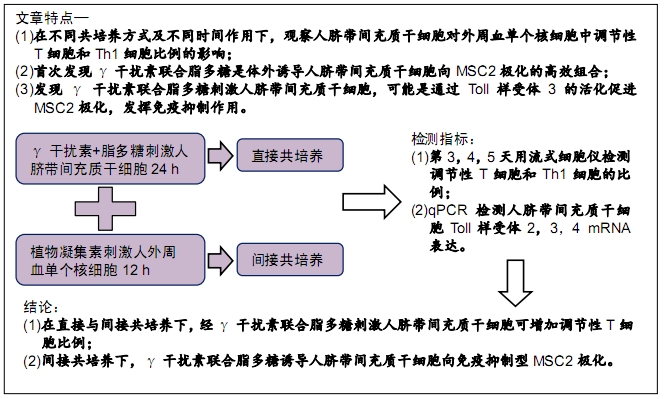
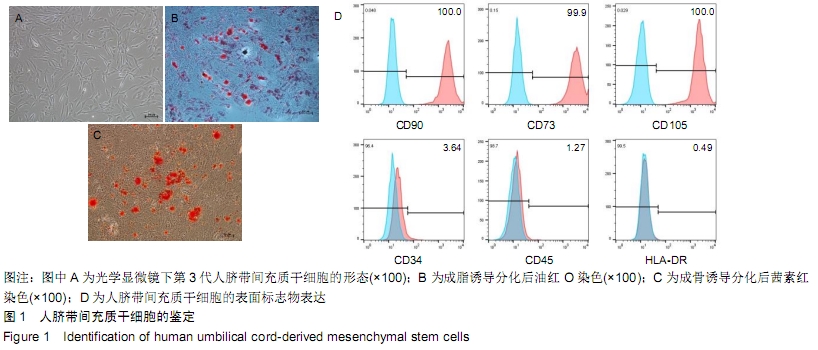
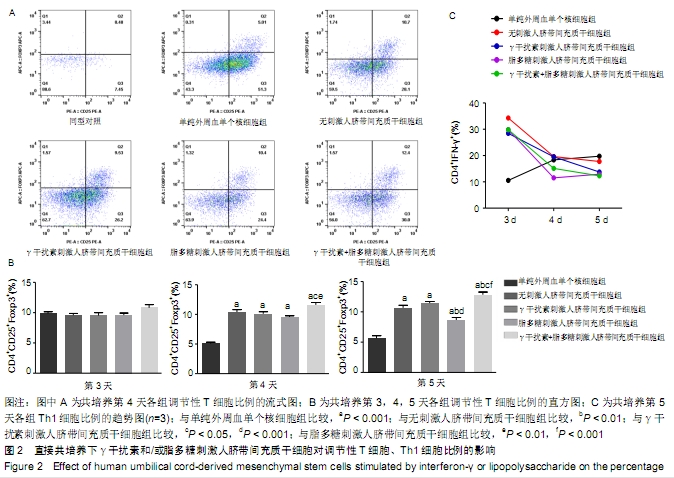
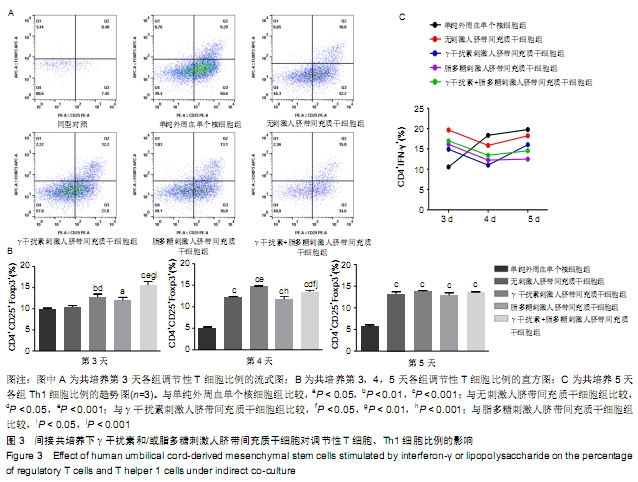
[1] WUCHTER P, BIEBACK K, SCHREZENMEIER H, et al. Standardization of Good Manufacturing Practice-compliant production of bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stromal cells for immunotherapeutic applications. Cytotherapy. 2015;17(2):128-139.
[2] TESSIER L, BIENZLE D, WILLIAMS LB, et al. Phenotypic and immunomodulatory properties of equine cord blood-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. PLoS One. 2015; 10(4):e0122954.
[3] XU AL, RODRIGUEZ LA 2ND, WALKER KP 3RD, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reconditioned in Their Own Serum Exhibit Augmented Therapeutic Properties in the Setting of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(10):1092-1106.
[4] WENG JY, DU X, GENG SX, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell as salvage treatment for refractory chronic GVHD. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2010;45(12):1732-1740.
[5] WANG Y, CHEN X, CAO W, et al. Plasticity of mesenchymal stem cells in immunomodulation: pathological and therapeutic implications. Nat Immunol. 2014;15(11):1009-1016.
[6] TOMCHUCK SL, ZWEZDARYK KJ, COFFELT SB, et al. Toll-like receptors on human mesenchymal stem cells drive their migration and immunomodulating responses. Stem Cells. 2008;26(1):99-107.
[7] WATERMAN RS, TOMCHUCK SL, HENKLE SL, et al. A new mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) paradigm: polarization into a pro-inflammatory MSC1 or an Immunosuppressive MSC2 phenotype. PLoS One. 2010;5(4):e10088.
[8] ROMIEU-MOUREZ R, FRANÇOIS M, BOIVIN MN, et al. Bouchentouf M,Cytokine modulation of TLR expression and activation in mesenchymal stromal cells leads to a proinflammatory phenotype. J Immunol. 2009;182(12): 7963-7973.
[9] DOMINICI M, LE BLANC K, MUELLER I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.
[10] CRAIN SK, ROBINSON SR, THANE KE, et al. Extracellular Vesicles from Wharton's Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells Suppress CD4 Expressing T Cells Through Transforming Growth Factor Beta and Adenosine Signaling in a Canine Model. Stem Cells Dev. 2019;28(3):212-226.
[11] SHI Y, WANG Y, LI Q, et al. Immunoregulatory mechanisms of mesenchymal stem and stromal cells in inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018;14(8):493-507.
[12] KHOSRAVI M, BIDMESHKIPOUR A, MORAVEJ A, et al. Induction of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells by mesenchymal stem cells is associated with RUNX complex factors. Immunol Res. 2018;66(1):207-218.
[13] 陈柄全,彭漪,肖轶,等.人脐血间充质干细胞对小鼠骨髓巨噬细胞M2亚型的转化作用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(25): 3987-3992.
[14] PENG Y, CHEN X, LIU Q, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells infusions improve refractory chronic graft versus host disease through an increase of CD5+ regulatory B cells producing interleukin 10. Leukemia. 2015;29(3):636-646.
[15] SAKAGUCHI S, YAMAGUCHI T, NOMURA T, et al. Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell. 2008;133(5): 775-787.
[16] WING K, SAKAGUCHI S. Regulatory T cells exert checks and balances on self tolerance and autoimmunity. Nat Immunol. 2010;11(1):7-13.
[17] LIN X, CHEN M, LIU Y, et al. Advances in distinguishing natural from induced Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013;6(2):116-123.
[18] CHAMBERS CA, KANG J, WU Y, et al. The lymphoproliferative defect in CTLA-4-deficient mice is ameliorated by an inhibitory NK cell receptor. Blood. 2002;99(12):4509-4516.
[19] COPSEL S, WOLF D, KOMANDURI KV, et al. The promise of CD4+FoxP3+ regulatory T-cell manipulation in vivo: applications for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica. 2019;104(7):1309-1321.
[20] TAYLOR PA, NOELLE RJ, BLAZAR BR. CD4(+)CD25(+) immune regulatory cells are required for induction of tolerance to alloantigen via costimulatory blockade. J Exp Med. 2001;193(11):1311-1318.
[21] BERES AJ, DROBYSKI WR. The role of regulatory T cells in the biology of graft versus host disease. Front Immunol. 2013;4:163.
[22] ELIAS S, RUDENSKY AY. Therapeutic use of regulatory T cells for graft-versus-host disease. Br J Haematol. 2019; 187(1):25-38.
[23] BRUNSTEIN CG, MILLER JS, MCKENNA DH, et al. Umbilical cord blood-derived T regulatory cells to prevent GVHD: kinetics, toxicity profile, and clinical effect. Blood. 2016;127(8): 1044-1051.
[24] BLAZAR BR, MACDONALD KPA, HILL GR. Immune regulatory cell infusion for graft-versus-host disease prevention and therapy. Blood. 2018;131(24):2651-2660.
[25] CHAN JL, TANG KC, PATEL AP, et al. Antigen-presenting property of mesenchymal stem cells occurs during a narrow window at low levels of interferon-gamma. Blood. 2006; 107(12):4817-4824.
[26] WATERMAN RS, HENKLE SL, BETANCOURT AM. Mesenchymal stem cell 1 (MSC1)-based therapy attenuates tumor growth whereas MSC2-treatment promotes tumor growth and metastasis. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45590.
[27] OPITZ CA, LITZENBURGER UM, LUTZ C, et al. Toll-like receptor engagement enhances the immunosuppressive properties of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by inducing indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase-1 via interferon-beta and protein kinase R. Stem Cells. 2009;27(4): 909-919.
[28] REN G, ZHANG L, ZHAO X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated immunosuppression occurs via concerted action of chemokines and nitric oxide. Cell Stem Cell. 2008; 2(2):141-150.
[29] BOLAND L, BURAND AJ, BROWN AJ, et al. IFN-γ and TNF-α Pre-licensing Protects Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from the Pro-inflammatory Effects of Palmitate. Mol Ther. 2018;26(3): 860-873.
[30] VEGA-LETTER AM, KURTE M, FERNÁNDEZ-O'RYAN C, et al. Differential TLR activation of murine mesenchymal stem cells generates distinct immunomodulatory effects in EAE. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):150.
[31] KRAMPERA M, GLENNIE S, DYSON J, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the response of naive and memory antigen-specific T cells to their cognate peptide. Blood. 2003;101(9):3722-3729.
[32] GLENNIE S, SOEIRO I, DYSON PJ, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induce division arrest anergy of activated T cells. Blood. 2005;105(7):2821-2827.
[33] DEL FATTORE A, LUCIANO R, PASCUCCI L, et al. Immunoregulatory Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles on T Lymphocytes. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(12):2615-2627.
[34] PIANTA S, BONASSI SIGNORONI P, MURADORE I, et al. Amniotic membrane mesenchymal cells-derived factors skew T cell polarization toward Treg and downregulate Th1 and Th17 cells subsets. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015;11(3):394-407.
[35] KAY AG, LONG G, TYLER G, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium Reduces Disease Severity and Immune Responses in Inflammatory Arthritis. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1):18019.
[36] POLCHERT D, SOBINSKY J, DOUGLAS G, et al. IFN-gamma activation of mesenchymal stem cells for treatment and prevention of graft versus host disease. Eur J Immunol. 2008;38(6):1745-1755.
[37] DUIJVESTEIN M, WILDENBERG ME, WELLING MM, et al. Pretreatment with interferon-γ enhances the therapeutic activity of mesenchymal stromal cells in animal models of colitis. Stem Cells. 2011;29(10):1549-1558.
[38] CASSANO JM, SCHNABEL LV, GOODALE MB, et al. The immunomodulatory function of equine MSCs is enhanced by priming through an inflammatory microenvironment or TLR3 ligand. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2018;195:33-39.
[39] MEISEL R, ZIBERT A, LARYEA M, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells inhibit allogeneic T-cell responses by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-mediated tryptophan degradation. Blood. 2004;103(12):4619-4621.
[40] GHANNAM S, BOUFFI C, DJOUAD F, et al. Immunosuppression by mesenchymal stem cells: mechanisms and clinical applications. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2010;1(1):2.
[41] KRAMPERA M, COSMI L, ANGELI R, et al. Role for interferon-gamma in the immunomodulatory activity of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2006; 24(2):386-398.
[42] LAI RC, YEO RW, LIM SK. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015;40:82-88.
[43] LIA G, BRUNELLO L, BRUNO S, et al. Extracellular vesicles as potential biomarkers of acute graft-vs-host disease. Leukemia. 2018;32(3):765-773.
[44] WANG L, GU Z, ZHAO X, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Released from Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Prevent Life-Threatening Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease in a Mouse Model of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Stem Cells Dev. 2016;25(24):1874-1883.
[45] KORDELAS L, REBMANN V, LUDWIG AK, et al. MSC-derived exosomes: a novel tool to treat therapy-refractory graft-versus-host disease. Leukemia. 2014;28(4):970-973.
[46] BRUNO S, DEREGIBUS MC, CAMUSSI G. The secretome of mesenchymal stromal cells: Role of extracellular vesicles in immunomodulation. Immunol Lett. 2015;168(2):154-158.
[47] LAI P, WENG J, GUO L, et al. Novel insights into MSC-EVs therapy for immune diseases. Biomark Res. 2019;7:6.
[48] LAI P, CHEN X, GUO L, et al. A potent immunomodulatory role of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stromal cells in preventing cGVHD. J Hematol Oncol. 2018;11(1):135.
|