| [1] 刘玉静,曹永梅,平凤,等. LPS诱导大鼠急性肺损伤后早期肺纤维化进展过程中肺组织AT1R/Mas受体表达的动态变化[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版),2016,36(5):636-641.[2] 鲁刚,马奎,付小兵. 脐带间充质干细胞对创伤后早期急性肺损伤作用的研究[J]. 感染、炎症、修复,2013,14(1):3-6.[3] Matthay MA, Thompson BT, Read EJ, et al. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells for severe acute lung injury. Chest. 2010;138(4):965-972.[4] Cribbs SK, Martin GS. Stem cells in sepsis and acute lung injury. Am J Med Sci. 2011;341(4):325-332. [5] Lee JW, Gupta N, Serikov V, et al. Potential application of mesenchymal stem cells in acute lung injury. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2009;9(10):1259-1270.[6] 朱峰,胡贞贞,郭光华. 肺外成体干细胞移植治疗急性肺损伤研究进展[J].第二军医大学学报,2009,30(6):713-716.[7] Soh BS, Zheng D, Li Yeo JS, et al. CD166(pos) subpopulation from differentiated human ES and iPS cells support repair of acute lung injury. Mol Ther. 2012;20(12):2335-2346.[8] Zhang Z, Li W, Heng Z, et al. Combination therapy of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and FTY720 attenuates acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide in a murine model. Oncotarget. 2017;8(44):77407-77414.[9] Zhu H, Xiong Y, Xia Y, et al. Therapeutic Effects of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Acute Lung Injury Mice. Sci Rep. 2017;7:39889.[10] Taki T, Masumoto H, Funamoto M, et al. Fetal mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate acute lung injury in a rat cardiopulmonary bypass model. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;153(3):726-734.[11] Xiang B, Chen L, Wang X, et al. Transplantation of Menstrual Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promotes the Repair of LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(4): E689.[12] Su VY, Chiou SH, Lin CS, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cells reduce neutrophil chemotaxis via activating GRK2 in endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. Respirology. 2017; 22(6):1156-1164.[13] Yang KY, Shih HC, How CK, et al. IV delivery of induced pluripotent stem cells attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. Chest. 2011;140(5):1243-1253.[14] 刘通,张铮.诱导性多能干细胞与心血管疾病[J].心血管病学进展,2011,32(6):873-876.[15] 王建军,赵平,靳雪源,等. 诱导性多能干细胞治疗小鼠肝损伤的初步研究[J].中国肝脏病杂志,2016,8(2):39-43.[16] 朱世琪,李峰. 诱导性多能干细胞在阿尔茨海默病治疗研究中的应用进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2017,21(21):3426-3431.[17] 任佩佩,樊晋宇,丰慧根,等.诱导性多能干细胞技术在帕金森病研究中的进展[J].医学研究生学报,2016,29(7):770-774.[18] 李萌萌,周建业,宋江平. 诱导性多能干细胞在心肌病中的应用[J]. 中国循环杂志,2017,32(9):934-936.[19] 王欢,方煌,李潇,等. 人诱导性多能干细胞的无饲养层培养及鉴定[J]. 骨科,2016,7(1):49-53.[20] Yao L, Chen R, Wang P, et al. Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells with high efficiency from human embryonic renal cortical cells. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8(11): 4982-4993.[21] 曲泽澎,管圆,崔璐,等.大鼠诱导性多能干细胞向神经前体细胞诱导分化研究[J]. 同济大学学报(医学版), 2013,34(3):1-6,11.[22] 陈旭东,范文娟,袁科理,等. 不同培养条件对小鼠诱导性多能干细胞分化为神经元样细胞的影响[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2015,31(9):1216-1223.[23] 高鹏飞,张锋,程彬彬,等. 核因子-κB介导脂多糖诱导急性肺损伤大鼠高迁移率族蛋白B1的表达[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2015, 31(3):278-281.[24] Wang D, Morales JE, Calame DG, et al. Transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived alveolar epithelial type II cells abrogates acute lung injury in mice. Mol Ther. 2010; 18(3):625-634. [25] 夏彦民,王文辰,张鸿,等.人羊膜上皮细胞气管内滴注对脂多糖诱导小鼠急性肺损伤的保护作用[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2017, 33(1):7-11.[26] 崔蕾,雷鑫,牛玉虎,等. 人脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗大鼠急性肺损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(14):2563-2569. [27] Mikawa K, Nishina K, Takao Y, et al. ONO-1714, a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in rabbits. Anesth Analg. 2003;97(6):1751-1755.[28] Xin X, Yan L, Guangfa Z, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promoted Lung Wound Repair through Hox A9 during Endotoxemia-Induced Acute Lung Injury. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:3648020.[29] 张自丽,刘慧莹,柏长青. 间充质干细胞治疗急性肺损伤的研究进展[J].临床肺科杂志,2015,20(11):2096-2097.[30] 王婷,梁华平,柴鉴深,等. 三种大鼠急性肺损伤模型的比较[J]. 成都医学院学报,2016,11(1):5-9.[31] 温保强,刘江华. LPS诱导鼠急性肺损伤模型的评价分析[J]. 中国医学创新,2017,14(26):137-140.[32] 佟昌慈,柳云恩,张玉彪,等. 脂肪干细胞治疗急性肺损伤研究进展[J]. 创伤与急危重病医学,2017,5(5):292-297.[33] Pedrazza L, Cunha AA, Luft C, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells improves survival in LPS-induced acute lung injury acting through inhibition of NETs formation. J Cell Physiol. 2017; 232(12):3552-3564. [34] Li D, Pan X, Zhao J, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Suppress Acute Lung Injury Induced by Lipopolysaccharide Through Inhibiting the TLR2, 4/NF-κB Pathway in Rats with Multiple Trauma. Shock. 2016;45(6): 641-646.[35] Hao Q, Zhu YG, Monsel A, et al. Study of Bone Marrow and Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Treatment of Escherichia coli Endotoxin-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(7): 832-840.[36] Zhang S, Danchuk SD, Bonvillain RW, et al. Interleukin 6 mediates the therapeutic effects of adipose-derived stromal/stem cells in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Stem Cells. 2014;32(6):1616-1628.[37] Li J, Huang S, Wu Y, et al. Paracrine factors from mesenchymal stem cells: a proposed therapeutic tool for acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Int Wound J. 2014;11(2):114-121.[38] Xu F, Hu Y, Zhou J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in acute lung injury: are they ready for translational medicine. J Cell Mol Med. 2013;17(8):927-935.[39] Martínez-González I, Roca O, Masclans JR, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing the IL-33 antagonist soluble IL-1 receptor-like-1 attenuate endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013;49(4): 552-562.[40] Li JW, Wu X. Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate LPS-induced acute lung injury through KGF promoting alveolar fluid clearance of alveolar type II cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19(13):2368-2378. |
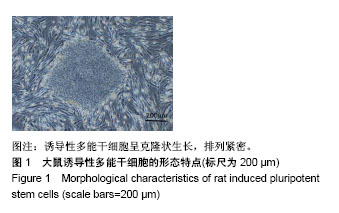
.jpg)
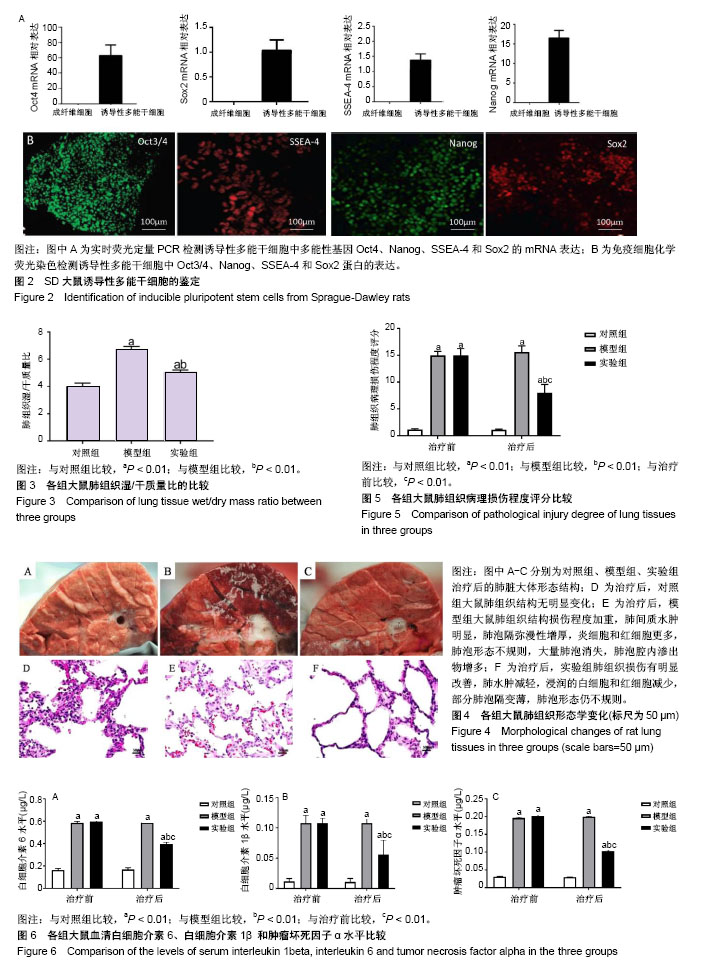
.jpg)
.jpg)