|
[1] ASAHARA T, MUROHARA T, SULLIVAN A, et al. Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science. 1997;275(5302):964-967.
[2] ASAHARA T, MASUDA H, TAKAHASHI T, et al. Bone marrow origin of endothelial progenitor cells responsible for postnatal vasculogenesis in physiological and pathological neovascularization. Circ Res. 1999;85(3):221-228.
[3] DOYLE B, METHAROM P, CAPLICE NM. Endothelial progenitor cells. Endothelium. 2006;13(6):403-410.
[4] LAING AJ, DILLON JP, CONDON ET, et al. Mobilization of endothelial precursor cells: systemic vascular response to musculoskeletal trauma. J Orthop Res. 2007;25(1):44-50.
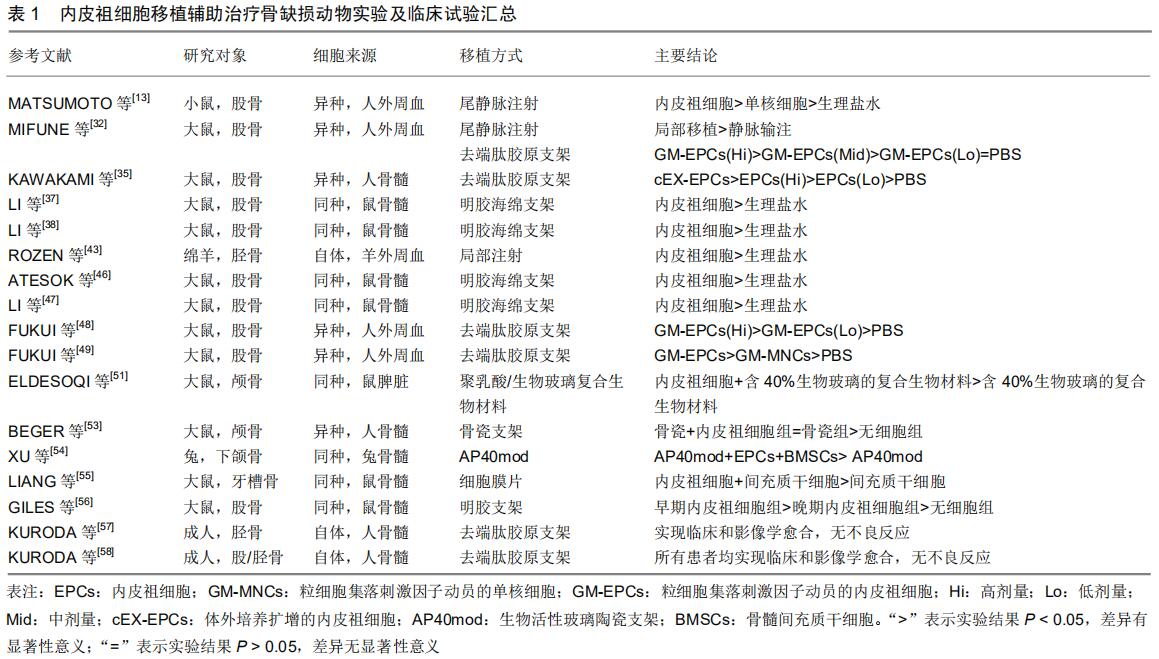
[5] MATSUMOTO T, KURODA R, MIFUNE Y, et al. Circulating endothelial/skeletal progenitor cells for bone regeneration and healing. Bone. 2008;43(3):434-439.
[6] RISAU W, SARIOLA H, ZERWES HG, et al. Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis in embryonic-stem-cell-derived embryoid bodies. Development. 1988;102(3):471-478.
[7] MARSH D. Concepts of fracture union, delayed union, and nonunion. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;(355 Suppl):S22-30.
[8] SCHMITZ JP, HOLLINGER JO. The critical size defect as an experimental model for craniomandibulofacial nonunions. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;(205):299-308.
[9] JANG BJ, BYEON YE, LIM JH, et al. Implantation of canine umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells mixed with beta-tricalcium phosphate enhances osteogenesis in bone defect model dogs. J Vet Sci. 2008;9(4):387-393.
[10] ZIGDON-GILADI H, BICK T, LEWINSON D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells stimulate bone regeneration and mineral density. J Periodontol. 2014;85(7):984-990.
[11] LIU Y, TEOH SH, CHONG MS, et al. Contrasting effects of vasculogenic induction upon biaxial bioreactor stimulation of mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells cocultures in three-dimensional scaffolds under in vitro and in vivo paradigms for vascularized bone tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(7-8):893-904.
[12] GEUZE RE, WEGMAN F, ONER FC, et al. Influence of endothelial progenitor cells and platelet gel on tissue-engineered bone ectopically in goats. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(11):3669-3677.
[13] MATSUMOTO T, KAWAMOTO A, KURODA R, et al. Therapeutic potential of vasculogenesis and osteogenesis promoted by peripheral blood CD34-positive cells for functional bone healing. Am J Pathol. 2006;169(4): 1440-1457.
[14] LU C, MICLAU T, HU D, et al. Ischemia leads to delayed union during fracture healing: a mouse model. J Orthop Res. 2007;25(1):51-61.
[15] EINHORN TA. Enhancement of fracture-healing. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77(6):940-956.
[16] COLNOT CI, HELMS JA. A molecular analysis of matrix remodeling and angiogenesis during long bone development. Mech Dev. 2001;100(2):245-250.
[17] CARANO RA, FILVAROFF EH. Angiogenesis and bone repair. Drug Discov Today. 2003;8(21):980-989.
[18] GLOWACKI J. Angiogenesis in fracture repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;(355 Suppl):S82-89.
[19] 汤文燕,栾佐.内皮祖细胞的生物学特性及其临床应用前景[J].中国生物工程杂志,2016,36(10):86-93.
[20] ASAHARA T, KAWAMOTO A, MASUDA H. Concise review: Circulating endothelial progenitor cells for vascular medicine. Stem Cells. 2011;29(11):1650-1655.
[21] LEE JH, HAH YS, CHO HY, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived CD34-positive endothelial progenitor cells stimulate osteoblastic differentiation of cultured human periosteal-derived osteoblasts. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014; 20(5-6):940-953.
[22] HUR J, YOON CH, KIM HS, et al. Characterization of two types of endothelial progenitor cells and their different contributions to neovasculogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24(2):288-293.
[23] MEDINA RJ, BARBER CL, SABATIER F, et al. Endothelial Progenitors: A Consensus Statement on Nomenclature. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(5):1316-1320.
[24] GILL M, DIAS S, HATTORI K, et al. Vascular trauma induces rapid but transient mobilization of VEGFR2(+)AC133(+) endothelial precursor cells. Circ Res. 2001;88(2):167-174.
[25] SHINTANI S, MUROHARA T, IKEDA H, et al. Mobilization of endothelial progenitor cells in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2001;103(23):2776-2779.
[26] MASUDA H, KALKA C, TAKAHASHI T, et al. Estrogen-mediated endothelial progenitor cell biology and kinetics for physiological postnatal vasculogenesis. Circ Res. 2007;101(6):598-606.
[27] II M, NISHIMURA H, IWAKURA A, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells are rapidly recruited to myocardium and mediate protective effect of ischemic preconditioning via "imported" nitric oxide synthase activity. Circulation. 2005; 111(9):1114-1120.
[28] LEE DY, CHO TJ, KIM JA, et al. Mobilization of endothelial progenitor cells in fracture healing and distraction osteogenesis. Bone. 2008;42(5):932-941.
[29] MATSUMOTO T, MIFUNE Y, KAWAMOTO A, et al. Fracture induced mobilization and incorporation of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells for bone healing. J Cell Physiol. 2008;215(1):234-242.
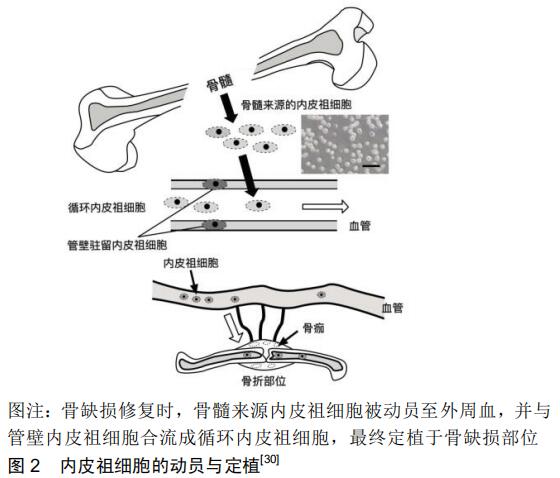
[30] KAWAKAMI Y, MATSUMOTO T, MIFUNE Y, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Endothelial Progenitor Cells in the Field of Orthopaedics. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;12(1):3-13.
[31] FORD JL, ROBINSON DE, SCAMMELL BE. Endochondral ossification in fracture callus during long bone repair: the localisation of 'cavity-lining cells' within the cartilage. J Orthop Res. 2004;22(2):368-375.
[32] MIFUNE Y, MATSUMOTO T, KAWAMOTO A, et al. Local delivery of granulocyte colony stimulating factor-mobilized CD34-positive progenitor cells using bioscaffold for modality of unhealing bone fracture. Stem Cells. 2008;26(6): 1395-1405.
[33] SEEBACH C, HENRICH D, KÄHLING C, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells and mesenchymal stem cells seeded onto beta-TCP granules enhance early vascularization and bone healing in a critical-sized bone defect in rats. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(6):1961-1970.
[34] AGUIRRE A, PLANELL JA, ENGEL E. Dynamics of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cell/mesenchymal stem cell interaction in co-culture and its implications in angiogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;400(2): 284-291.
[35] KAWAKAMI Y, II M, ALEV C, et al. Local transplantation of ex vivo expanded bone marrow-derived CD34-positive cells accelerates fracture healing. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(12): 2689-2709.
[36] FOLKMAN J, SHING Y. Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1992; 267(16):10931-10934.
[37] LI R, NAUTH A, LI C, et al. Expression of VEGF gene isoforms in a rat segmental bone defect model treated with EPCs. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26(12):689-692.
[38] LI R, NAUTH A, GANDHI R, et al. BMP-2 mRNA expression after endothelial progenitor cell therapy for fracture healing. J Orthop Trauma. 2014;28 Suppl 1:S24-27.
[39] KAWAMOTO A, ASAHARA T, LOSORDO DW. Transplantation of endothelial progenitor cells for therapeutic neovascularization. Cardiovasc Radiat Med. 2002;3(3-4): 221-225.
[40] JUJO K, II M, LOSORDO DW. Endothelial progenitor cells in neovascularization of infarcted myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008;45(4):530-544.
[41] MIYAMOTO Y, SUYAMA T, YASHITA T, et al. Bone marrow subpopulations contain distinct types of endothelial progenitor cells and angiogenic cytokine-producing cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2007;43(5):627-635.
[42] 周诺,廖妮,韦山良.一氧化氮合酶在犬下颌骨牵张成骨过程中的表达和意义[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2009,27(6):676-680.
[43] ROZEN N, BICK T, BAJAYO A, et al. Transplanted blood-derived endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) enhance bridging of sheep tibia critical size defects. Bone. 2009; 45(5):918-924.
[44] SMADJA DM, CORNET A, EMMERICH J, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells: characterization, in vitro expansion, and prospects for autologous cell therapy. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2007;23(4):223-239.
[45] 韩志琪,蒋伟东,周诺.干细胞组织工程技术辅助下颌牵张成骨的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(25):4037-4043.
[46] ATESOK K, LI R, STEWART DJ, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells promote fracture healing in a segmental bone defect model. J Orthop Res. 2010;28(8):1007-1014.
[47] LI R, ATESOK K, NAUTH A, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells for fracture healing: a microcomputed tomography and biomechanical analysis. J Orthop Trauma. 2011;25(8): 467-471.
[48] FUKUI T, MATSUMOTO T, MIFUNE Y, et al. Local transplantation of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-mobilized human peripheral blood mononuclear cells for unhealing bone fractures. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(4): 707-721.
[49] FUKUI T, MIFUNE Y, MATSUMOTO T, et al. Superior Potential of CD34-Positive Cells Compared to Total Mononuclear Cells for Healing of Nonunion Following Bone Fracture. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(7):1379-1393.
[50] JELL G, STEVENS MM. Gene activation by bioactive glasses. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2006;17(11):997-1002.
[51] ELDESOQI K, SEEBACH C, NGUYEN NGOC C, et al. High calcium bioglass enhances differentiation and survival of endothelial progenitor cells, inducing early vascularization in critical size bone defects. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e79058.
[52] BOSE S, TARAFDER S. Calcium phosphate ceramic systems in growth factor and drug delivery for bone tissue engineering: a review. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(4):1401-1421.
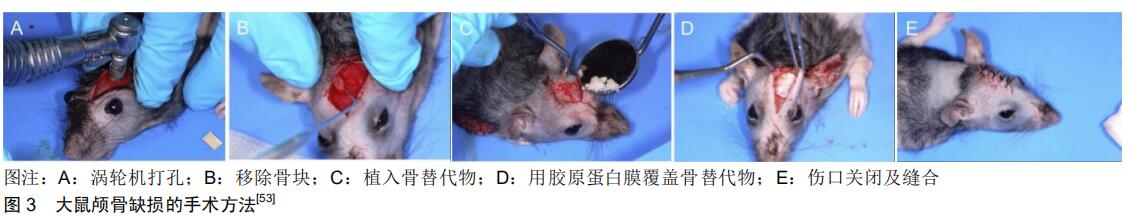
[53] BEGER B, BLATT S, PABST AM, et al. Biofunctionalization of synthetic bone substitutes with angiogenic stem cells: Influence on regeneration of critical-size bone defects in an in vivo murine model. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2018;46(9): 1601-1608.
[54] XU F, REN H, ZHENG M, et al. Development of biodegradable bioactive glass ceramics by DLP printed containing EPCs/BMSCs for bone tissue engineering of rabbit mandible defects. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2019;103: 103532.
[55] LIANG Y, WEN L, SHANG F, et al. Endothelial progenitors enhanced the osteogenic capacities of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and in a rat alveolar bone defect model. Arch Oral Biol. 2016;68:123-130.
[56] GILES EM, GODBOUT C, CHI W, et al. Subtypes of endothelial progenitor cells affect healing of segmental bone defects differently. Int Orthop. 2017;41(11):2337-2343.
[57] KURODA R, MATSUMOTO T, MIWA M, et al. Local transplantation of G-CSF-mobilized CD34(+) cells in a patient with tibial nonunion: a case report. Cell Transplant. 2011; 20(9):1491-1496.
[58] KURODA R, MATSUMOTO T, NIIKURA T, et al. Local transplantation of granulocyte colony stimulating factor-mobilized CD34+ cells for patients with femoral and tibial nonunion: pilot clinical trial. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014; 3(1):128-134.
|