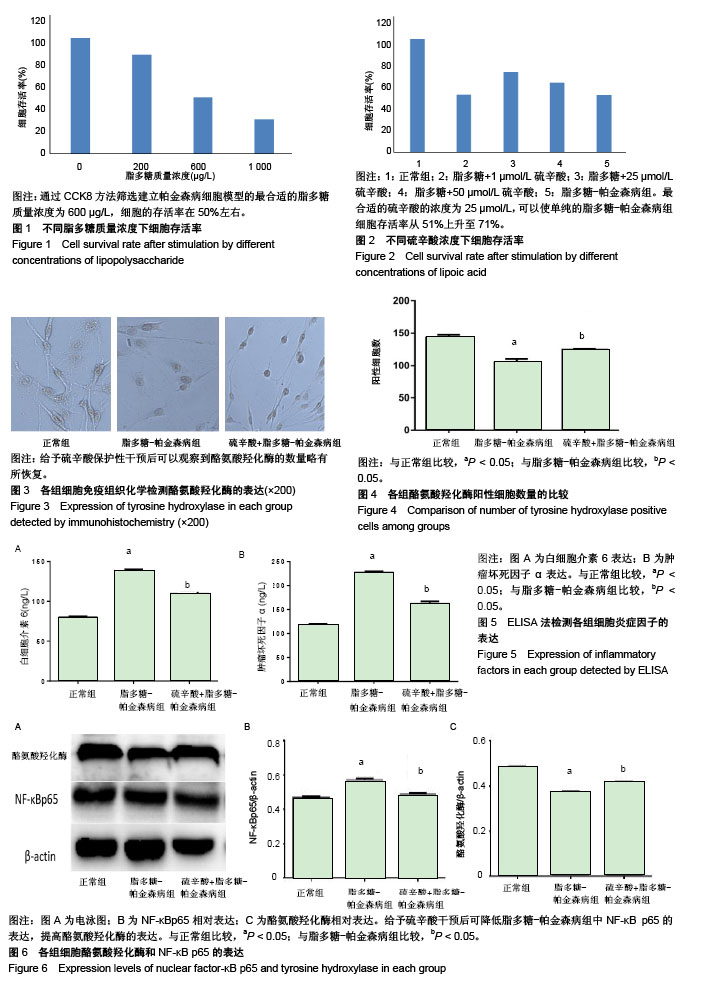
.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
小胶质细胞的活化:小胶质细胞作为构成中枢神经系统免疫防御的第一线,如果在一定条件下受到损伤,这些细胞将被激活并在这种状态下改变它们的形态、增殖状态,迁移到破坏位点,影响相关酶类和受体的表达,释放多种炎症因子,如一氧化氮,肿瘤坏死因子α,白细胞介素6等。#br#
神经炎症:血脑屏障的存在被认为可以阻止外周的免疫细胞进入脑内,所以中枢神经系统被认为是“免疫豁免区”。但研究表明脑内的胶质细胞可以发挥免疫应答功能与外周免疫细胞相同,它们的激活时可以介导脑内炎症免疫的发生。#br#
#br#
#br#
文题释义:#br#
小胶质细胞的活化:小胶质细胞作为构成中枢神经系统免疫防御的第一线,如果在一定条件下受到损伤,这些细胞将被激活并在这种状态下改变它们的形态、增殖状态,迁移到破坏位点,影响相关酶类和受体的表达,释放多种炎症因子,如一氧化氮,肿瘤坏死因子α,白细胞介素6等。#br#
神经炎症:血脑屏障的存在被认为可以阻止外周的免疫细胞进入脑内,所以中枢神经系统被认为是“免疫豁免区”。但研究表明脑内的胶质细胞可以发挥免疫应答功能与外周免疫细胞相同,它们的激活时可以介导脑内炎症免疫的发生。#br#
#br#