| [1] Hervault A,Thanh NT.Magnetic nanoparticle-based therapeutic agents for thermo-chemotherapy treatment of cancer.Nanoscale. 2014;6(20): 11553-11573.[2] Guardia P,Di Corato R,Lartigue L,et al.Water-Soluble Iron Oxide Nanocubes with High Values of Specific Absorption Rate for Cancer Cell Hyperthermia Treatment.ACS Nano.2012;6(4):3080-3091.[3] Fang J,Nakamura H,Maeda H.The EPR effect: unique features of tumor blood vessels for drug delivery, factors involved, and limitations and augmentation of the effect.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63(3): 136-151.[4] Ding W,Guo L.Immobilized transferrin Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticle with high doxorubicin loading for dual-targeted tumor drug delivery.Int J Nanomedicine.2013;8:4631-4639.[5] Kaur P,Aliru ML,Chadha AS,et al.Hyperthermia using nanoparticles-promises and pitfalls.Int J Hyperther. 2016;32:76-88.[6] Dennis CL,Ivkov R.Physics of heat generation using magnetic nanoparticles for hyperthermia.Int J Hyperther. 2013;29:715-729.[7] Sanz B,Calatayud MP,Torres TE,et al.Magnetic hyperthermia enhances cell toxicity with respect to exogenous heating. Biomaterials. 2017;114:62-70.[8] Kaur P,Aliru ML,Chadha AS,et al.Hyperthermia using nanoparticles- promises and pitfalls.Int J Hyperther. 2016;32:76-88.[9] Dennis CL,Ivkov R.Physics of heat generation using magnetic nanoparticles for hyperthermia.Int J Hyperther 2013;29:715-729.[10] Zhou Z,Sun Y,Shen J,etal.Iron/iron oxide core/shell nanoparticles for magnetic targeting MRI and near-infrared photothermal therapy. Biomaterials.2014;35(26):7470-7478.[11] Tong S,Hou SJ,Zheng ZL,et al.Coating Optimization of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for High T-2 Relaxivity. Nano Lett.2010;10:4607-4613.[12] Lee SY,Yang CY,Peng CL,et al.A theranostic micelleplex co-delivering SN-38 and VEGF siRNA for colorectal cancer therapy.Biomaterials. 2016;86:92-105. [13] Baldi G,Ravagli C,Mazzantini F,et al.In vivo anticancer evaluation of the hyperthermic efficacy of anti-human epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted PEG-based nanocarrier containing magnetic nanoparticles.Int J Nanomedicine.2014;9:3037-3056.[14] Lee N,Kim H,Choi SH,et al.Magnetosome-like ferrimagnetic iron oxide nanocubes for highly sensitive MRI of single cells and transplanted pancreatic islets.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(7):2662-2667.[15] Nandwana V,Ryoo SR,Kanthala S,et al.Engineered Theranostic Magnetic Nanostructures: Role of Composition and Surface Coating on Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast and Thermal Activation.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(11):6953-6961.[16] Knecht LD,Ali N,Wei Y,et al.Nanoparticle-mediated remote control of enzymatic activity.ACS Nano. 2012;6(10):9079-9086.[17] Guo M,Que C,Wang C,et al.Multifunctional superparamagnetic nanocarriers with folate-mediated and pH-responsive targeting properties for anticancer drug delivery.Biomaterials. 2011;32(1): 185-194.[18] Li F,Lu J,Kong X,et al.Dynamic Nanoparticle Assemblies for Biomedical Applications.Adv Mater. 2017;29(14). doi:10.1002/adma.201605897.[19] Zhang ZQ,Song SC.Multiple hyperthermia-mediated release of TRAIL/SPION nanocomplex from thermosensitive polymeric hydrogels for combination cancer therapy. Biomaterials.2017;132:16-27.[20] Yoo D,Jeong H,Noh SH,et al.Magnetically triggered dual functional nanoparticles for resistance-free apoptotic hyperthermia.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013;52(49):13047-13051.[21] Yang HW,Liu HL,Li ML,et al.Magnetic gold-nanorod/ PNIPAAmMA nanoparticles for dual magnetic resonance and photoacoustic imaging and targeted photothermal therapy. Biomaterials. 2013;34(22): 5651-5660.[22] Datta NR,Krishnan S,Speiser DE,et al.Magnetic nanoparticle-induced hyperthermia with appropriate payloads: Paul Ehrlich's "magic (nano)bullet" for cancer theranostics? Cancer Treat Rev. 2016;50: 217-227.[23] Tarangelo A,Dixon SJ.Nanomedicine: An iron age for cancer therapy. Nat Nanotechnol.2016;11(11):921-922.[24] Goya GF,Asín L,Ibarra MR.Cell death induced by AC magnetic fields and magnetic nanoparticles:Current state and perspectives.Int J Hyperthermia.2013;29(8):810-818.[25] Xie J,Zhang Y,Yan C,et al.High-performance PEGylated Mn-Zn ferrite nanocrystals as a passive-targeted agent for magnetically induced cancer theranostics.Biomaterials. 2014;35(33):9126-9136. [26] Yallapu MM,Othman SF,Curtis ET,et al.Curcumin-loaded magnetic nanoparticles for breast cancer therapeutics and imaging applications.Int J Nanomedicine.2012;7:1761-1779.[27] Zhang E,Kircher MF,Koch M,et al.Dynamic magnetic fields remote-control apoptosis via nanoparticle rotation.ACS Nano. 2014;8(4):3192-3201.[28] Oh Y,Lee N,Kang HW,et al.In vitro study on apoptotic cell death by effective magnetic hyperthermia with chitosan-coated MnFe(2)O(4).Nanotechnology. 2016;27(11):115101-115122.[29] Makridis A,Tziomaki M,Topouridou K,et al.A novel strategy combining magnetic particle hyperthermia pulses with enhanced performance binary ferrite carriers for effective in vitro manipulation of primary human osteogenic sarcoma cells.Int J Hyperthermia. 2016;32(7): 778-785. [30] Yallapu MM,Chauhan N,Othman SF,et al.Implications of protein corona on physico-chemical and biological properties of magnetic nanoparticles.Biomaterials.2015;46:1-12.[31] Shah BP,Pasquale N,De G,et al.Core-shell nanoparticle-based peptide therapeutics and combined hyperthermia for enhanced cancer cell apoptosis.ACS Nano.2014;8(9):9379-9387.[32] Creixell M,Bohórquez AC,Torres-Lugo M,et al.EGFR-targeted magnetic nanoparticle heaters kill cancer cells without a perceptible temperature rise.ACS Nano.2011;5(9):7124-7129.[33] Connord V,Clerc P,Hallali N,et al.Real-Time Analysis of Magnetic Hyperthermia Experiments on Living Cells under a Confocal Microscope.Small.2015;11(20):2437-2445.[34] Ding X,Liu Y,Li J,et al.Hydrazone-bearing PMMA-functionalized magnetic nanocubes as pH-responsive drug carriers for remotely targeted cancer therapy in vitro and in vivo.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(10):7395-7407.[35] Di Corato R,Espinosa A,Lartigue L,et al.Magnetic hyperthermia efficiency in the cellular environment for different nanoparticle designs.Biomaterials. 2014;35(24):6400-6411. [36] Berciaud S,Lasne D,Blab GA,et al.Photothermal Heterodyne Imaging of Individual Metallic Nanoparticles: Theory versus Experiment.Phys Rev B.2006;73:045424.[37] Bogart LK,Taylor A,Cesbron Y,et al.Photothermal microscopy of the core of dextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticles during cell uptake.ACS Nano.2012;6(7):5961-5971.[38] Silva AH,Lima E Jr,Mansilla MV,et al.Superparamagnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles mPEG350- and mPEG2000-coated: cell uptake and biocompatibility evaluation.Nanomedicine. 2016;12(4):909-919.[39] Kyoung Ah Min,Meong Cheol Shin,Faquan Yu,et al.Pulsed Magnetic Field Improves the Transport of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles through Cell Barriers.Acs Nano. 2013;7(3):2161-2171.[40] Zysler RD,Lima E Jr,Vasquez Mansilla M,et al.A New Quantitative Method to Determine the Uptake of SPIONs in Animal Tissue and Its Application to Determine the Quantity of Nanoparticles in the Liver and Lung of Balb-c Mice Exposed to the SPIONs.J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2013;9(1):142-145.[41] Hildebrandt B, Peter Wustp, Thoralf Kerner T, et al. The cellular and molecular basis of hyperthermia.Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 2002;43: 33-56.[42] Gordon RT,Hines JR,Gordon D.Intracellular hyperthermia. A biophysical approach to cancer treatment via intracellular temperature and biophysical alterations.Med Hypotheses. 1979;5(1):83-102.[43] Min KA,Shin MC,Yu F,et al.Pulsed Magnetic Field Improves the Transport of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles through Cell Barriers.ACS Nano. 2013;7(3):2161-2171.[44] Luetke A,Meyers PA,Lewis I,et al.Osteosarcoma treatment - where do we stand? A state of the art review.Cancer Treat Rev. 2014;40(4): 523-532.[45] Mou X,Ali Z,Li S,et al.Applications of Magnetic Nanoparticles in Targeted Drug Delivery System.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015;15(1): 54-62.[46] Grossman JH,McNeil SE.Nanotechnology in Cancer Medicine.Physics Today.2012;65(8):38-42.[47] Yoo D,Jeong H,Noh SH,et al.Magnetically triggered dual functional nanoparticles for resistance-free apoptotic hyperthermia.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013;52(49):13047-13051. |
.jpg)
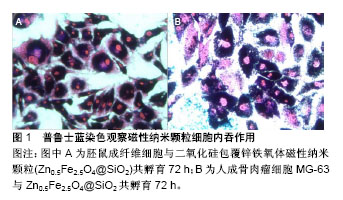
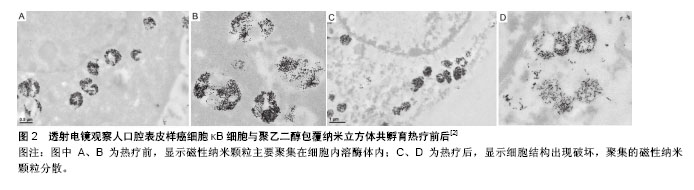

.jpg)
.jpg)